A Comprehensive Exploration of Asian Countries on the World Map
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of Asian Countries on the World Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Exploration of Asian Countries on the World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Exploration of Asian Countries on the World Map

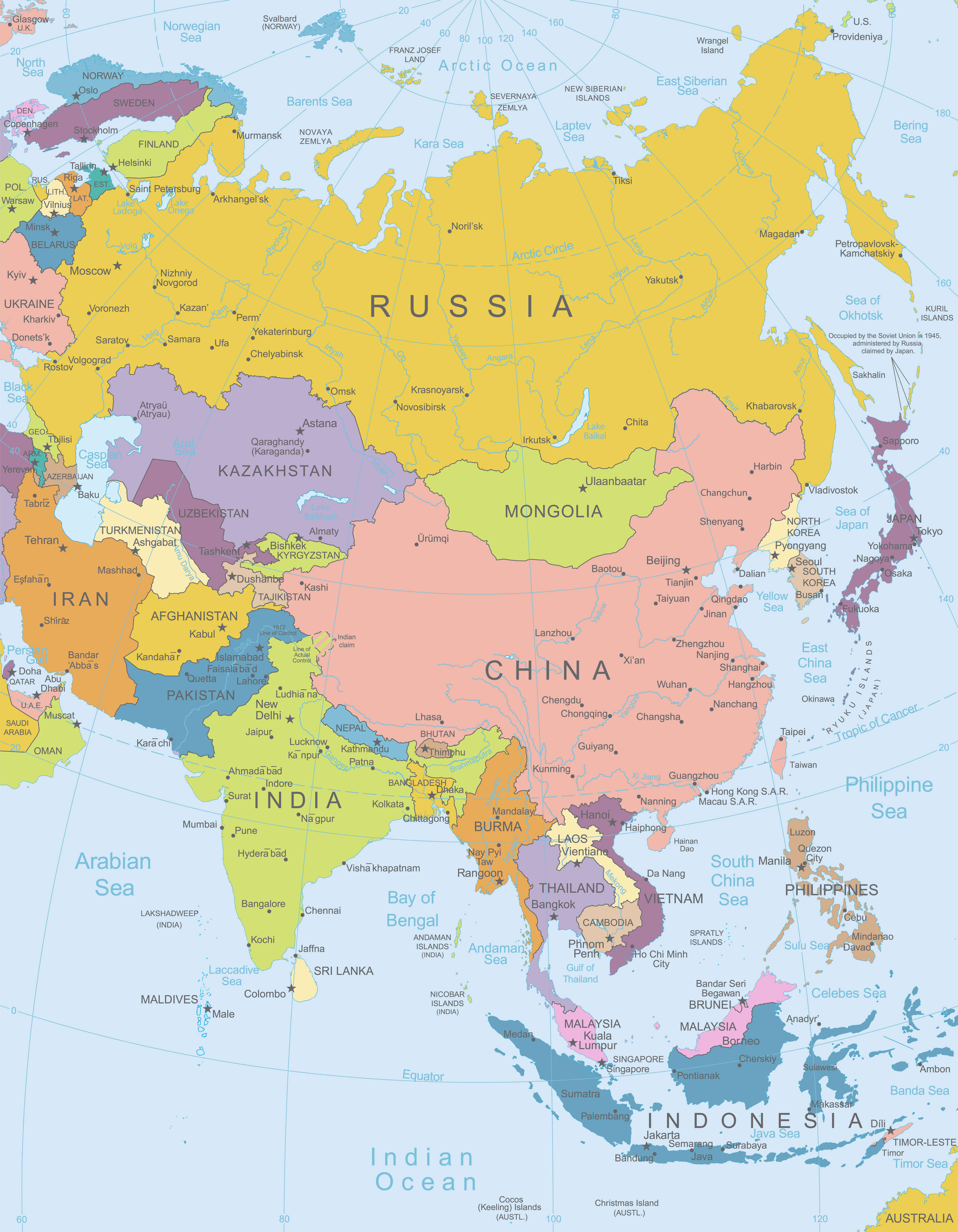
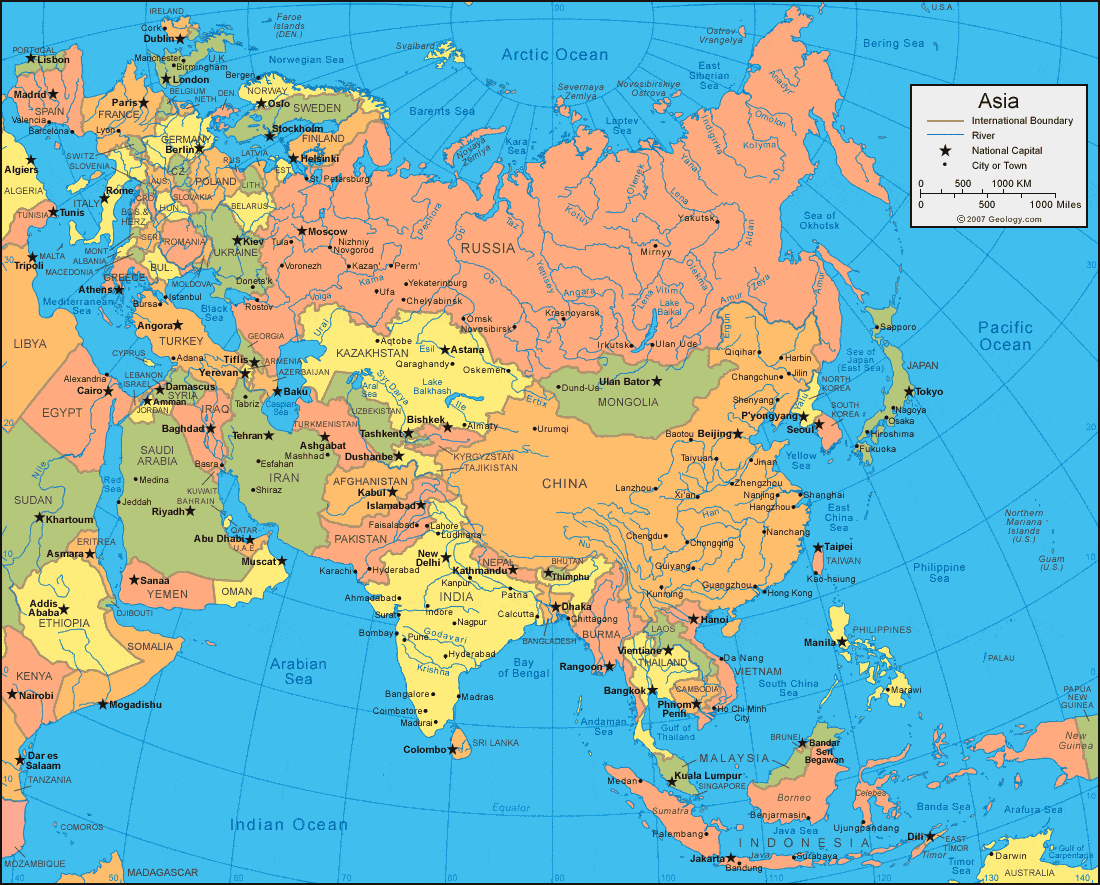
Asia, the largest and most populous continent, holds a vast tapestry of cultures, languages, and landscapes, making it a fascinating subject of study. Understanding the geographical distribution of Asian countries on the world map offers a crucial lens through which to appreciate its diverse socio-political, economic, and historical complexities.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the geographical positioning of Asian nations, highlighting their unique characteristics and the implications of their location.
Understanding the Asian Landscape
Asia spans a massive expanse, encompassing over 49.7 million square kilometers, covering nearly 30% of the Earth’s total landmass. It stretches from the eastern edge of Europe across the northern part of the Indian Ocean to the Pacific Ocean. Its diverse geography includes towering mountain ranges like the Himalayas, vast deserts like the Gobi, fertile river valleys like the Yangtze, and extensive coastal regions.
Dividing the Continent: Regional Geographic Insights
For better understanding, Asia is often divided into several geographical regions:
- East Asia: Comprising China, Japan, North Korea, South Korea, Mongolia, and Taiwan, this region is characterized by its strong cultural ties, advanced economies, and technological prowess.
- Southeast Asia: This region encompasses countries like Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and the Philippines. Known for its rich biodiversity, tropical climates, and diverse cultural heritage, Southeast Asia is a hub of tourism and economic activity.
- South Asia: Home to India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan, and the Maldives, South Asia boasts a vibrant cultural landscape, a rapidly growing economy, and a rich history.
- Central Asia: This region, encompassing Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, is characterized by its vast steppes, mountainous terrain, and strategic location along the Silk Road.
- West Asia: Often referred to as the Middle East, this region comprises countries like Turkey, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. It is known for its historical significance, vast oil reserves, and diverse cultural and religious landscape.
- Northern Asia: This region, encompassing Russia (with its Asian territory), is characterized by its vast size, harsh climate, and abundant natural resources.
The Significance of Geographical Positioning
The geographical location of Asian countries significantly influences their history, culture, economy, and international relations.
- Trade and Connectivity: Asia’s strategic location at the crossroads of major trade routes has historically fostered economic growth and cultural exchange. The Silk Road, for instance, connected the East with the West, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies.
- Natural Resources: The continent’s diverse landscape offers a vast array of natural resources, including oil, natural gas, minerals, and fertile land. This has played a crucial role in shaping economic development and global trade.
- Climate and Environment: Asia’s varied climates, from the frigid Arctic to the humid tropics, have influenced agricultural practices, settlement patterns, and cultural adaptations. The region is also home to a diverse range of ecosystems, including rainforests, deserts, and mountains.
- Political and Security Dynamics: The geographical proximity of Asian countries, coupled with their shared history and cultural ties, creates complex political and security dynamics. Regional conflicts, territorial disputes, and international alliances are all influenced by the geographical positioning of Asian nations.
Understanding the Asian World through the Map
Examining the world map with an eye toward Asian countries reveals crucial insights:
- The Rise of Asia: The map showcases the rapid economic development of several Asian nations, particularly in East and Southeast Asia. Their rising influence on the global stage is evident.
- Regional Power Dynamics: The map highlights the intricate web of relationships between Asian countries, including alliances, rivalries, and potential conflicts. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the complexities of the Asian region.
- Global Connectivity: The map demonstrates Asia’s interconnectedness with the rest of the world, showcasing its role in global trade, migration, and cultural exchange.
FAQs about Asian Countries on the World Map
Q1: Which Asian country is the largest in terms of land area?
A: Russia, with its Asian territory, holds the title of the largest country in Asia.
Q2: Which Asian country has the largest population?
A: China boasts the largest population in Asia and the world.
Q3: Which Asian country is known as the "Land of the Rising Sun"?
A: Japan, with its eastern location on the globe, is known as the "Land of the Rising Sun."
Q4: What is the highest mountain in Asia and the world?
A: Mount Everest, located in the Himalayas, is the highest peak on Earth.
Q5: Which Asian country is home to the world’s largest rainforest?
A: The Amazon rainforest, which extends across the border of Brazil and several other South American countries, is the world’s largest rainforest. However, the largest rainforest in Asia is the Borneo rainforest, shared by Indonesia, Malaysia, and Brunei.
Tips for Studying Asian Countries on the World Map
- Use Interactive Maps: Online interactive maps offer a dynamic way to explore Asian countries, providing detailed information about geography, demographics, and economic activity.
- Focus on Regional Divisions: Understanding the major geographical divisions of Asia, like East Asia, Southeast Asia, and South Asia, can help streamline your study.
- Explore Country Profiles: Each country has a unique history, culture, and economic profile. Researching these profiles can provide a deeper understanding of the Asian landscape.
- Connect Geography with History: Studying the historical development of Asian countries in conjunction with their geographical location can provide valuable insights into their current circumstances.
- Engage with Visual Resources: Utilize maps, photographs, and videos to visualize the diverse landscapes, cities, and cultures of Asia.
Conclusion
The world map serves as a vital tool for understanding the geographical distribution of Asian countries, highlighting their unique characteristics and their interconnectedness within the global landscape. Through exploring the map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the continent’s diverse cultures, economies, and political dynamics. Recognizing the significance of geographical positioning allows us to better understand the challenges and opportunities facing Asian nations and their role in shaping the global future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Exploration of Asian Countries on the World Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!