A Journey Through Latin America’s Diverse Landforms: From Andes to Amazon
Related Articles: A Journey Through Latin America’s Diverse Landforms: From Andes to Amazon
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Latin America’s Diverse Landforms: From Andes to Amazon. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Latin America’s Diverse Landforms: From Andes to Amazon

Latin America, a vast and vibrant region stretching from the northern reaches of Mexico to the southern tip of Argentina, is renowned for its rich cultural tapestry and diverse landscapes. Its geographical makeup is a captivating blend of towering mountains, sprawling plains, dense rainforests, and arid deserts, shaping its ecosystems, influencing its history, and impacting the lives of its people. This article delves into the fascinating world of Latin America’s landforms, exploring their unique characteristics, their impact on the region’s biodiversity and human life, and the challenges and opportunities they present.
The Majestic Andes: A Spine of Mountains
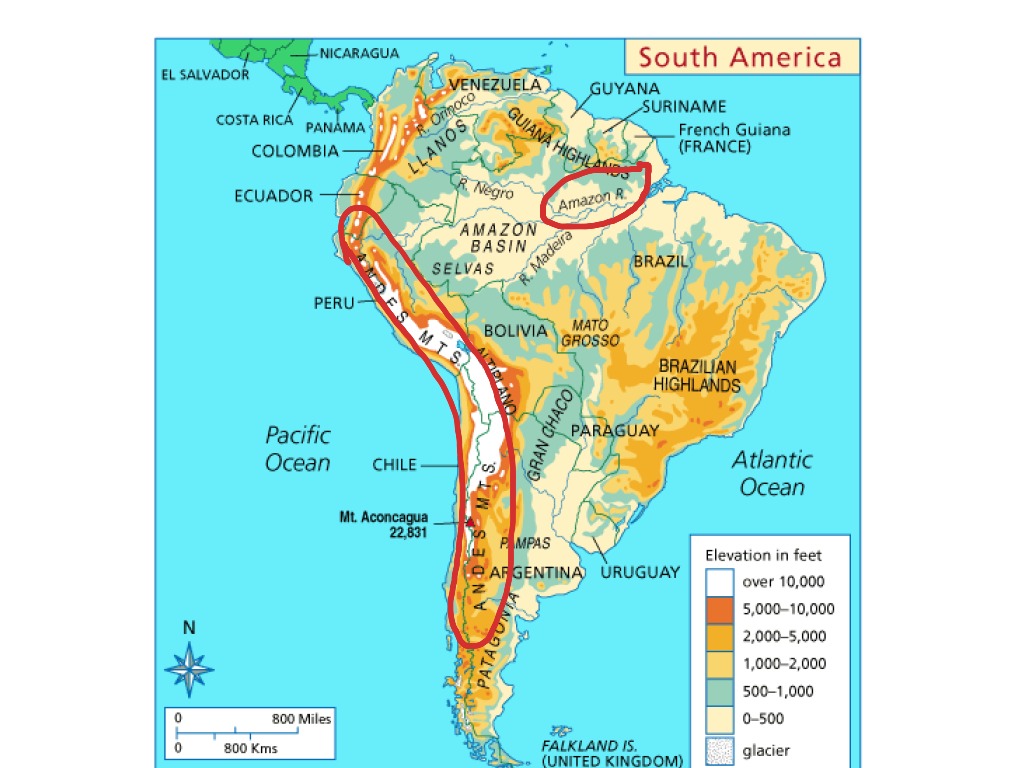
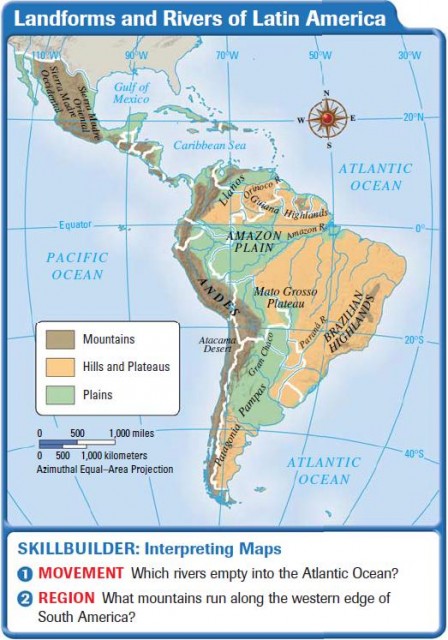
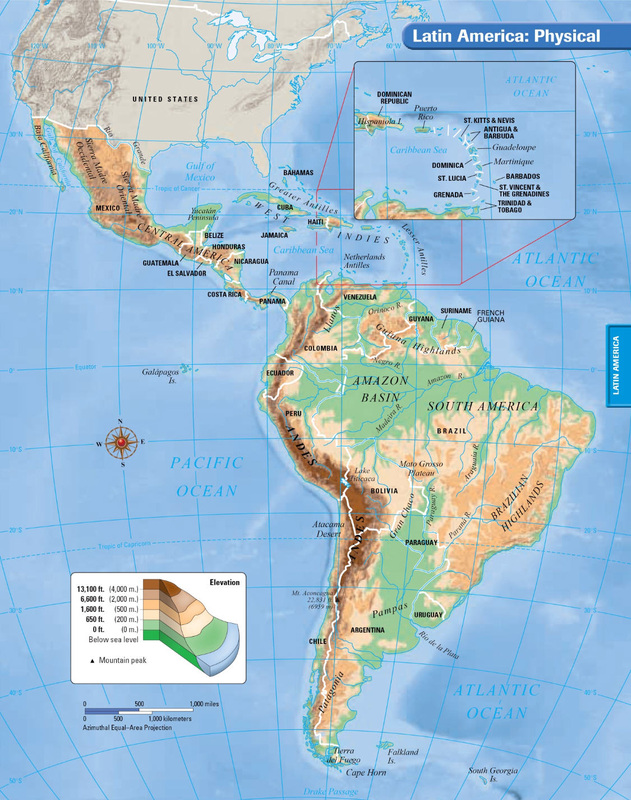
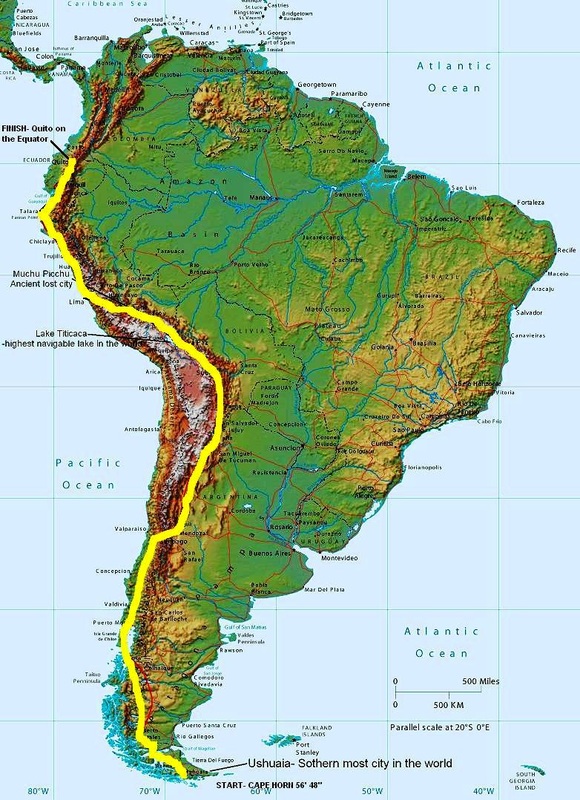
The Andes Mountains, the longest mountain range in the world, form the backbone of western Latin America. Stretching over 7,000 kilometers from north to south, they traverse Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. The Andes are a testament to the Earth’s tectonic forces, resulting from the collision of the Nazca and South American plates.
The Andes are not a singular entity but a complex system of ranges, plateaus, and valleys. The towering peaks, including Aconcagua, the highest mountain outside of Asia, are a constant reminder of the immense power of nature. The Andes are a significant source of water for the region, feeding rivers that flow eastward to the Amazon Basin and westward to the Pacific Ocean.
The Amazon Basin: A Realm of Biodiversity
The Amazon Basin, home to the world’s largest rainforest, is a testament to the power of water. The Amazon River, the world’s largest by volume, and its tributaries create a vast network of waterways, draining a region encompassing parts of nine countries. The Amazon rainforest is a treasure trove of biodiversity, harboring an estimated 10% of the world’s known species.
The rainforest’s dense canopy, humid climate, and rich soils provide ideal conditions for a diverse array of flora and fauna. The Amazon Basin is a crucial carbon sink, absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, playing a critical role in regulating the global climate.
The Mesoamerican Highlands: A Cradle of Civilization
The Mesoamerican Highlands, a region encompassing parts of Mexico, Guatemala, and Honduras, are characterized by a series of volcanic plateaus and mountain ranges. The region’s volcanic soils are fertile, making it ideal for agriculture. The highlands were the cradle of several ancient civilizations, including the Maya, Aztec, and Olmec, who thrived in this region due to its abundant resources and favorable climate.
The Mesoamerican Highlands are also home to a variety of ecosystems, from pine forests to grasslands. The region’s diverse landscape has shaped the cultures and traditions of its people, leaving an indelible mark on the region’s history and heritage.
The Pampas: A Vast and Fertile Plain
The Pampas, a vast expanse of grassland stretching across Argentina and Uruguay, is a testament to the power of nature’s forces. Formed by the deposition of sediments from the Andes, the Pampas are characterized by their flat terrain and rich, fertile soils. This makes them ideal for cattle ranching and agriculture, contributing significantly to the region’s economy.
The Pampas are also home to a diverse array of wildlife, including the pampas deer, rhea, and various bird species. The region’s unique ecosystem has been shaped by the interplay of climate, soil, and human activity, creating a landscape that is both productive and beautiful.
The Atacama Desert: A Realm of Aridity
The Atacama Desert, located in northern Chile, is one of the driest places on Earth. The desert’s aridity is due to a combination of factors, including the rain shadow effect of the Andes, the cold Humboldt Current, and the high-pressure system over the Pacific Ocean. Despite its extreme conditions, the Atacama Desert is not devoid of life.
The desert is home to a unique array of flora and fauna adapted to survive in its harsh environment. The Atacama Desert is also a site of significant astronomical research, with its clear skies and dry climate providing ideal conditions for observing the stars.
The Caribbean Islands: A Tapestry of Landscapes
The Caribbean Islands, scattered across the Caribbean Sea, are a diverse group of islands with varying landscapes. Some islands are volcanic, with towering peaks and lush rainforests, while others are low-lying, with sandy beaches and coral reefs. The islands’ diverse landscapes have contributed to their rich cultural heritage, influenced by indigenous populations, European colonization, and African influences.
The Caribbean Islands are a popular tourist destination, attracting visitors from all over the world who come to enjoy their beautiful beaches, crystal-clear waters, and vibrant cultures. The islands’ diverse ecosystems are also home to a variety of flora and fauna, including endemic species found nowhere else on Earth.
The Impact of Landforms on Latin America
Latin America’s diverse landforms have a profound impact on the region’s biodiversity, economy, and human life. The Andes Mountains, for example, are a vital source of water for millions of people, and their rich mineral deposits have played a significant role in the region’s economic development.
The Amazon Basin, with its vast rainforest, plays a crucial role in regulating the global climate, while the Pampas provide fertile land for agriculture, supporting a significant portion of the region’s population. The Atacama Desert, despite its harsh conditions, is a site of significant astronomical research and is home to unique ecosystems.
Challenges and Opportunities
Latin America’s landforms also present a range of challenges and opportunities. The region’s mountainous terrain can make transportation and communication difficult, while its vast rainforests are vulnerable to deforestation and climate change.
However, the region’s natural resources also offer tremendous opportunities for sustainable development. The Andes Mountains, for example, are a potential source of renewable energy, while the Amazon Basin has the potential to become a global leader in ecotourism.
FAQs about Latin America’s Landforms
Q: What are the major landforms in Latin America?
A: Latin America is characterized by a variety of landforms, including the Andes Mountains, the Amazon Basin, the Mesoamerican Highlands, the Pampas, the Atacama Desert, and the Caribbean Islands.
Q: How have landforms shaped Latin America’s history and culture?
A: Landforms have played a significant role in shaping Latin America’s history and culture. The Andes Mountains, for example, have acted as a barrier between different cultures, while the Amazon Basin has provided a home for indigenous populations for centuries.
Q: What are the environmental challenges facing Latin America’s landforms?
A: Latin America’s landforms face a range of environmental challenges, including deforestation, climate change, and pollution.
Q: What are the economic opportunities presented by Latin America’s landforms?
A: Latin America’s landforms offer a range of economic opportunities, including tourism, agriculture, mining, and renewable energy.
Tips for Exploring Latin America’s Landforms
- Plan your trip carefully: Research the different landforms you wish to visit and consider the best time of year to travel.
- Be respectful of the environment: Leave no trace and follow local regulations.
- Support local communities: Patronize local businesses and learn about the region’s culture and traditions.
- Be prepared for different climates: Pack accordingly for the varying temperatures and weather conditions you may encounter.
- Embrace the diversity: Latin America is a region of incredible diversity, both in its landscapes and its people.
Conclusion
Latin America’s landforms are a testament to the Earth’s power and beauty. From the towering peaks of the Andes to the vast expanse of the Amazon Basin, each landform has its unique characteristics, shaping the region’s biodiversity, economy, and human life. Understanding these landforms is crucial for appreciating the region’s rich history, culture, and potential for sustainable development. By exploring and respecting these remarkable landscapes, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of the natural world and the importance of protecting it for future generations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Latin America’s Diverse Landforms: From Andes to Amazon. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!