Charting a Course Through Time: A Journey Through the 13th Century European Map
Related Articles: Charting a Course Through Time: A Journey Through the 13th Century European Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting a Course Through Time: A Journey Through the 13th Century European Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting a Course Through Time: A Journey Through the 13th Century European Map
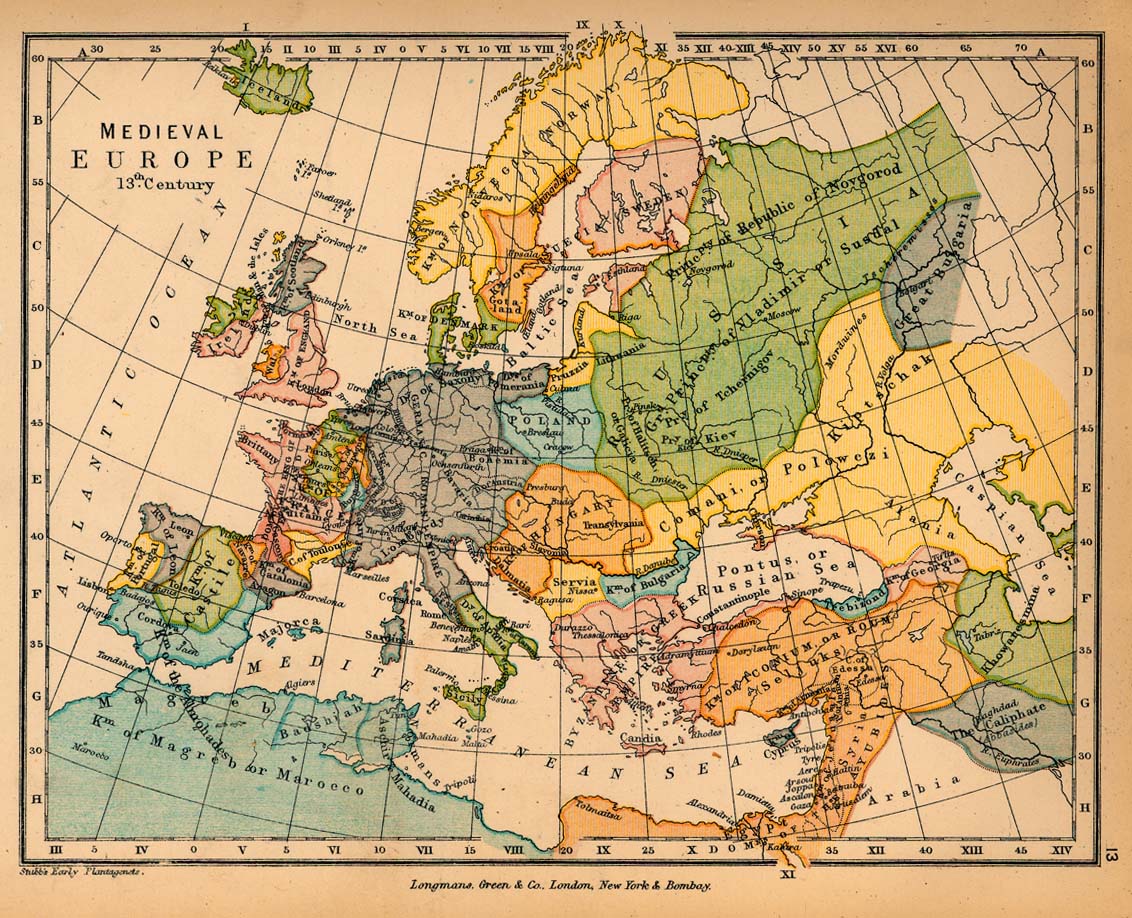
The 13th century in Europe was a period of significant change and development, marked by the rise of powerful kingdoms, the flourishing of trade, and the emergence of new cultural and intellectual movements. A 13th-century European map serves as a fascinating snapshot of this era, offering insights into the political, economic, and social landscape of the time.
A Mosaic of Kingdoms and Empires:
The map reveals a fragmented Europe, a patchwork of kingdoms and empires vying for power and influence. The Holy Roman Empire, though fragmented and often beset by internal conflicts, still held sway over much of Central Europe. The Kingdom of France, under the Capetian dynasty, was gradually consolidating its power, expanding its territories and establishing a centralized administration. England, under the Plantagenet kings, had emerged as a formidable force, engaging in a series of conflicts with France. In the Iberian Peninsula, the Christian kingdoms of Castile, Leon, and Portugal were slowly pushing back against the Islamic Almohad dynasty.
The Rise of Trade and Urban Centers:
The 13th century witnessed a surge in trade throughout Europe. The map highlights the burgeoning trade routes that crisscrossed the continent, connecting major cities and ports. Cities like Venice, Genoa, and Bruges became centers of commerce, attracting merchants from across Europe and beyond. The growth of trade led to the emergence of a new merchant class, which played a crucial role in the economic and social development of Europe.
A Landscape of Faith and Conflict:
The map also reflects the profound influence of religion on European life. The Catholic Church was a powerful institution, holding significant political and social influence. The map shows the spread of Christianity across Europe, with the Church playing a vital role in education, healthcare, and social welfare. However, the 13th century was also marked by religious conflict, particularly the Crusades, which saw European Christians clash with Muslims in the Holy Land.
Navigating the Map: Key Features and Geographic Insights
Political Landscape:
- The Holy Roman Empire: While fragmented and often facing internal struggles, the Holy Roman Empire dominated Central Europe.
- The Kingdom of France: Under the Capetian dynasty, France was consolidating its power, gradually expanding its territories.
- England: The Plantagenet kings of England emerged as a formidable force, engaging in conflicts with France and vying for control over territories in France.
- The Iberian Peninsula: The Christian kingdoms of Castile, Leon, and Portugal were slowly pushing back against the Islamic Almohad dynasty.
- The Scandinavian Kingdoms: Denmark, Sweden, and Norway were establishing their own independent kingdoms.
- The Byzantine Empire: Though weakened, the Byzantine Empire still held sway over the Eastern Mediterranean, facing pressures from both internal and external forces.
Economic Networks:
- Trade Routes: The map highlights the bustling trade routes that connected major cities and ports across Europe.
- Urban Centers: Cities like Venice, Genoa, Bruges, and Cologne emerged as centers of commerce and cultural exchange.
- The Hanseatic League: This powerful trading alliance of northern German cities controlled trade routes across the Baltic and North Seas.
Cultural and Religious Influences:
- The Spread of Christianity: The map showcases the widespread influence of the Catholic Church across Europe.
- The Crusades: The map reveals the routes taken by European Christians during the Crusades, highlighting the ongoing conflict with Muslims in the Holy Land.
- The Rise of Universities: The 13th century saw the establishment of universities in major cities, contributing to the intellectual and cultural development of Europe.
Understanding the 13th Century European Map: FAQs
1. What are the major political entities depicted on the map?
The map showcases a variety of political entities, including the Holy Roman Empire, the Kingdom of France, the Kingdom of England, the Iberian kingdoms, the Scandinavian kingdoms, and the Byzantine Empire.
2. How does the map reflect the economic situation in 13th century Europe?
The map highlights the flourishing trade routes that crisscrossed the continent, connecting major cities and ports. It also shows the emergence of important urban centers like Venice, Genoa, and Bruges, which were centers of commerce and economic activity.
3. What role did religion play in 13th century Europe, as depicted on the map?
The map reflects the profound influence of the Catholic Church, which held significant political and social power. It also shows the spread of Christianity across Europe, as well as the ongoing conflict with Islam, as evidenced by the Crusades.
4. What were some of the key cultural developments in 13th century Europe?
The map reflects the rise of universities, which contributed to the intellectual and cultural development of Europe. It also shows the flourishing of art, literature, and architecture, particularly in the Gothic style.
5. How can we use the 13th century European map to understand the history of the time?
The map provides a valuable snapshot of the political, economic, and social landscape of 13th century Europe. It allows us to understand the relationships between different kingdoms and empires, the flow of trade and commerce, and the influence of religion and culture.
Tips for Using the 13th Century European Map
- Focus on key features: Pay attention to the major political entities, trade routes, urban centers, and religious centers depicted on the map.
- Consider the context: Remember that the map is a snapshot of a specific point in time, and the political and economic landscape was constantly evolving.
- Compare and contrast: Compare the 13th century map with maps from other periods to see how Europe changed over time.
- Connect the dots: Use the map to explore the connections between different regions, cultures, and events.
Conclusion
The 13th century European map is a valuable tool for understanding a pivotal period in European history. It provides insights into the political, economic, and social landscape of the time, highlighting the rise of powerful kingdoms, the flourishing of trade, and the influence of religion and culture. By studying this map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and dynamism of medieval Europe.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting a Course Through Time: A Journey Through the 13th Century European Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!