Charting the Italian Peninsula: A Journey Through Medieval Maps
Related Articles: Charting the Italian Peninsula: A Journey Through Medieval Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Charting the Italian Peninsula: A Journey Through Medieval Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Italian Peninsula: A Journey Through Medieval Maps
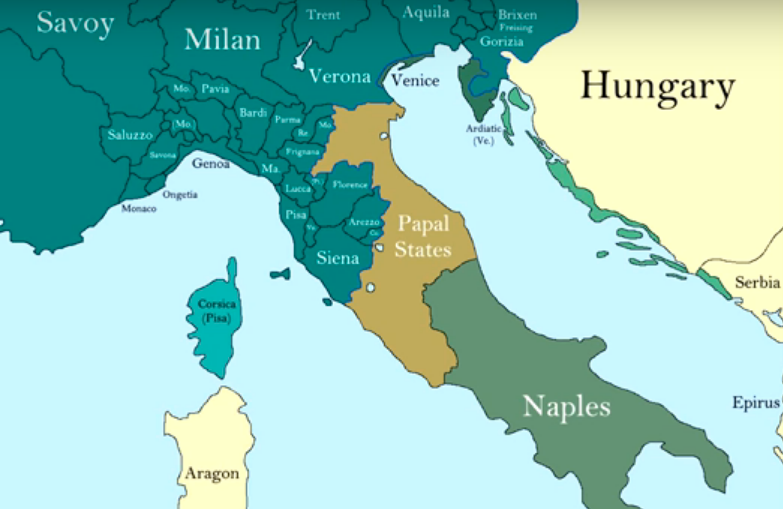
The Italian peninsula, a land of diverse landscapes and rich history, has long captivated the imaginations of cartographers. Throughout the Middle Ages, maps of Italy served as crucial tools for navigation, trade, and understanding the world. These maps, while often lacking the precision of modern cartography, offer invaluable insights into the medieval perception of Italy, its political landscape, and the evolving understanding of geography.
The Evolution of Medieval Italian Cartography:
The development of medieval maps of Italy can be traced back to the Roman era, where the legacy of Roman cartography, particularly the "Tabula Peutingeriana," provided a foundation for later mapmakers. However, with the decline of the Roman Empire, the knowledge and techniques of mapmaking were largely lost, leading to a period of cartographic stagnation.
The revival of mapmaking in the Middle Ages began with the influence of Arab cartography, which introduced new techniques and perspectives. During the 11th and 12th centuries, the rise of trade and pilgrimage routes spurred the creation of portolan charts, navigational maps that emphasized coastlines and harbors. These charts, often adorned with elaborate decorations and compass roses, proved instrumental in facilitating maritime trade across the Mediterranean.
The Influence of Religious and Political Power:
Religious and political influences played a significant role in shaping medieval maps of Italy. The Church, with its vast network of monasteries and its role in disseminating knowledge, actively supported mapmaking. Maps were often used for teaching, illustrating religious texts, and promoting pilgrimages to holy sites.
Political power also influenced the representation of Italy on medieval maps. The rise of city-states and the fragmentation of the peninsula into numerous independent entities led to the development of maps that emphasized these political boundaries. Cities like Venice, Florence, and Genoa, centers of trade and cultural influence, were often prominently depicted on maps, reflecting their growing importance in the medieval world.
Key Features of Medieval Italian Maps:
Medieval maps of Italy, while diverse in their styles and purposes, shared certain key features:
-
Emphasis on Symbolic Representation: Unlike modern maps, medieval maps were often symbolic, reflecting the cartographer’s understanding of the world and their belief systems. The placement of cities, mountains, and rivers was not always based on accurate measurements but rather on their perceived significance and symbolic importance.
-
The T-O Map: A common representation of the world during the Middle Ages was the T-O map, where the known world was depicted as a circular disc surrounded by the ocean. This map, with its three continents of Europe, Asia, and Africa, symbolized the Christian understanding of the world with Jerusalem at its center.
-
Emphasis on Religious Sites: The importance of pilgrimage routes and holy sites is evident in medieval maps of Italy. Jerusalem, Rome, and other significant locations associated with Christianity were often prominently depicted, highlighting the religious significance of these places.
-
The Role of the Compass Rose: The compass rose, a symbol of navigation and direction, became increasingly prominent on medieval maps, reflecting the growing importance of maritime trade and exploration. The compass rose also served as a reminder of the divine order and the role of God in guiding sailors and travelers.
The Importance of Medieval Italian Maps:
Medieval maps of Italy, despite their limitations in terms of accuracy and scale, offer invaluable insights into the past. They provide a window into the medieval worldview, revealing the beliefs, values, and cultural perspectives of the time. These maps also serve as a testament to the ingenuity and creativity of medieval cartographers, who, despite limited resources and technology, managed to create maps that served practical and symbolic purposes.
FAQs on Medieval Maps of Italy:
1. What were the main purposes of medieval maps of Italy?
Medieval maps of Italy served various purposes, including navigation, trade, pilgrimage, religious instruction, and political representation. They were used to guide travelers, facilitate trade routes, promote pilgrimages to holy sites, illustrate religious texts, and depict the political landscape of the Italian peninsula.
2. How did medieval maps of Italy differ from modern maps?
Medieval maps of Italy were often symbolic and lacked the precision of modern maps. They emphasized religious and political significance over accuracy and relied on visual representations rather than precise measurements.
3. What were the key features of medieval maps of Italy?
Key features of medieval maps of Italy include the T-O map, emphasis on religious sites, the use of compass roses, and symbolic representations of geographic features.
4. What were the main influences on medieval maps of Italy?
Medieval maps of Italy were influenced by Roman cartography, Arab cartography, the Church, and political power. The Church played a significant role in promoting mapmaking for religious purposes, while political entities influenced the representation of their territories on maps.
5. What is the significance of medieval maps of Italy today?
Medieval maps of Italy provide valuable insights into the medieval worldview, revealing the beliefs, values, and cultural perspectives of the time. They also serve as a testament to the ingenuity and creativity of medieval cartographers.
Tips for Studying Medieval Maps of Italy:
- Contextualize the maps: Consider the historical context of the map, including the time period, the creator, and the intended audience.
- Pay attention to symbols: Analyze the symbols used on the map and their potential meanings.
- Compare different maps: Compare different maps of Italy from the same period to observe variations in style, content, and perspective.
- Consult scholarly resources: Research the history of cartography and the specific features of medieval Italian maps to gain a deeper understanding of their significance.
Conclusion:
Medieval maps of Italy offer a fascinating glimpse into the past, revealing the evolving understanding of geography, the influence of religious and political forces, and the ingenuity of medieval cartographers. These maps, while often lacking the precision of modern cartography, serve as valuable sources of information about the past, providing insights into the medieval worldview and the cultural landscape of the Italian peninsula. By studying these maps, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the historical context of Italy and the evolution of cartography over time.

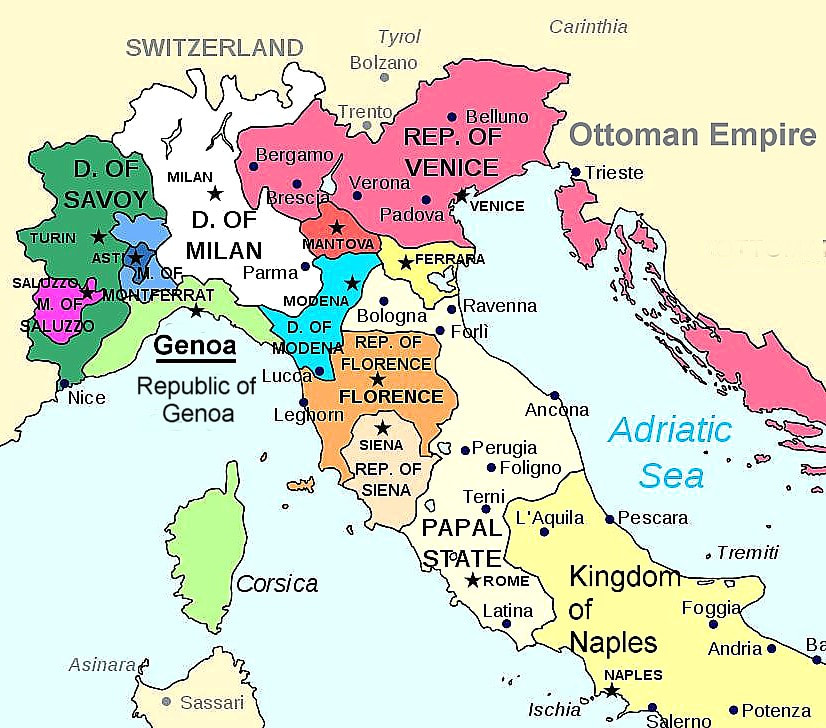
![The Italian Peninsula in 1494 - [855 × 1,024] : r/MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/i2qfjiOD0eyEBTIi7eTO9BplmHvQ1e0YlF5cDpe5rlY.png?auto=webpu0026s=6281dec3481ec692c34dab310716d23008388896)
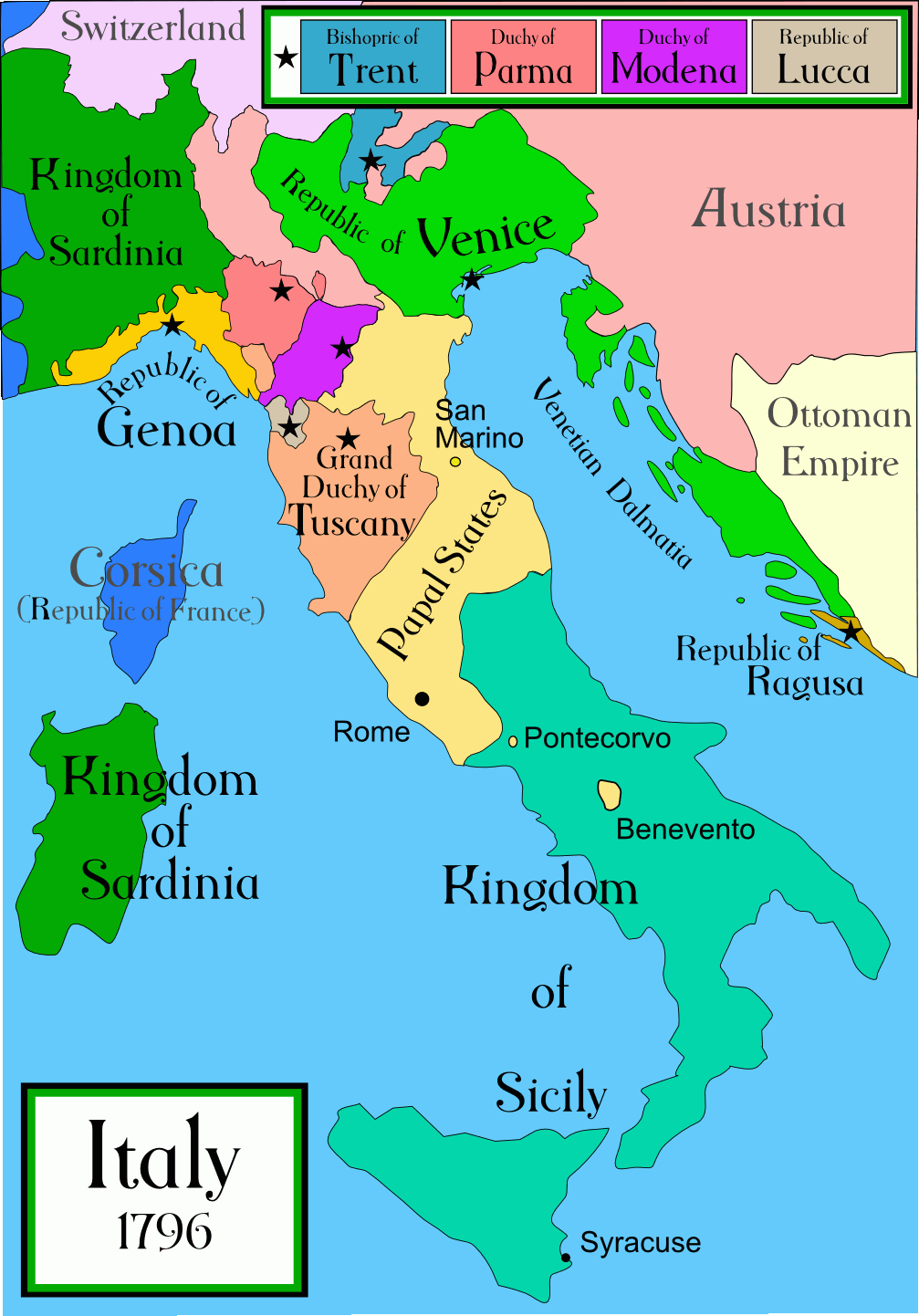



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Italian Peninsula: A Journey Through Medieval Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!