Delving into India’s Administrative Tapestry: Understanding the Districts Map
Related Articles: Delving into India’s Administrative Tapestry: Understanding the Districts Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delving into India’s Administrative Tapestry: Understanding the Districts Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into India’s Administrative Tapestry: Understanding the Districts Map

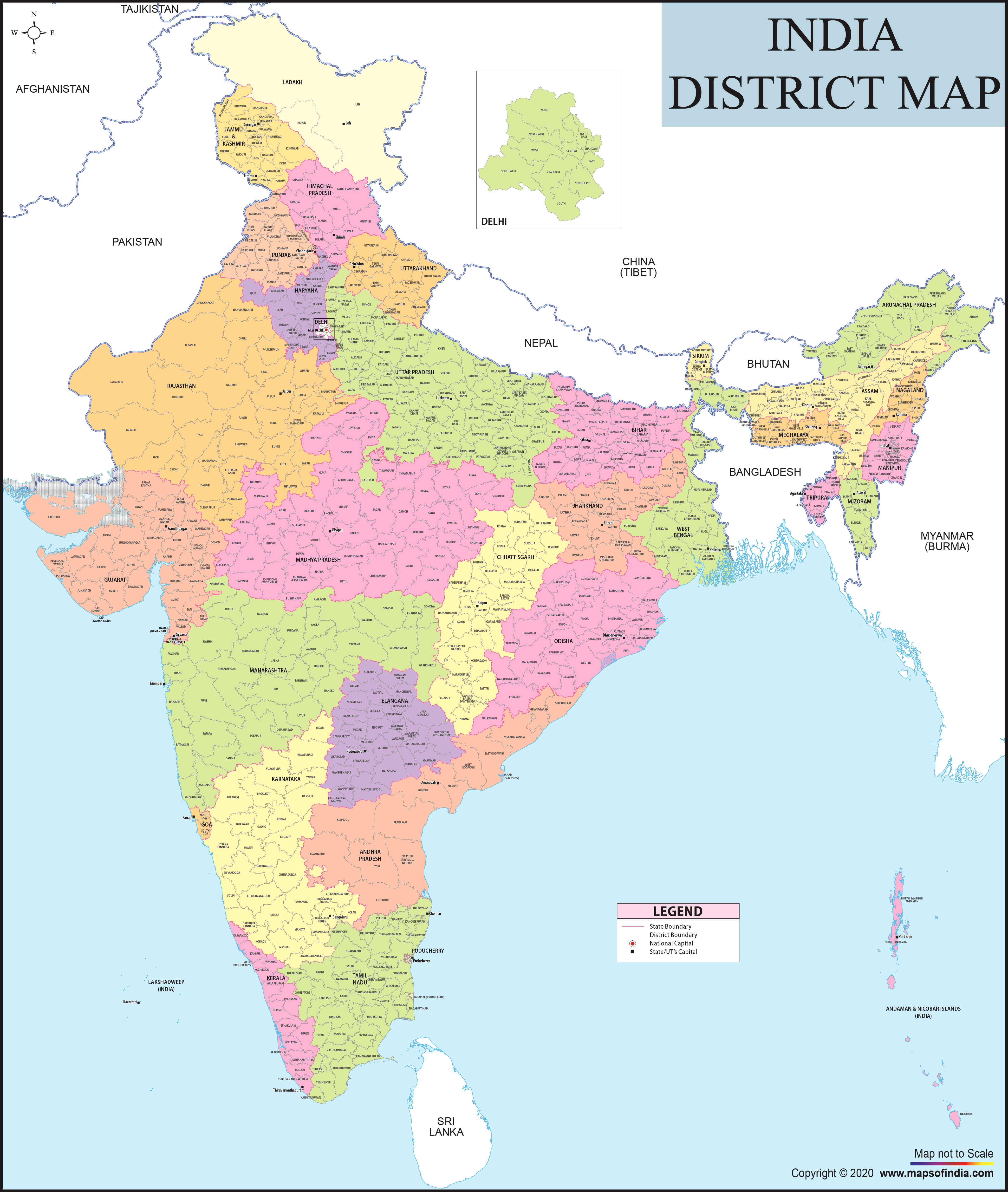
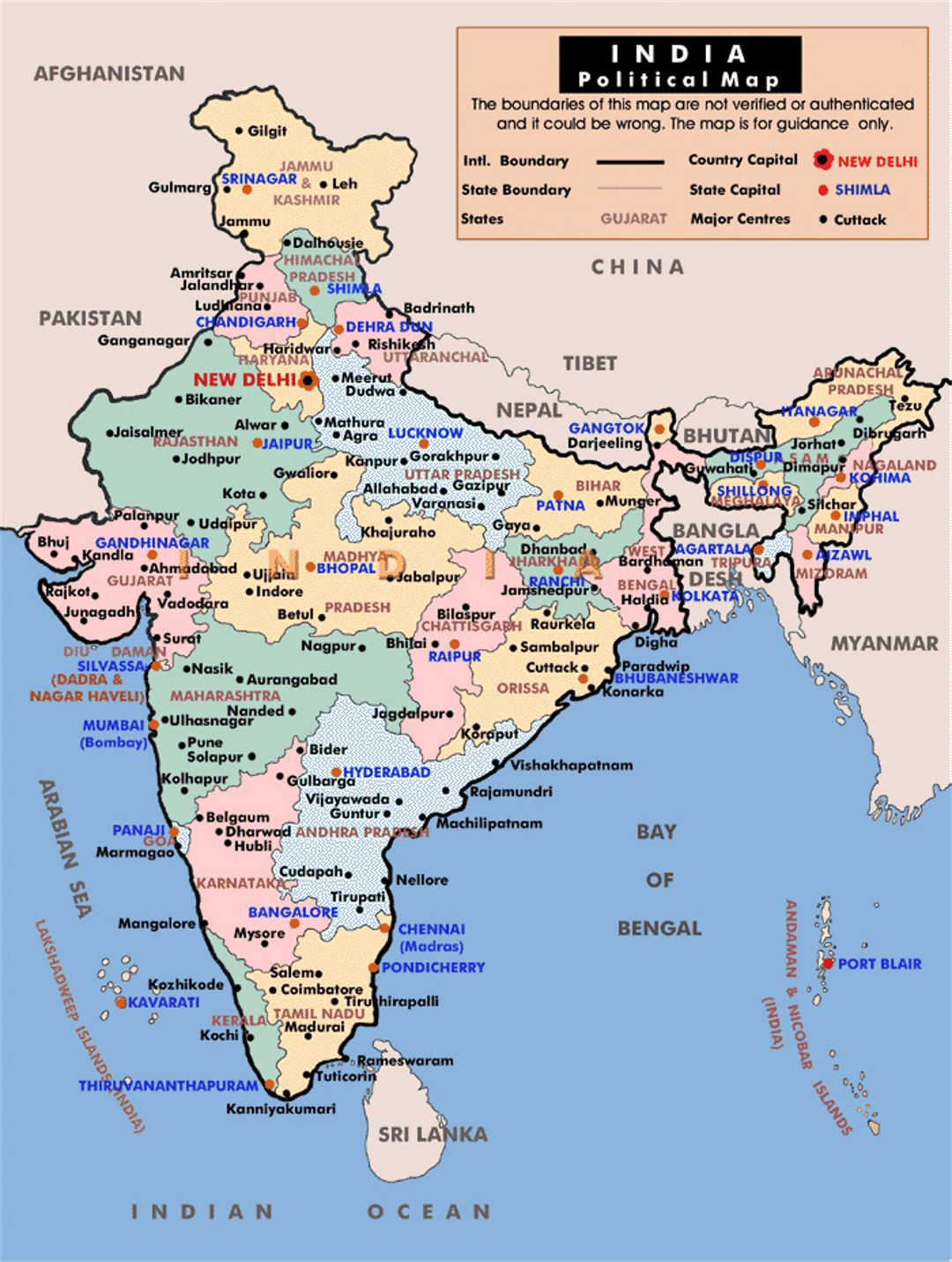
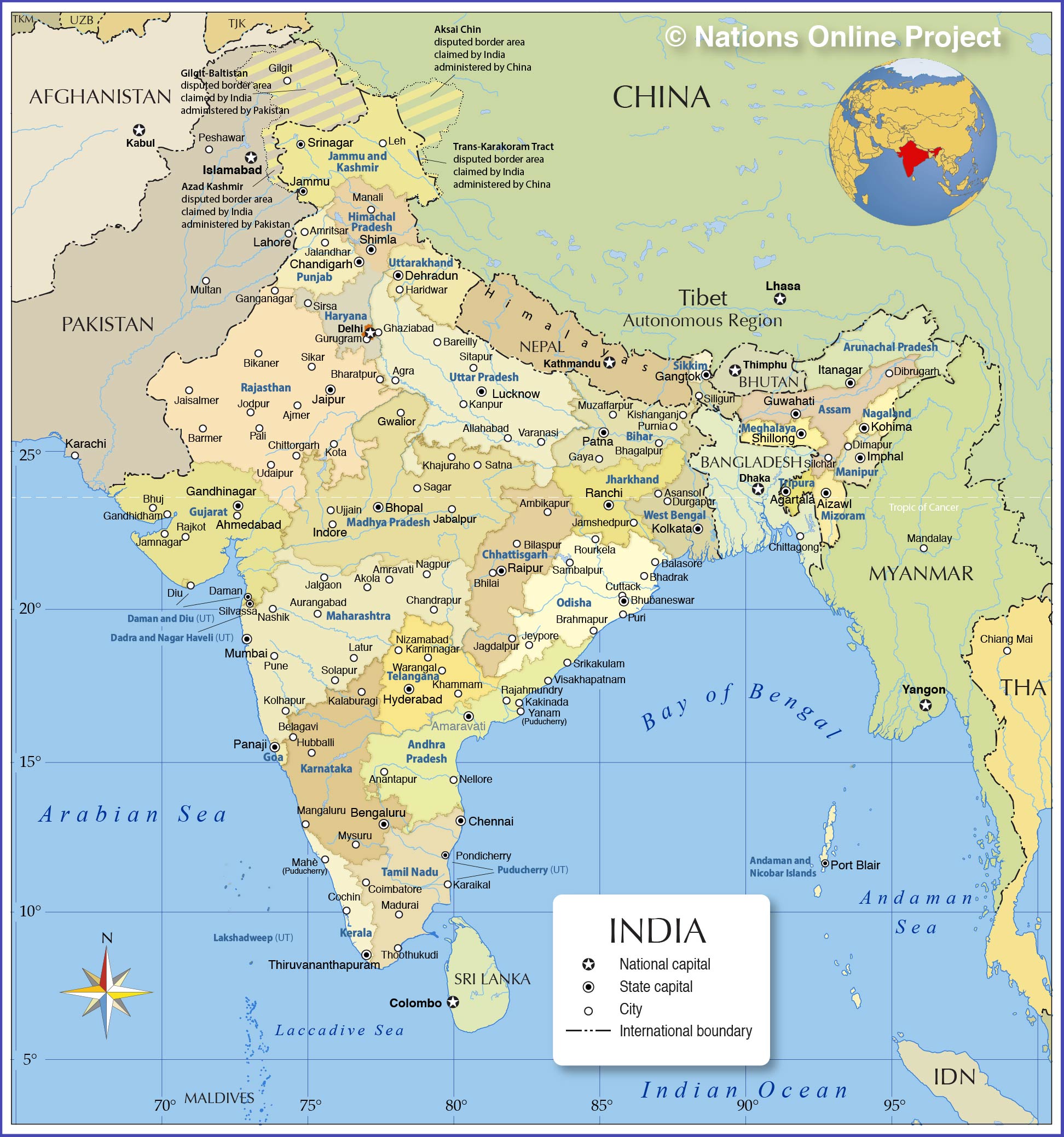
India, a vast and diverse nation, is intricately divided into administrative units known as districts. These districts, forming the bedrock of governance and development, play a crucial role in shaping the nation’s socio-economic landscape. Understanding the districts map of India is essential for comprehending the country’s administrative structure, its regional variations, and the challenges it faces in achieving equitable development.
The Evolution of Districts in India
The concept of districts in India has its roots in the British colonial era. During their rule, the British divided the country into administrative units for efficient governance and revenue collection. These units, initially known as "zilahs," were further subdivided into smaller units like "tehsils" and "parganas."
Post-independence, India retained the district system, albeit with modifications. The number of districts has grown significantly over the years, reflecting the nation’s population growth, administrative needs, and the desire for better governance at the grassroots level.
Key Features of the Districts Map of India
The districts map of India is a powerful tool for understanding the country’s administrative and geographical diversity. Here are some key features:
- Number of Districts: India currently has 753 districts, spread across 28 states and 8 union territories. The number of districts in each state varies, reflecting its size, population density, and administrative requirements.
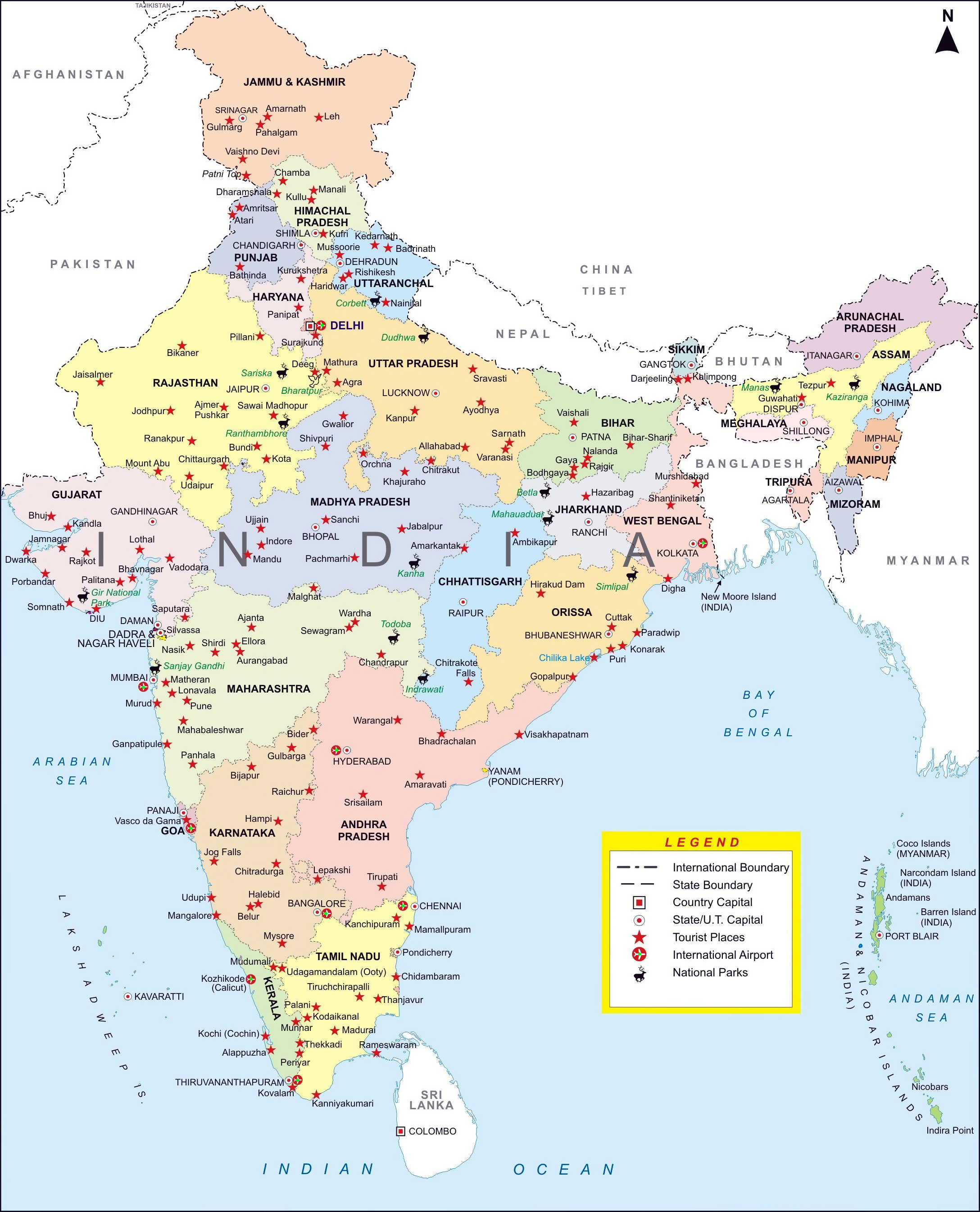
- Geographical Distribution: Districts are distributed across diverse landscapes, ranging from the snow-capped Himalayas to the fertile plains of the Ganges, from the arid Thar Desert to the lush rainforests of the Western Ghats. Each district possesses its unique geographical features, influencing its economy, culture, and way of life.
- Administrative Structure: Each district is headed by a District Collector or Deputy Commissioner, who is responsible for implementing government policies, overseeing development programs, and maintaining law and order. Districts are further subdivided into smaller administrative units like tehsils, blocks, and panchayats, creating a hierarchical structure of governance.
- Demographic Diversity: India’s districts exhibit remarkable demographic diversity. They house a wide range of languages, religions, ethnicities, and cultural practices, contributing to the nation’s rich tapestry. Understanding the demographic composition of each district is crucial for formulating targeted policies and development strategies.
- Economic Variations: Districts differ significantly in their economic profiles. Some are heavily reliant on agriculture, while others are hubs of industry, technology, or tourism. These variations necessitate tailored economic policies and development programs to address the specific needs of each district.
Significance of the Districts Map
The districts map of India holds immense significance for various stakeholders:
- Government: It provides a framework for efficient governance, enabling policymakers to formulate targeted policies and development programs based on the unique characteristics of each district.
- Development Agencies: It helps identify areas requiring special attention and facilitates the allocation of resources for poverty alleviation, infrastructure development, and social welfare programs.
- Businesses: It assists in understanding the market potential of different regions, facilitating informed investment decisions and market expansion strategies.
- Researchers: It provides a valuable resource for studying regional variations in social, economic, and environmental indicators, aiding in research and analysis.
- Citizens: It empowers citizens by providing them with information about their local government, development initiatives, and access to public services.
Benefits of Studying the Districts Map
- Informed Decision Making: Understanding the districts map enables informed decision-making in various sectors, from government policies to business strategies.
- Targeted Development: It facilitates the creation of targeted development programs that address the specific needs of each district, promoting equitable growth.
- Regional Understanding: It fosters a deeper understanding of India’s regional variations, fostering inclusivity and appreciation for the country’s diverse cultural heritage.
- Enhanced Governance: It supports effective governance by enabling local authorities to address the unique challenges and opportunities of their respective districts.
- Citizen Empowerment: It empowers citizens by providing them with information about their local government and its initiatives, promoting transparency and accountability.
FAQs about the Districts Map of India
Q1: What is the largest district in India by area?
A: The largest district in India by area is Kutch in Gujarat, covering over 45,652 square kilometers.
Q2: What is the most populous district in India?
A: Thane in Maharashtra is the most populous district with a population exceeding 11 million.
Q3: How many districts are there in each state?
A: The number of districts varies from state to state. For example, Uttar Pradesh has the highest number of districts with 75, while Sikkim has only four districts.
Q4: How are districts created or changed?
A: The creation or modification of districts is a complex process that involves legislative action by the state government. It typically involves considerations like population growth, administrative needs, and geographical factors.
Q5: What are the key challenges faced by districts in India?
A: Districts in India face various challenges, including poverty, lack of infrastructure, unemployment, social inequalities, and environmental degradation. These challenges vary in intensity across different districts, necessitating targeted interventions.
Tips for Studying the Districts Map of India
- Visualize the Data: Use interactive maps and online resources to visualize the districts map and understand the spatial distribution of various indicators.
- Compare and Contrast: Compare and contrast different districts based on their demographic, economic, and social characteristics to identify patterns and regional variations.
- Explore Case Studies: Analyze case studies of successful development programs implemented in specific districts to gain insights into best practices and lessons learned.
- Engage with Local Communities: Interact with local communities to understand their perspectives and challenges, enriching your understanding of the districts map.
- Stay Updated: Regularly update your knowledge about changes in district boundaries, administrative structures, and key development initiatives.
Conclusion
The districts map of India serves as a vital tool for understanding the country’s administrative structure, regional variations, and development challenges. By studying this map, we gain insights into the diverse socio-economic landscape of India, enabling informed decision-making and promoting equitable growth. It is crucial to engage with this map and its nuances to foster effective governance, targeted development, and a deeper understanding of the nation’s rich tapestry.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into India’s Administrative Tapestry: Understanding the Districts Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!