Mapping the Global Threat: Understanding the Prevalence of Malaria
Related Articles: Mapping the Global Threat: Understanding the Prevalence of Malaria
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Global Threat: Understanding the Prevalence of Malaria. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Global Threat: Understanding the Prevalence of Malaria
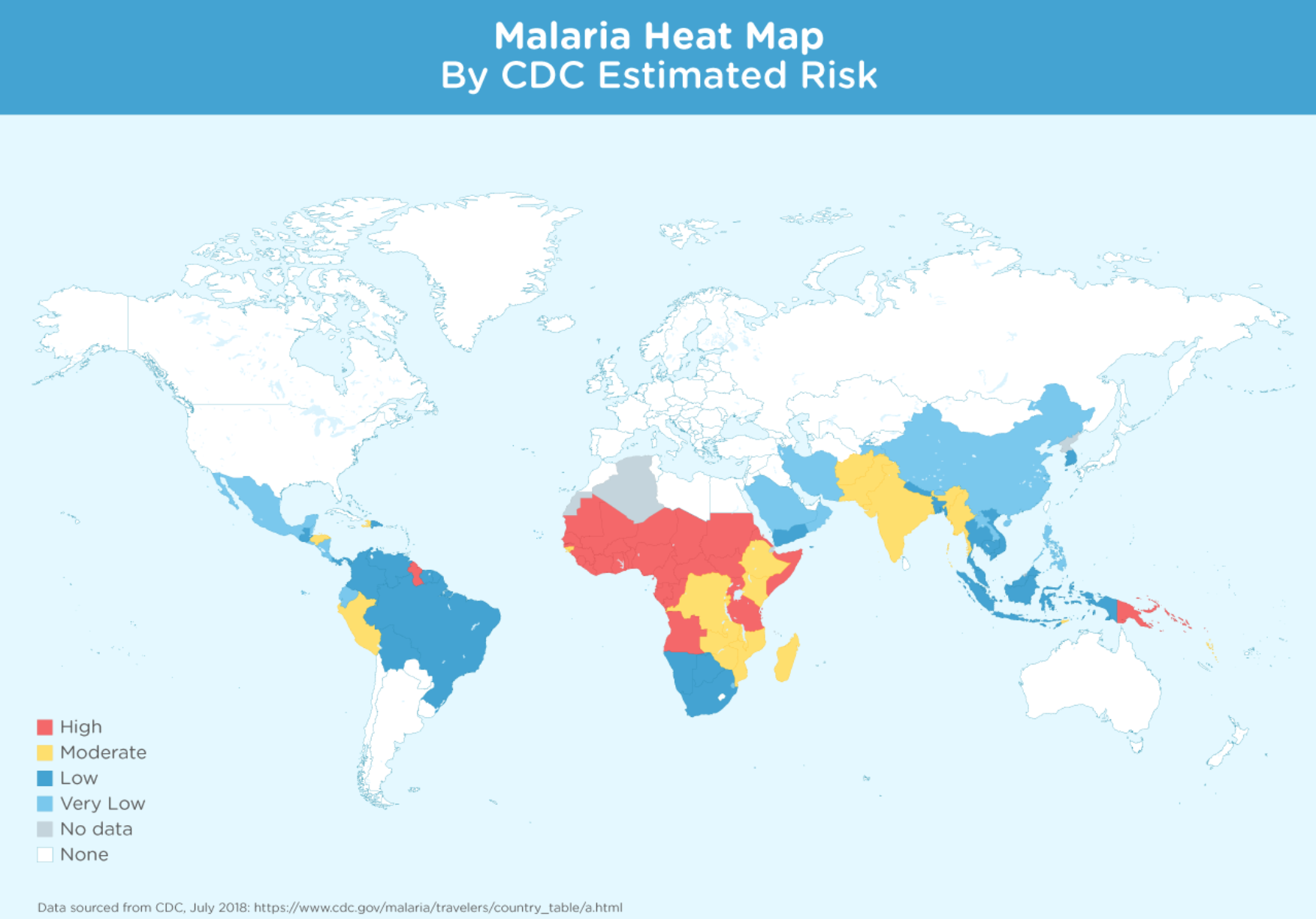
Malaria, a life-threatening mosquito-borne disease, continues to pose a significant public health challenge in many parts of the world. Visualizing the global distribution of malaria is crucial for understanding the disease’s reach, identifying high-risk areas, and guiding effective interventions. Maps serve as powerful tools for visualizing this complex issue, providing a clear and concise representation of malaria’s geographic footprint.
The Global Landscape of Malaria: A Visual Guide
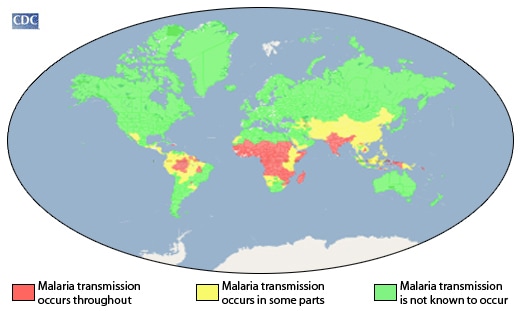
A map of malaria-endemic countries offers a comprehensive overview of the regions most affected by this disease. The map highlights the following key aspects:
- Geographic Distribution: Malaria is prevalent primarily in tropical and subtropical regions, where the conditions are favorable for the mosquito vectors that transmit the parasite.
- Intensity of Transmission: Maps can depict the intensity of malaria transmission, ranging from areas with high transmission rates to regions with low or intermittent transmission.
- Risk Zones: Maps can identify specific areas with high risk of malaria infection, allowing travelers and residents to take appropriate preventive measures.
- Progress in Malaria Control: Maps can track the progress of malaria control programs, showing areas where transmission has been reduced or eliminated.
Understanding the Map: Key Insights
The map of malaria-endemic countries reveals several crucial insights:
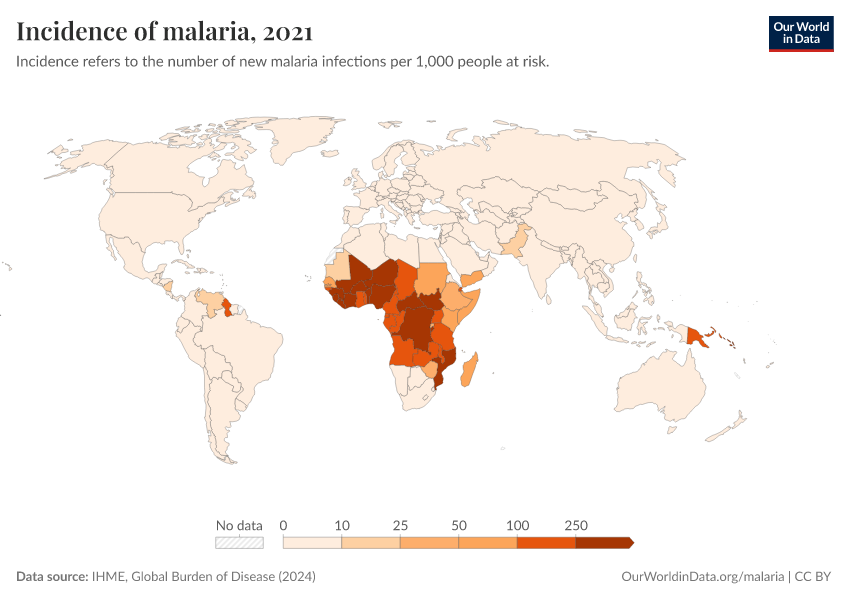
- Sub-Saharan Africa: The Epicenter of Malaria: The majority of malaria cases occur in Sub-Saharan Africa, accounting for roughly 95% of global cases. This region faces a disproportionate burden of the disease, with millions of children particularly vulnerable to its deadly effects.
- Other Affected Regions: While Africa bears the brunt of the malaria burden, other regions are also affected, including South America, Southeast Asia, and parts of the Middle East.
- Changing Landscape: The distribution of malaria is not static. Climate change, environmental factors, and human migration patterns can influence the spread of the disease, leading to shifts in the geographic distribution of malaria over time.
The Importance of Mapping Malaria
Maps play a critical role in the global fight against malaria:
- Targeted Interventions: Maps allow for the identification of high-risk areas, enabling the targeted allocation of resources, such as mosquito nets, antimalarial drugs, and vector control measures.
- Effective Surveillance: Maps facilitate the monitoring of malaria transmission patterns, providing crucial data for early detection of outbreaks and the implementation of timely interventions.
- Research and Development: Maps serve as valuable tools for researchers studying the epidemiology of malaria, helping them understand the factors influencing disease transmission and develop effective prevention and treatment strategies.
- Public Awareness: Maps can raise awareness about the global threat of malaria, encouraging individuals to take preventive measures and support global efforts to combat the disease.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Malaria Maps
Q: What information is typically included on a malaria map?
A: Malaria maps typically include:
- Geographic boundaries: Countries, regions, and specific locations affected by malaria.
- Transmission intensity: Areas with high, moderate, or low transmission rates.
- Risk zones: Areas with high risk of malaria infection, such as tourist destinations or areas with high mosquito populations.
- Data sources: The sources used to compile the map data, such as national surveillance programs or research studies.
Q: How often are malaria maps updated?
A: Malaria maps are typically updated annually or bi-annually to reflect the latest data on malaria transmission patterns and control efforts.
Q: How can I use a malaria map?
A: You can use a malaria map to:
- Plan your travel: Identify high-risk areas and take appropriate preventive measures.
- Understand the global malaria situation: Gain insight into the geographic distribution and intensity of malaria transmission.
- Support malaria control efforts: Educate yourself about the disease and contribute to global efforts to combat malaria.
Tips for Using Malaria Maps
- Consult reputable sources: Ensure the map you are using is based on reliable data and updated regularly.
- Consider the map’s purpose: Different maps may be designed for different purposes, such as travel planning or research.
- Interpret the data carefully: Pay attention to the map’s legend and the scales used to represent different levels of transmission.
- Combine with other resources: Use malaria maps in conjunction with other information sources, such as travel advisories or health guidelines.
Conclusion: The Power of Visual Representation
Maps serve as powerful tools for understanding and combating the global threat of malaria. By providing a visual representation of the disease’s geographic distribution and transmission patterns, maps empower individuals, organizations, and governments to take targeted actions to prevent, treat, and ultimately eliminate malaria. As we continue to strive for a malaria-free world, the use of maps will remain essential for guiding our efforts and ensuring a healthier future for all.

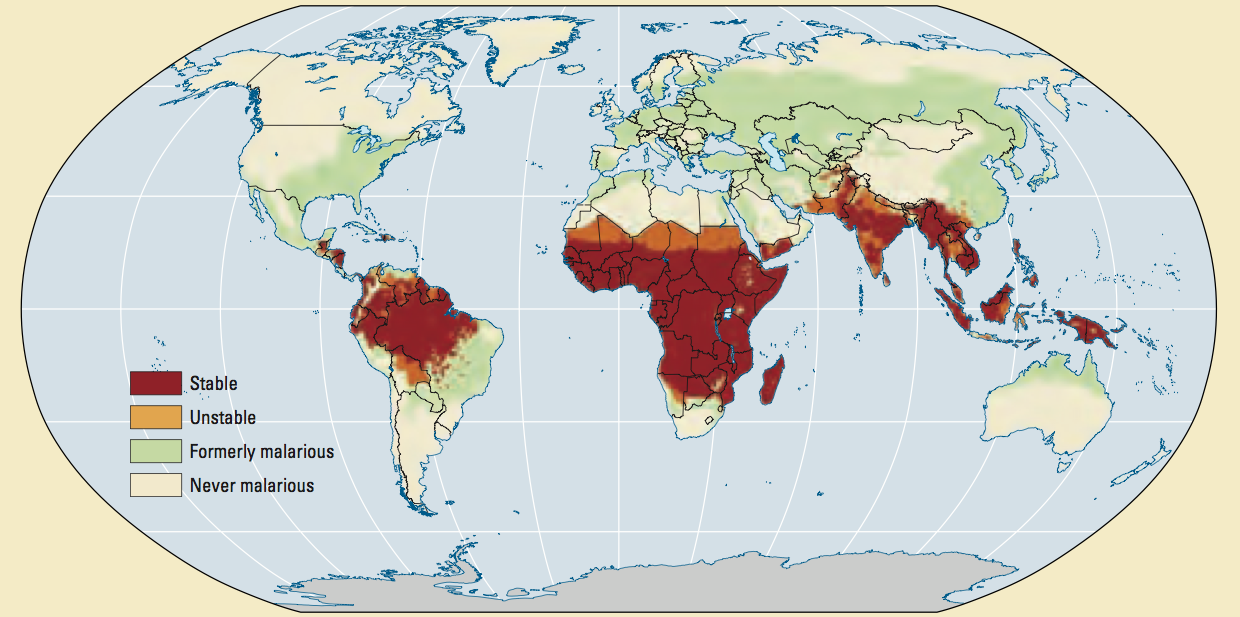
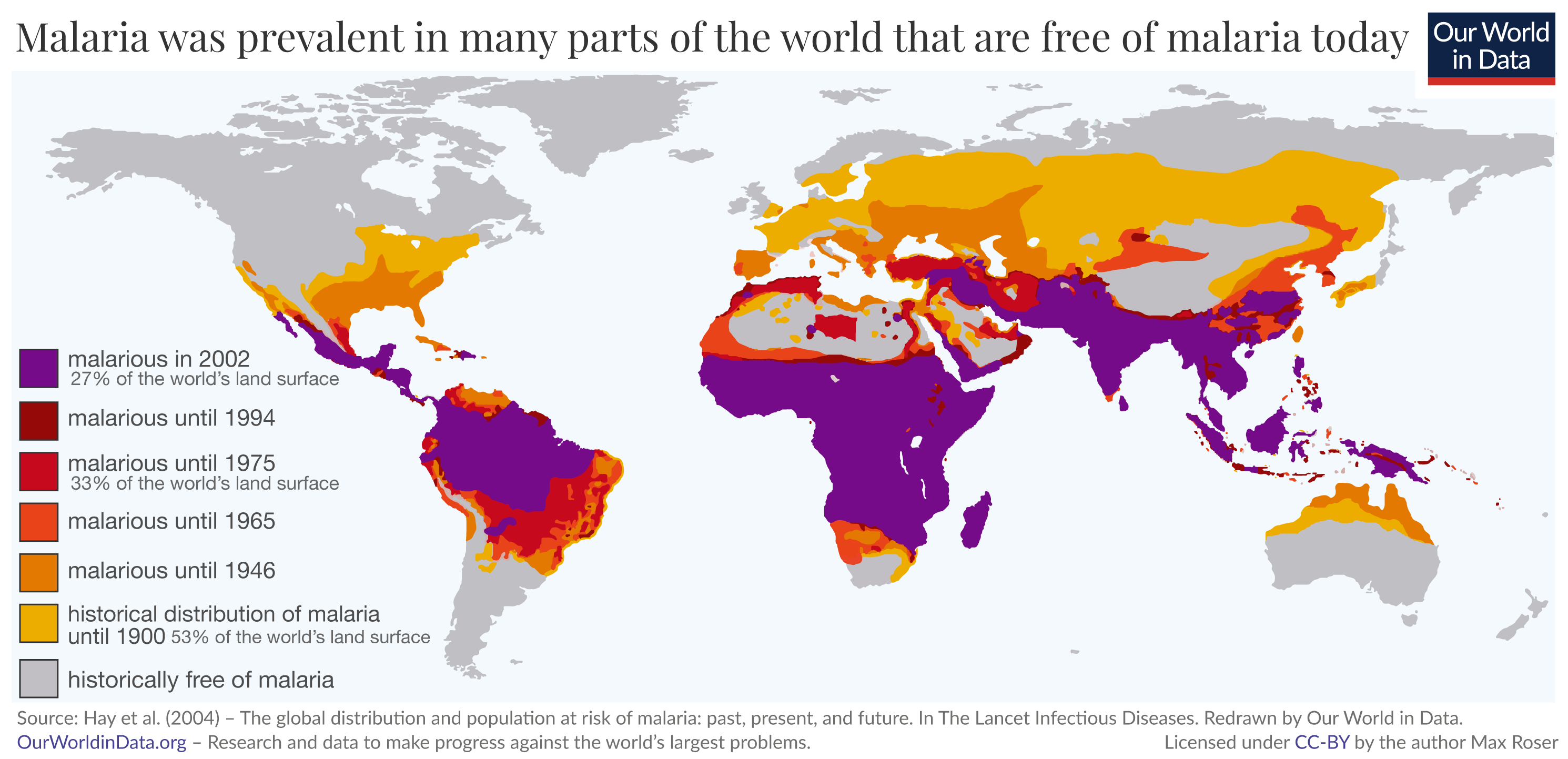
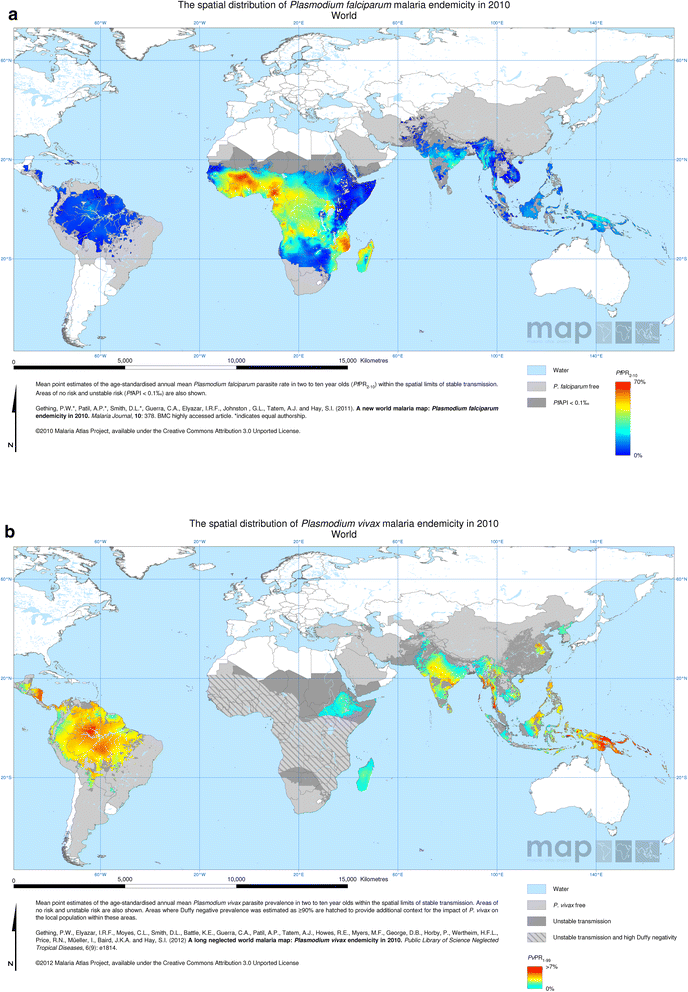

![Malaria risk zones in the world. - [1427x628] : MapPorn](http://www.mappery.com/maps/Malaria-Risk-Map.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Global Threat: Understanding the Prevalence of Malaria. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!