Mongolia and China: A Geopolitical Tapestry Woven Through History and Geography
Related Articles: Mongolia and China: A Geopolitical Tapestry Woven Through History and Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mongolia and China: A Geopolitical Tapestry Woven Through History and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mongolia and China: A Geopolitical Tapestry Woven Through History and Geography

The relationship between Mongolia and China is a complex and multifaceted one, deeply intertwined by geography, history, and shared cultural elements. This article delves into the geographical relationship between the two nations, exploring the significance of their shared border, the influence of their respective landscapes, and the historical and cultural connections that have shaped their interactions over centuries.
A Borderland of Influence:
Mongolia and China share a 4,677-kilometer-long border, the fifth-longest land border in the world. This extensive boundary stretches from the Gobi Desert in the south to the Taiga forests in the north, traversing diverse landscapes that have profoundly shaped the history and culture of both nations.
Geographic Features and Their Significance:
- The Gobi Desert: The Gobi Desert, a vast expanse of arid land, dominates the southern portion of the border. Its harsh environment has acted as a natural barrier, influencing the flow of people and goods between the two countries. The Gobi’s harshness has also shaped the nomadic cultures of both Mongolia and northern China, fostering resilience and resourcefulness.
- The Altai Mountains: The Altai Mountains, rising along the western portion of the border, represent a natural divide between the two nations. Their towering peaks have served as a geographical barrier, influencing the movement of people and trade routes. The Altai’s rich mineral resources have also contributed to economic ties between Mongolia and China.
- The Mongolian Steppe: The vast Mongolian steppe, stretching across the northern part of the country, provides a fertile ground for pastoralism, a traditional way of life that has shaped Mongolian culture and identity. The steppe’s proximity to China’s northern provinces has facilitated cultural exchange and trade throughout history.
Historical Intertwining:
The history of Mongolia and China is deeply intertwined, marked by periods of conflict and cooperation. The nomadic Mongol empires, notably the Yuan Dynasty under Kublai Khan, exerted significant influence over China, leaving a lasting impact on Chinese culture and society. However, the relationship between the two nations has also been marked by periods of conflict, as evidenced by the Ming Dynasty’s efforts to push back against Mongol influence.
Modern Interactions:
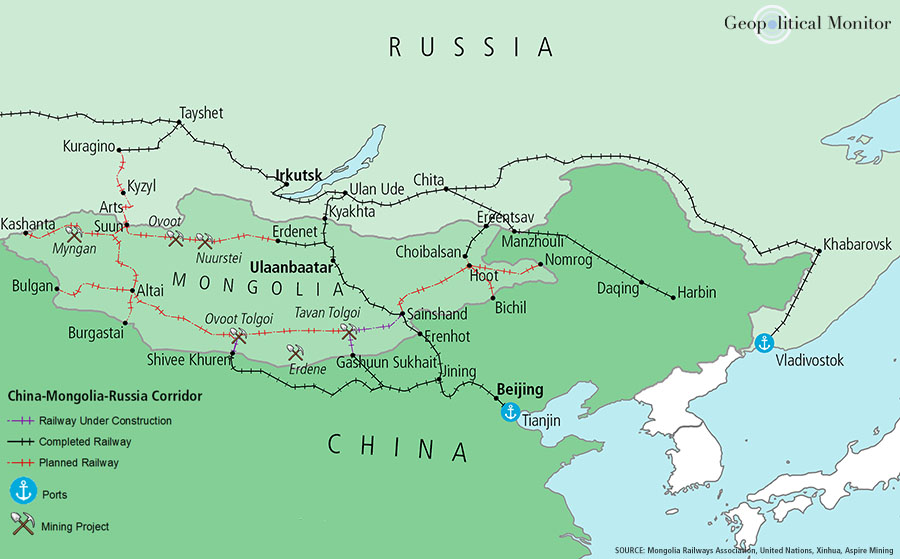
In modern times, the relationship between Mongolia and China has evolved into one of strategic partnership. China has emerged as a major economic and political player in the region, investing heavily in Mongolia’s infrastructure and natural resources. This economic interdependence has fostered close ties between the two nations, creating opportunities for cooperation in areas such as mining, energy, and infrastructure development.
Cultural Connections:
The shared border and historical interactions have fostered significant cultural exchange between Mongolia and China. The Mongol Empire’s influence on Chinese culture is evident in aspects such as language, cuisine, and art. Similarly, Mongolian culture has been influenced by Chinese traditions, particularly in areas such as religion, literature, and music.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite the close ties between Mongolia and China, their relationship is not without challenges. Concerns about China’s growing influence in Mongolia, particularly in areas such as resource extraction and infrastructure development, have led to anxieties about economic dependence and potential loss of sovereignty. However, the two nations also have opportunities for cooperation in areas such as environmental protection, combating climate change, and promoting regional stability.
FAQ:
Q: What are the main geographical features along the Mongolia-China border?
A: The Mongolia-China border traverses a diverse landscape, encompassing the Gobi Desert, the Altai Mountains, and the Mongolian Steppe. These features have historically influenced the relationship between the two nations, acting as barriers and facilitating trade and cultural exchange.
Q: How has the Gobi Desert influenced the relationship between Mongolia and China?
A: The Gobi Desert has acted as a natural barrier, limiting the flow of people and goods between the two countries. It has also shaped the nomadic cultures of both Mongolia and northern China, fostering resilience and resourcefulness.
Q: What is the significance of the Altai Mountains in the context of Mongolia and China?
A: The Altai Mountains, rising along the western portion of the border, represent a natural divide between the two nations. Their towering peaks have served as a geographical barrier, influencing the movement of people and trade routes. The Altai’s rich mineral resources have also contributed to economic ties between Mongolia and China.
Q: What are some of the key historical events that have shaped the relationship between Mongolia and China?
A: Key historical events include the rise of the Mongol Empire, the Yuan Dynasty under Kublai Khan, the Ming Dynasty’s efforts to push back against Mongol influence, and the establishment of the People’s Republic of China in 1949.
Q: How has the relationship between Mongolia and China evolved in modern times?
A: In modern times, the relationship between Mongolia and China has evolved into one of strategic partnership. China has emerged as a major economic and political player in the region, investing heavily in Mongolia’s infrastructure and natural resources. This economic interdependence has fostered close ties between the two nations.
Q: What are some of the challenges and opportunities facing the relationship between Mongolia and China?
A: Challenges include concerns about China’s growing influence in Mongolia, particularly in areas such as resource extraction and infrastructure development. Opportunities for cooperation exist in areas such as environmental protection, combating climate change, and promoting regional stability.
Tips:
- Understanding the historical context: It is crucial to understand the historical interactions between Mongolia and China to fully grasp the complexities of their current relationship.
- Recognizing the geographical influences: The diverse landscapes along the border have significantly influenced the relationship, shaping the cultures, economies, and historical interactions of both nations.
- Appreciating the cultural connections: The shared border and historical interactions have fostered significant cultural exchange between Mongolia and China, resulting in shared traditions and influences.
- Analyzing the economic interdependence: China’s growing economic influence in Mongolia has created opportunities for cooperation but also raises concerns about economic dependence and potential loss of sovereignty.
Conclusion:
The relationship between Mongolia and China is a complex and dynamic one, shaped by geography, history, and culture. The shared border, the diverse landscapes, and the historical interactions have all contributed to the multifaceted nature of their relationship. Understanding this complex tapestry is essential for comprehending the geopolitical dynamics of the region and appreciating the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead for both nations. As Mongolia and China continue to navigate their shared future, the understanding of their unique relationship will be crucial for fostering cooperation and promoting stability in the region.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mongolia and China: A Geopolitical Tapestry Woven Through History and Geography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!