Navigating the Complexities of Knowledge: A Deep Dive into Faction Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of Knowledge: A Deep Dive into Faction Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complexities of Knowledge: A Deep Dive into Faction Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of Knowledge: A Deep Dive into Faction Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Complexities of Knowledge: A Deep Dive into Faction Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Structure of a Faction Map
- 3.2 The Benefits of Utilizing Faction Maps
- 3.3 Applications of Faction Maps in Various Fields
- 3.4 Creating and Utilizing a Faction Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Faction Mapping
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Complexities of Knowledge: A Deep Dive into Faction Maps
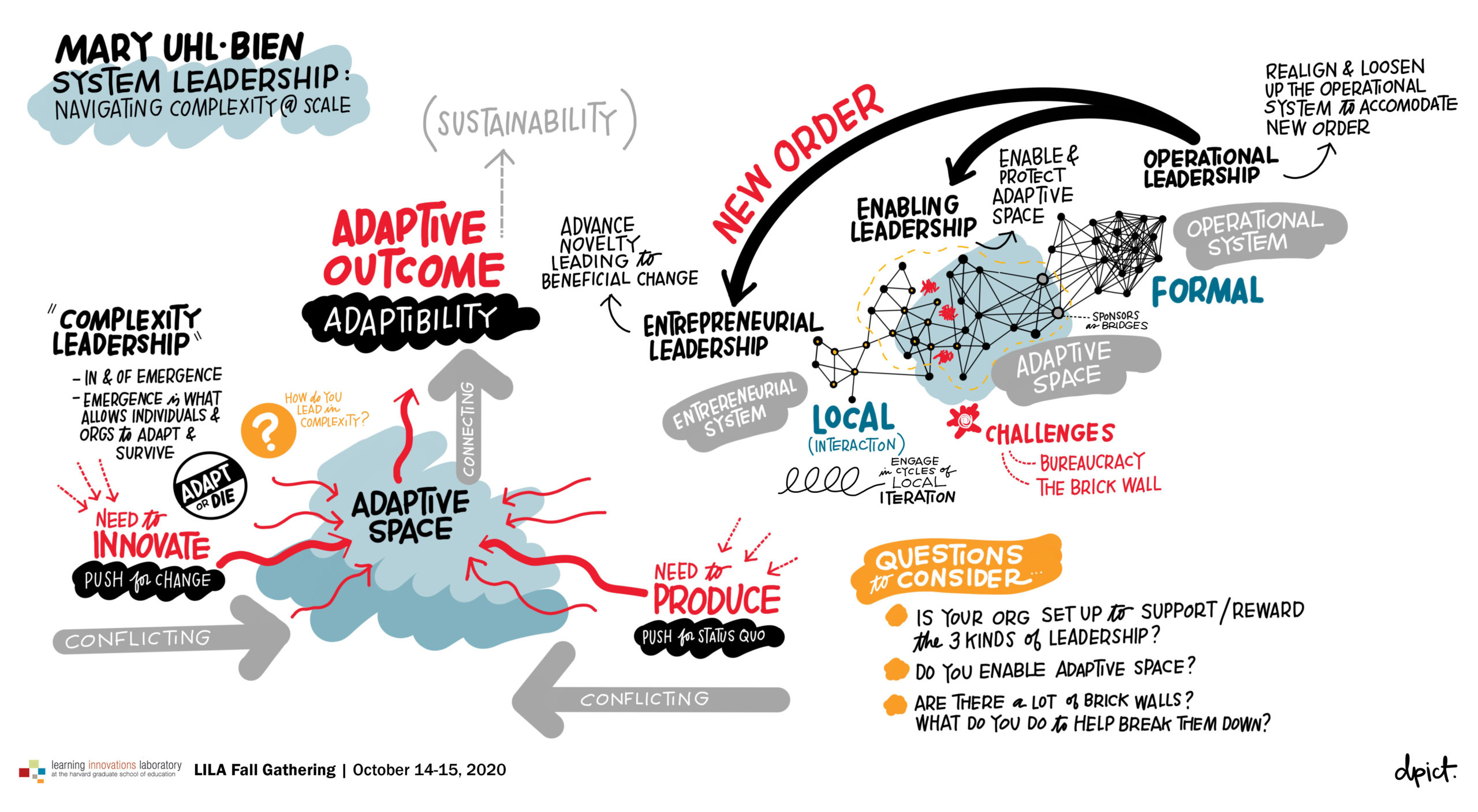
In the realm of knowledge management and information organization, the concept of a faction map emerges as a powerful tool for navigating complex landscapes of ideas, opinions, and perspectives. A faction map, also known as a belief map, is a visual representation of the diverse viewpoints and arguments surrounding a particular topic or issue. This map serves as a roadmap, helping individuals understand the intricate web of beliefs, ideologies, and positions held by different groups or factions within a given domain.
Understanding the Structure of a Faction Map
A faction map is typically constructed as a network diagram, where nodes represent different factions or groups. These factions are interconnected by edges that depict the relationships between them, such as agreement, disagreement, or conflict. Each node can be further elaborated with information about the faction’s core beliefs, key arguments, and supporting evidence.
Key Components of a Faction Map:
- Nodes: Each node represents a distinct faction, group, or individual holding a specific viewpoint. These can be political parties, religious organizations, scientific communities, or even individuals with unique perspectives.
-
Edges: Edges connect the nodes and indicate the relationship between factions. These relationships can be categorized as:
- Agreement: When two factions share similar beliefs or perspectives.
- Disagreement: When two factions hold opposing views or clash on specific issues.
- Conflict: When two factions are actively engaged in a struggle or debate.
-
Attributes: Each node can be further annotated with additional information, including:
- Core Beliefs: The fundamental principles and values that define the faction’s worldview.
- Key Arguments: The main points and reasoning used to support their position.
- Supporting Evidence: The data, research, or examples used to substantiate their claims.
- Influence: The level of impact or sway the faction holds within the discourse.
The Benefits of Utilizing Faction Maps
Faction maps offer several significant benefits, making them valuable tools for various applications, including:
- Enhanced Understanding: By visually representing the diverse perspectives surrounding a topic, faction maps provide a clear and comprehensive overview of the landscape, facilitating a deeper understanding of the complexities involved.
- Improved Communication: Faction maps can help bridge communication gaps by offering a common framework for understanding different viewpoints. This shared understanding can foster more productive and respectful dialogue, even when disagreements exist.
- Strategic Planning: By identifying the key players, their positions, and the dynamics of the discourse, faction maps can aid in developing effective strategies for navigating complex situations, whether in business, politics, or social activism.
- Conflict Resolution: Recognizing the different perspectives and understanding the underlying reasons for disagreement can contribute to more effective conflict resolution by fostering empathy and identifying common ground.
- Knowledge Management: Faction maps serve as powerful tools for organizing and visualizing knowledge, facilitating the identification of gaps in understanding, and promoting further research and exploration.
Applications of Faction Maps in Various Fields
Faction maps find practical applications in various domains, including:
- Politics: Understanding the political landscape, identifying key players, and analyzing the dynamics of political discourse.
- Business: Identifying market segments, understanding customer preferences, and analyzing competitive landscapes.
- Education: Facilitating discussions on complex topics, fostering critical thinking skills, and promoting understanding of diverse viewpoints.
- Social Sciences: Analyzing social movements, understanding cultural dynamics, and investigating the interplay of different beliefs and ideologies.
- Research and Development: Identifying research gaps, understanding the evolution of scientific thought, and facilitating interdisciplinary collaboration.
Creating and Utilizing a Faction Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating and utilizing a faction map involves a systematic process:
1. Defining the Scope: Clearly define the topic or issue you want to map, ensuring its focus is sufficiently narrow to be manageable.
2. Identifying the Key Players: Identify the major groups or individuals holding distinct perspectives on the chosen topic.
3. Researching Each Faction: Conduct thorough research to understand each faction’s core beliefs, key arguments, and supporting evidence.
4. Mapping the Relationships: Visualize the connections between the factions, identifying areas of agreement, disagreement, and conflict.
5. Analyzing the Map: Analyze the map to identify patterns, emerging themes, and potential areas for further investigation or discussion.
6. Communicating the Map: Clearly communicate the insights gained from the faction map to the intended audience, using appropriate visualization tools and language.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the limitations of faction maps?
A: Faction maps are inherently simplified representations of complex realities. They can be subject to bias, oversimplification, and the potential for misinterpretation. It is crucial to remember that faction maps are tools for understanding, not definitive statements of truth.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy and objectivity of a faction map?
A: Strive for inclusivity by incorporating diverse viewpoints and perspectives. Utilize credible sources and research to support the information presented. Be transparent about the biases and limitations of the map, encouraging critical engagement with its content.
Q: Can faction maps be used for persuasive purposes?
A: While faction maps can help understand different perspectives, they should not be used to manipulate or persuade others. Instead, they should be employed as tools for facilitating open dialogue, promoting understanding, and fostering informed decision-making.
Tips for Effective Faction Mapping
- Maintain a neutral perspective: Strive for objectivity in representing different viewpoints, avoiding biased language or framing.
- Use clear and concise language: Avoid jargon and ensure the map is accessible to a diverse audience.
- Prioritize relevant information: Focus on the most important aspects of each faction, avoiding unnecessary details.
- Encourage collaboration: Involve multiple perspectives in the map-building process to ensure inclusivity and accuracy.
- Regularly review and update: As new information emerges or perspectives evolve, update the faction map to reflect the latest developments.
Conclusion
Faction maps offer a valuable tool for navigating the complexities of knowledge and understanding diverse perspectives. By providing a visual representation of the intricate web of beliefs and ideologies surrounding a topic, faction maps facilitate deeper comprehension, promote productive dialogue, and support strategic decision-making. While they are not without limitations, faction maps remain a powerful instrument for fostering informed understanding and navigating the ever-evolving landscape of ideas.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complexities of Knowledge: A Deep Dive into Faction Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!