Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Egypt and the Middle East
Related Articles: Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Egypt and the Middle East
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Egypt and the Middle East. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Egypt and the Middle East
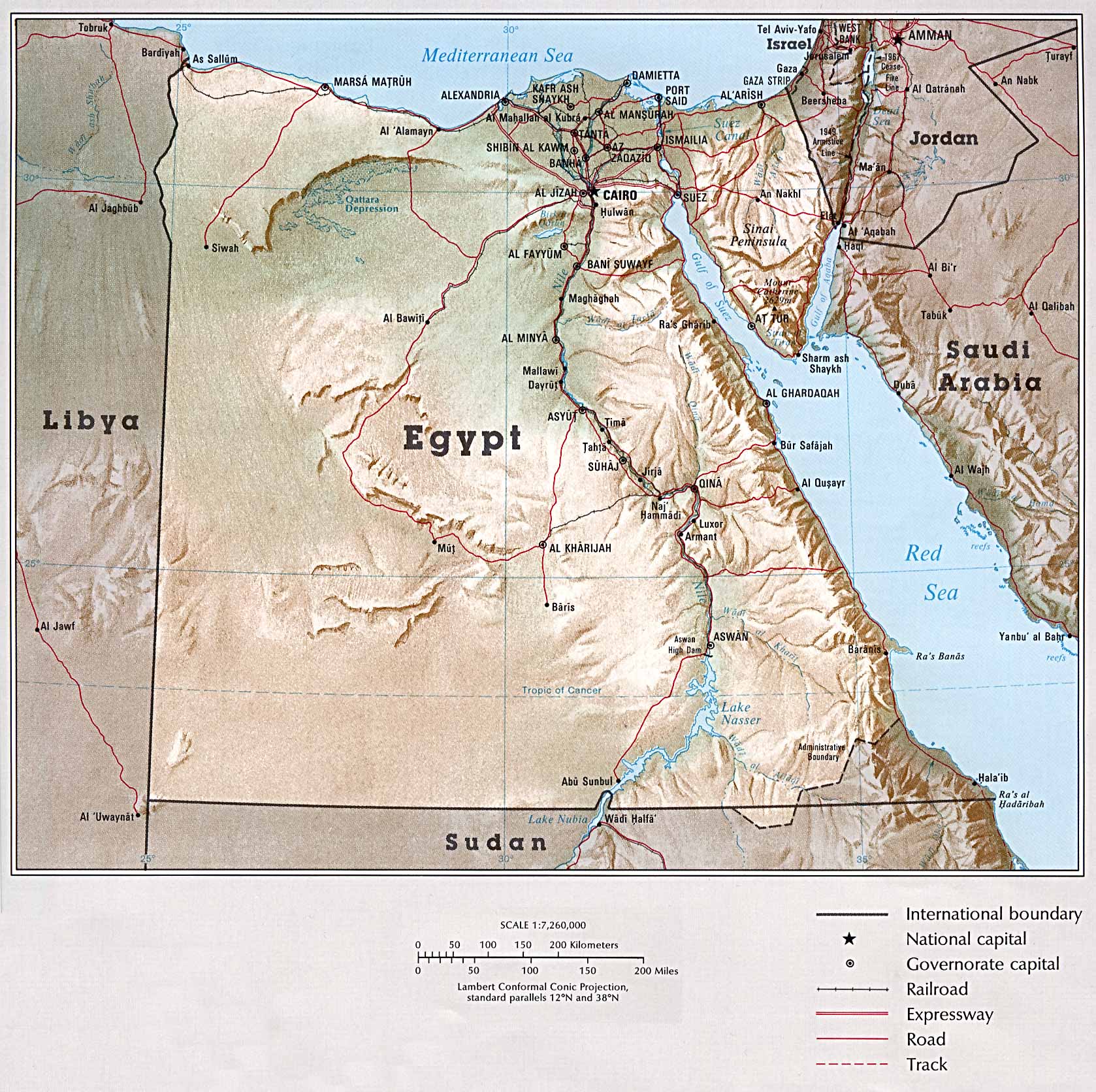
The Middle East, a region steeped in history, culture, and geopolitical significance, is a tapestry woven with diverse landscapes, vibrant civilizations, and complex relationships. Understanding its geography, particularly the position of Egypt within this intricate mosaic, is crucial for comprehending the region’s dynamics and its impact on the world.
A Geographic Overview
The Middle East, a broad term encompassing Southwest Asia and Northeast Africa, is defined by its unique geographical features. The region is characterized by:
- Arid and Semi-arid Landscapes: Dominated by deserts, such as the Sahara in North Africa and the Arabian Desert in the Arabian Peninsula, the region faces significant water scarcity challenges.
- Strategic Waterways: The Nile River in Egypt, the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in Mesopotamia, and the Persian Gulf are vital waterways that have shaped civilizations and influenced trade routes for millennia.
- Mountain Ranges: The Zagros Mountains in Iran, the Taurus Mountains in Turkey, and the Atlas Mountains in North Africa provide natural barriers and influence weather patterns.
- Rich Coastal Areas: The Mediterranean Sea, the Red Sea, the Persian Gulf, and the Indian Ocean offer access to global trade and connect the region to other continents.
Egypt: A Bridge Between Continents
Egypt, a land of ancient wonders and enduring cultural heritage, occupies a pivotal position within the Middle East. Located in the northeastern corner of Africa, it acts as a bridge between Africa, Asia, and Europe. Its strategic location has shaped its history and its role in the region’s affairs.
- The Nile River: The lifeblood of Egypt, the Nile flows through the country from south to north, providing fertile land for agriculture and sustaining a vibrant civilization for millennia.
- The Suez Canal: This artificial waterway, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, is a vital global shipping route, facilitating trade between Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- Desert Landscapes: While the Nile Valley is a fertile oasis, the majority of Egypt is covered by the vast Sahara Desert, presenting unique challenges and opportunities.
- Cultural Crossroads: Egypt has been a crossroads of civilizations for centuries, absorbing influences from Africa, the Middle East, and Europe, resulting in a rich cultural tapestry.
Understanding the Map: A Key to the Region’s Complexity
The map of Egypt and the Middle East is not merely a static representation of landmasses. It is a dynamic tool for understanding:
- Historical Connections: The map reveals the historical pathways of civilizations, trade routes, and migrations, illuminating the region’s interconnectedness.
- Geopolitical Dynamics: The map highlights the strategic location of key countries, their proximity to vital waterways, and the potential for conflict or cooperation.
- Resource Distribution: The map reveals the distribution of natural resources, such as oil and gas, water, and fertile land, which significantly influences the region’s economy and politics.
- Cultural Diversity: The map illustrates the vast cultural mosaic of the region, encompassing Arabic, Persian, Turkish, Kurdish, and other languages and traditions.
Navigating the Challenges: The Importance of Understanding the Map
The Middle East faces numerous challenges, including:
- Political Instability: The region is characterized by ongoing conflicts, political transitions, and social unrest, making it a volatile and unpredictable area.
- Water Scarcity: The arid climate and increasing population place immense pressure on water resources, leading to tensions and competition.
- Economic Disparities: The region experiences significant economic disparities, with some countries enjoying significant oil wealth while others struggle with poverty and unemployment.
- Religious and Ethnic Tensions: The Middle East is home to a diverse array of religious and ethnic groups, leading to potential tensions and conflicts.
Understanding the map of Egypt and the Middle East provides a framework for navigating these challenges. It helps to:
- Identify Key Players: The map helps to identify the major countries and their respective roles in regional affairs.
- Analyze Power Dynamics: The map reveals the strategic location of key resources, infrastructure, and military bases, providing insights into power dynamics.
- Understand Conflict Zones: The map highlights areas of tension and conflict, aiding in the understanding of the root causes and potential solutions.
- Promote Cooperation: By understanding the shared challenges and interconnectedness of the region, the map can foster cooperation and dialogue between nations.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Map
Q: What is the significance of the Suez Canal?
A: The Suez Canal is a vital shipping route connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, facilitating trade between Europe, Asia, and Africa. It significantly reduces travel time and transportation costs, making it a crucial artery for global commerce.
Q: What are the major oil-producing countries in the Middle East?
A: The Middle East is home to some of the world’s largest oil reserves. Major oil-producing countries include Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, and the United Arab Emirates.
Q: What are the main cultural and linguistic groups in the Middle East?
A: The Middle East is a diverse region with a rich tapestry of cultures and languages. Major groups include Arabs, Persians, Turks, Kurds, and various ethnic minorities.
Q: What are the major religions practiced in the Middle East?
A: Islam, Christianity, and Judaism are the dominant religions in the Middle East. Each religion has a significant historical and cultural presence in the region.
Q: What are the main environmental challenges facing the Middle East?
A: The Middle East faces significant environmental challenges, including water scarcity, desertification, air pollution, and climate change. These challenges are exacerbated by population growth and economic development.
Tips for Understanding the Map
- Focus on Key Geographic Features: Pay attention to major waterways, mountain ranges, and desert areas, as they significantly influence the region’s dynamics.
- Identify Strategic Locations: Understand the location of major cities, ports, oil fields, and military bases, as they play crucial roles in regional affairs.
- Explore Historical Context: Research the historical connections and interactions between countries and civilizations, providing context for contemporary events.
- Consider Political and Economic Factors: Analyze the political systems, economic structures, and resource distribution, as they influence the region’s stability and development.
- Embrace Cultural Diversity: Recognize the diverse cultural and religious traditions within the region, fostering respect and understanding.
Conclusion: A Complex Tapestry of History, Culture, and Geopolitics
The map of Egypt and the Middle East is a powerful tool for understanding the region’s history, culture, and geopolitical dynamics. It reveals the interconnectedness of nations, the strategic importance of key resources, and the challenges faced by the region. By studying the map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and significance of this vital part of the world. Navigating the challenges and opportunities of the Middle East requires a nuanced understanding of its geography, history, and culture, all of which are illuminated by the intricate tapestry of the map.


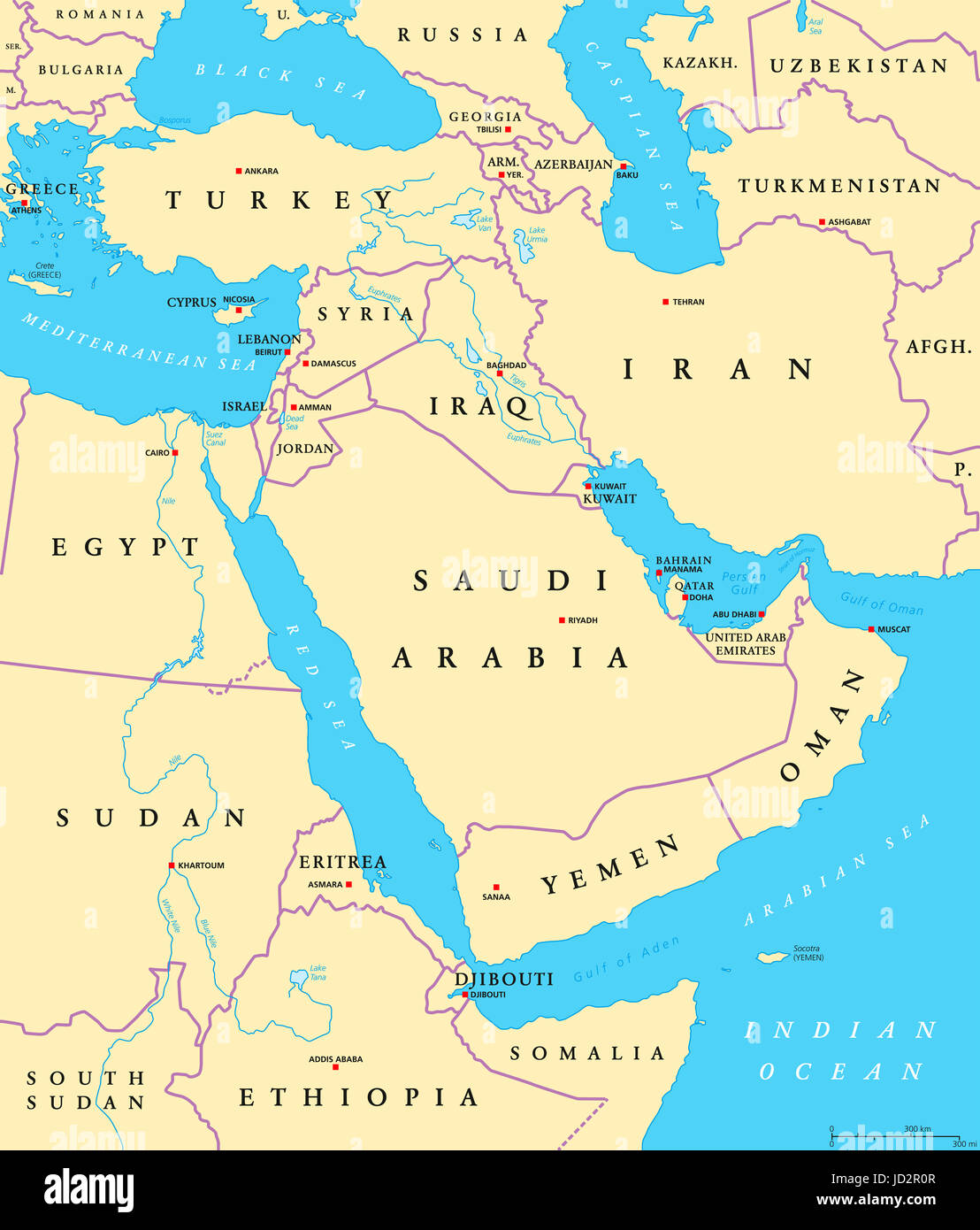



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Crossroads: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Egypt and the Middle East. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!