Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Physical and Political Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Physical and Political Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Physical and Political Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Physical and Political Maps

Europe, a continent brimming with history, culture, and diverse landscapes, demands a nuanced understanding. Two crucial tools for navigating this intricate tapestry are physical and political maps. These maps, while seemingly simple, provide a powerful lens through which to explore the continent’s geographical features and political realities.
Unveiling the Physical Fabric of Europe:
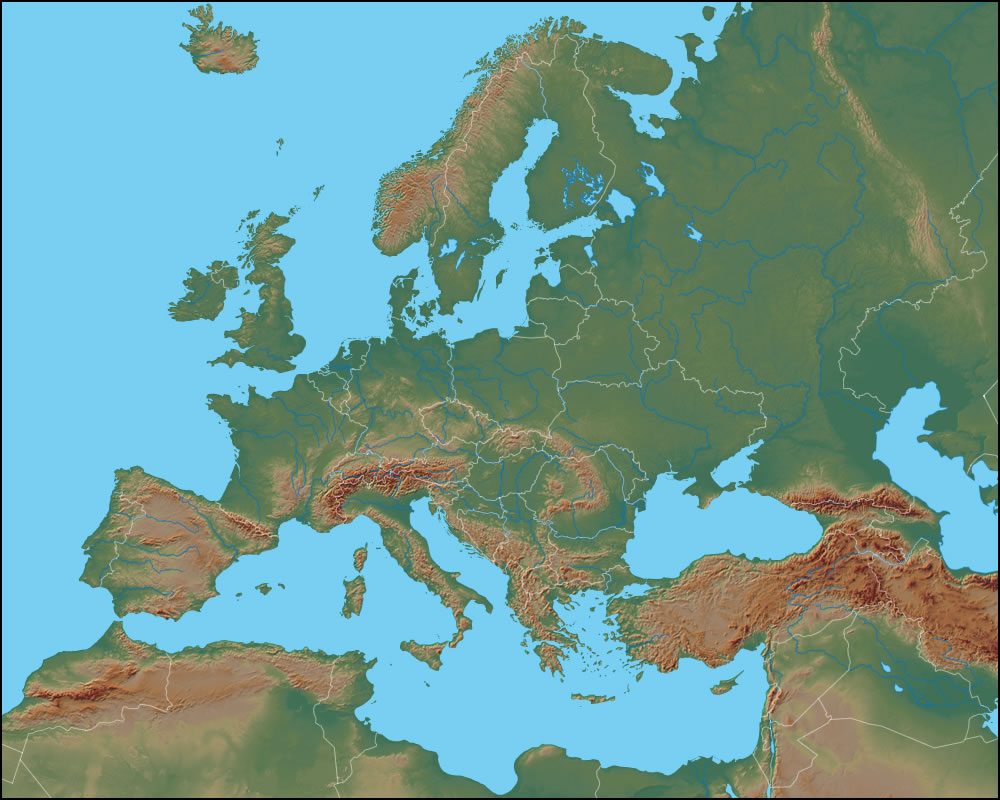
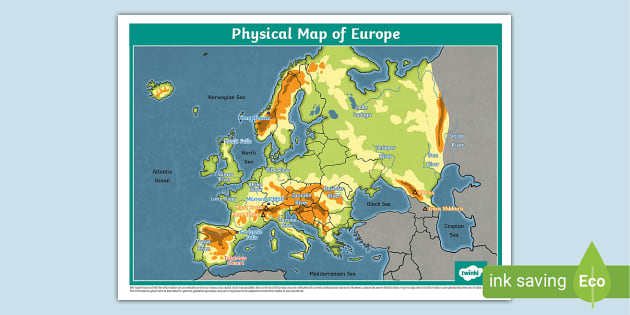
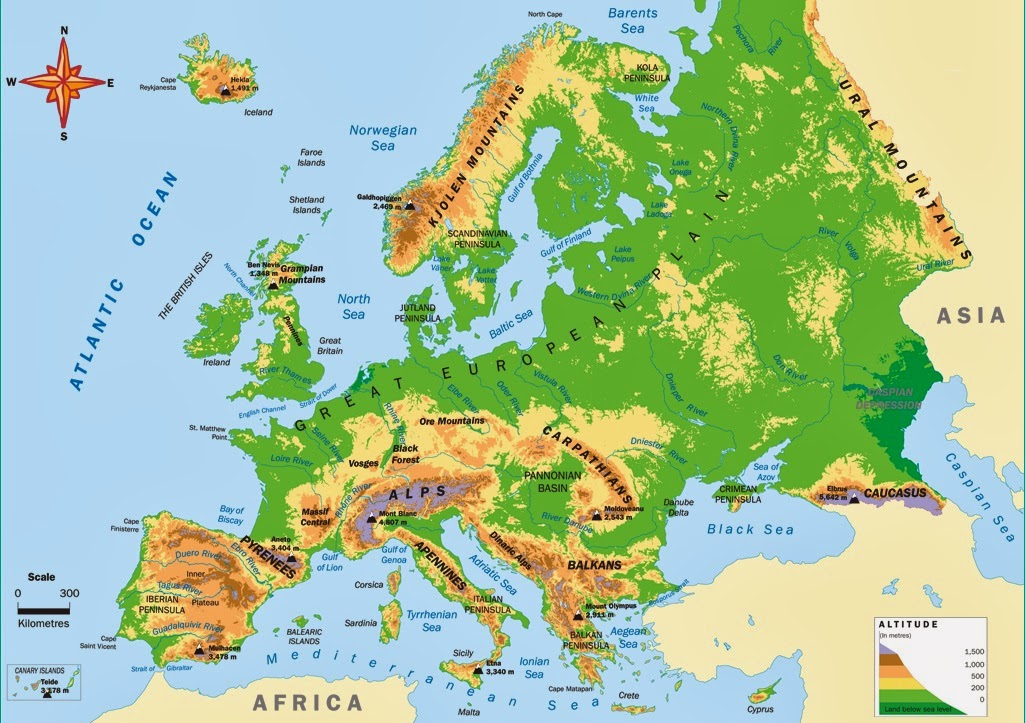
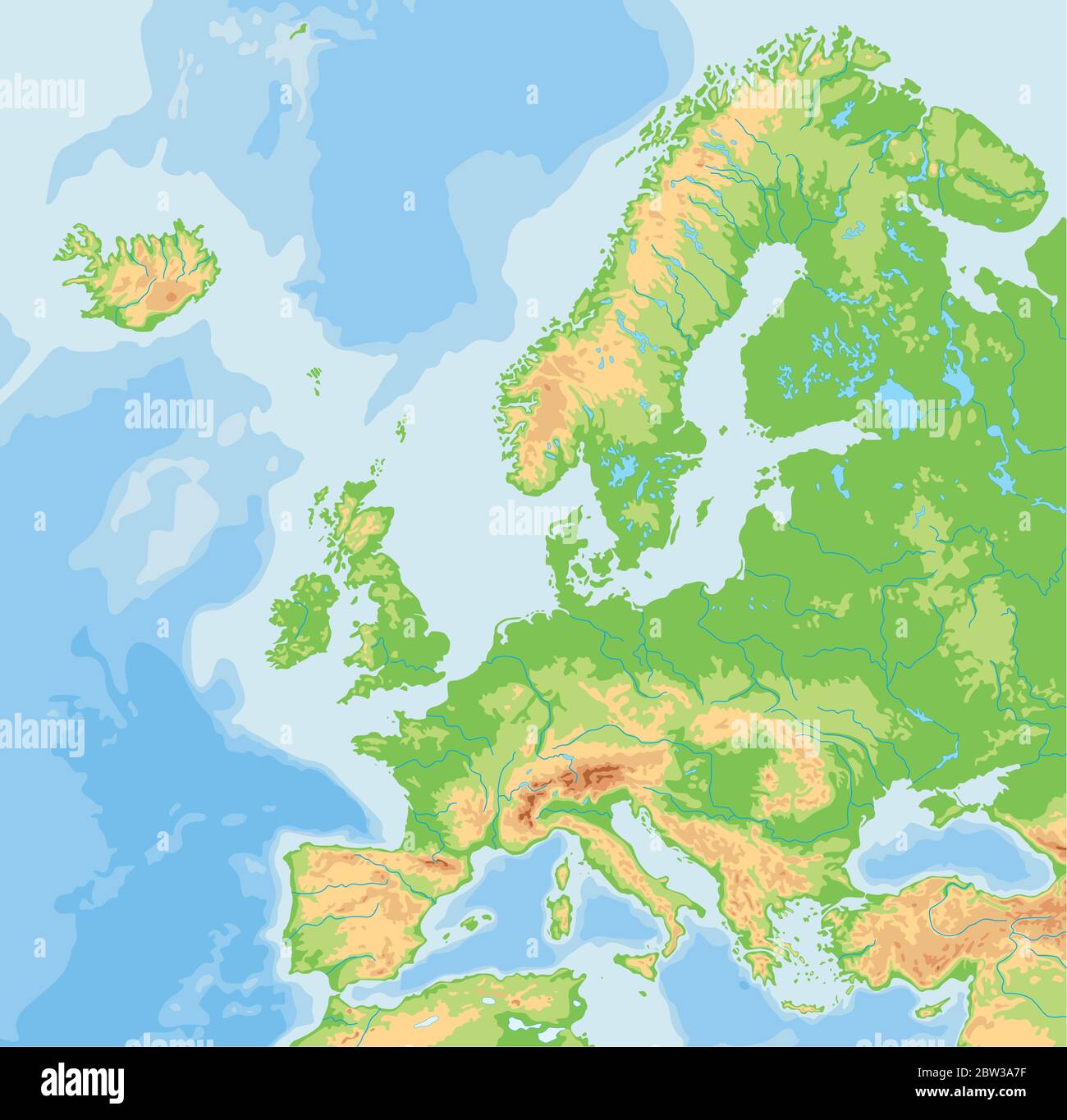
A physical map of Europe reveals the continent’s intricate tapestry of landforms, showcasing the dramatic interplay of mountains, plains, rivers, and coastlines. This visual representation allows for a deeper understanding of the continent’s diverse environments and the forces that have shaped them over millennia.
Mountains and Plateaus:
The Alps, stretching across central Europe, stand as a monumental backbone, influencing weather patterns and shaping the lives of surrounding populations. The Pyrenees, Carpathians, and Apennines, each with their distinct characteristics, add to the continent’s varied topography. Plateaus like the Iberian, Massif Central, and Bohemian Plateaus, offer contrasting landscapes, contributing to the continent’s rich agricultural diversity.
Plains and Lowlands:
Vast plains like the North European Plain and the Great Hungarian Plain provide fertile ground for agriculture and serve as corridors for transportation. The lowlands along the Baltic Sea and the Black Sea contribute to the continent’s diverse coastline and create ideal conditions for maritime activities.
Rivers and Coastlines:
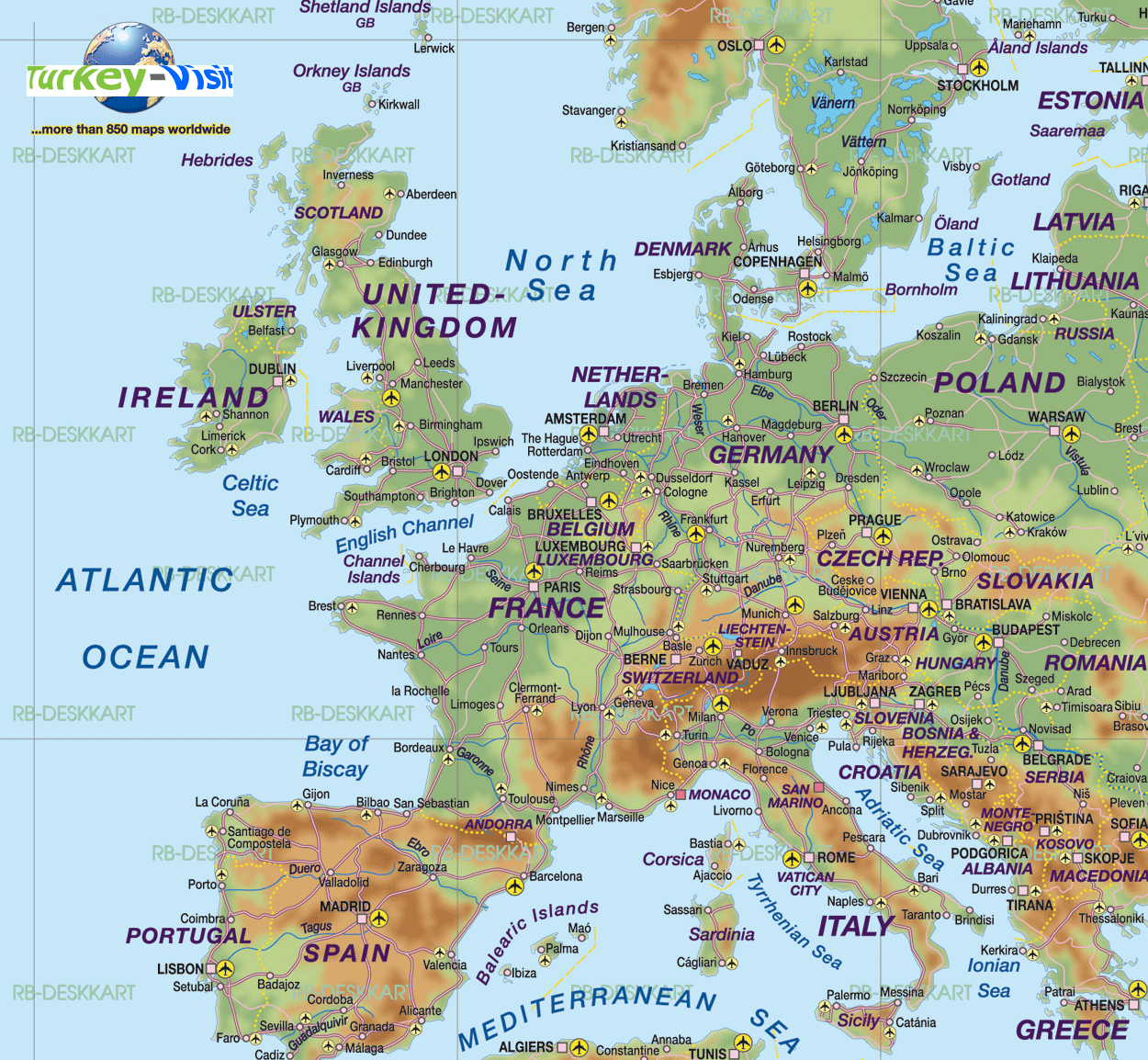
The Danube, Rhine, and Volga rivers are arteries of trade and transportation, connecting cities and facilitating economic growth. The continent’s extensive coastline, featuring numerous peninsulas, islands, and seas, has played a pivotal role in shaping European history, culture, and trade.
Understanding the Political Landscape:
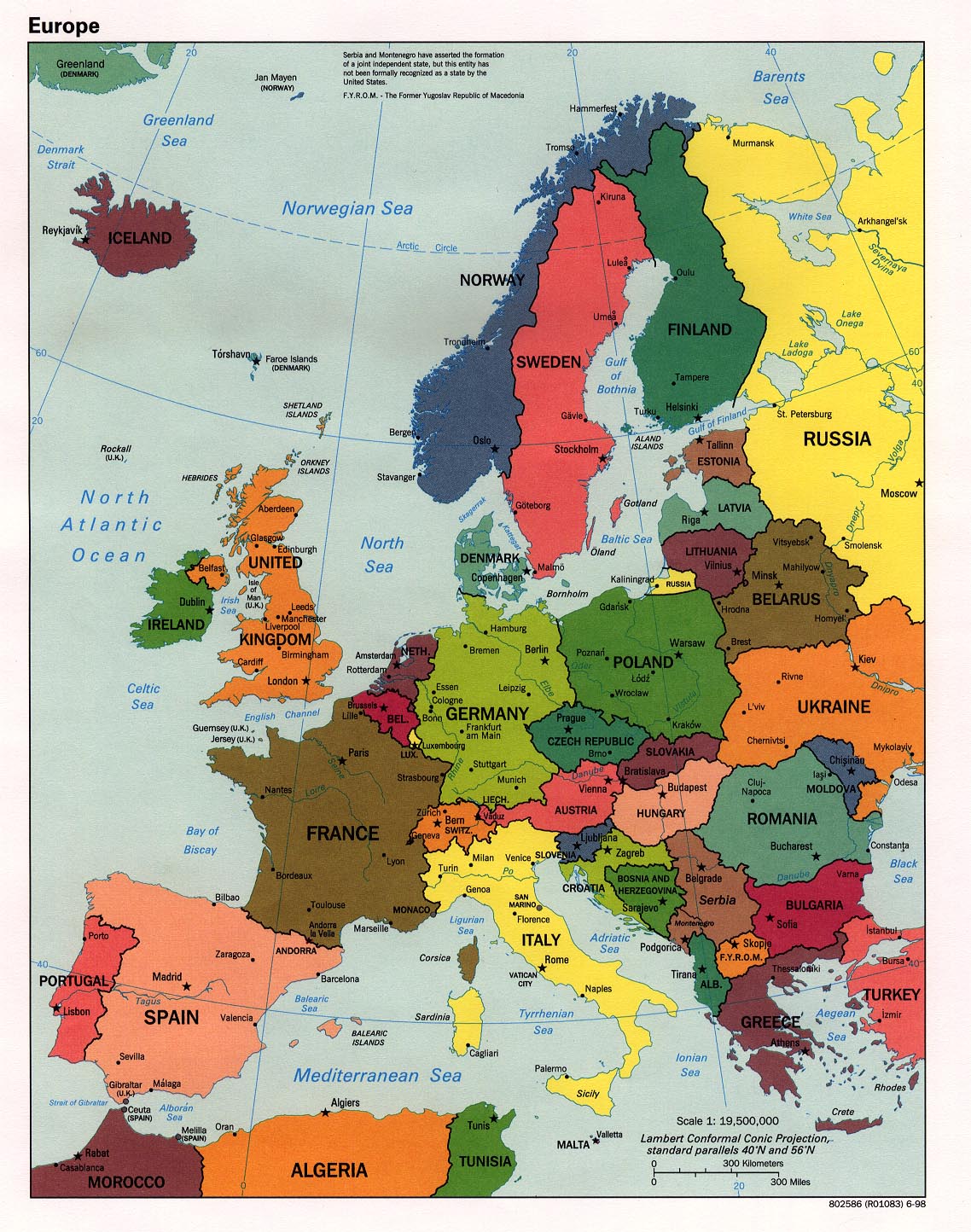
The political map of Europe presents a dynamic picture of the continent’s modern-day divisions, highlighting the intricate web of national borders, political systems, and alliances. This map provides a crucial framework for understanding the complexities of European politics and the evolving geopolitical landscape.
National Borders and States:
The political map delineates the boundaries of sovereign states, each with its unique history, culture, and political system. The map provides a visual representation of the diverse political landscape, reflecting the continent’s history of empires, revolutions, and nation-building.
Political Systems and Alliances:
The map showcases the diversity of political systems across Europe, from monarchies to republics, from parliamentary democracies to presidential systems. It also highlights major political alliances like the European Union, NATO, and the Council of Europe, demonstrating the interconnectedness of European nations.
The Importance of Maps in Understanding Europe:
Both physical and political maps are essential tools for understanding Europe’s complex and dynamic nature. They offer a visual framework for comprehending the continent’s diverse landscapes, its rich history, and the evolving political landscape.
Benefits of Studying Maps:
- Spatial Awareness: Maps foster spatial awareness, helping individuals understand the relative locations of countries, cities, and geographical features.
- Historical Context: Studying maps provides insights into historical events, migration patterns, and the evolution of political boundaries.
- Environmental Understanding: Physical maps highlight the continent’s diverse ecosystems, climate patterns, and resource distribution.
- Political Insights: Political maps offer a visual representation of the complex political landscape, facilitating understanding of international relations and regional dynamics.
- Educational Value: Maps are invaluable educational tools, promoting geographical literacy and fostering a deeper understanding of the world.
FAQs about Physical and Political Maps of Europe:
Q: What is the difference between a physical and a political map?
A: A physical map focuses on the natural features of a region, such as mountains, rivers, and coastlines. A political map, on the other hand, emphasizes human-made boundaries and political divisions, such as national borders, cities, and states.
Q: Why are maps important for understanding Europe?
A: Maps provide a visual representation of the continent’s diverse landscapes, its rich history, and its complex political landscape. They help us understand the relative locations of countries, cities, and geographical features, as well as the historical events that have shaped the continent.
Q: How can I use maps to learn more about Europe?
A: Explore interactive online maps, consult atlases, and visit museums and historical sites. Engage with educational resources, such as documentaries and articles, that utilize maps to explain historical events and geographical phenomena.
Tips for Using Physical and Political Maps of Europe:
- Focus on Key Features: Identify major geographical features, such as mountain ranges, rivers, and major cities.
- Compare and Contrast: Compare physical and political maps to understand how geographical features have influenced political boundaries and human settlements.
- Analyze Historical Events: Use maps to trace historical events, such as migrations, wars, and the rise and fall of empires.
- Explore Regional Differences: Pay attention to the unique characteristics of different regions, such as the Mediterranean, the Balkans, and Scandinavia.
- Engage in Active Learning: Use maps for research projects, presentations, and discussions.
Conclusion:
Physical and political maps of Europe are essential tools for understanding the continent’s intricate tapestry of landscapes, history, and politics. By studying these maps, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the diverse cultures, languages, and geographical features that make Europe a unique and fascinating region of the world. Whether exploring the continent’s majestic mountains or navigating its complex political landscape, maps provide a valuable framework for understanding the multifaceted nature of Europe.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Physical and Political Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!