Navigating the Vastness: Understanding Canada’s Geography through Latitude
Related Articles: Navigating the Vastness: Understanding Canada’s Geography through Latitude
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Vastness: Understanding Canada’s Geography through Latitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Vastness: Understanding Canada’s Geography through Latitude
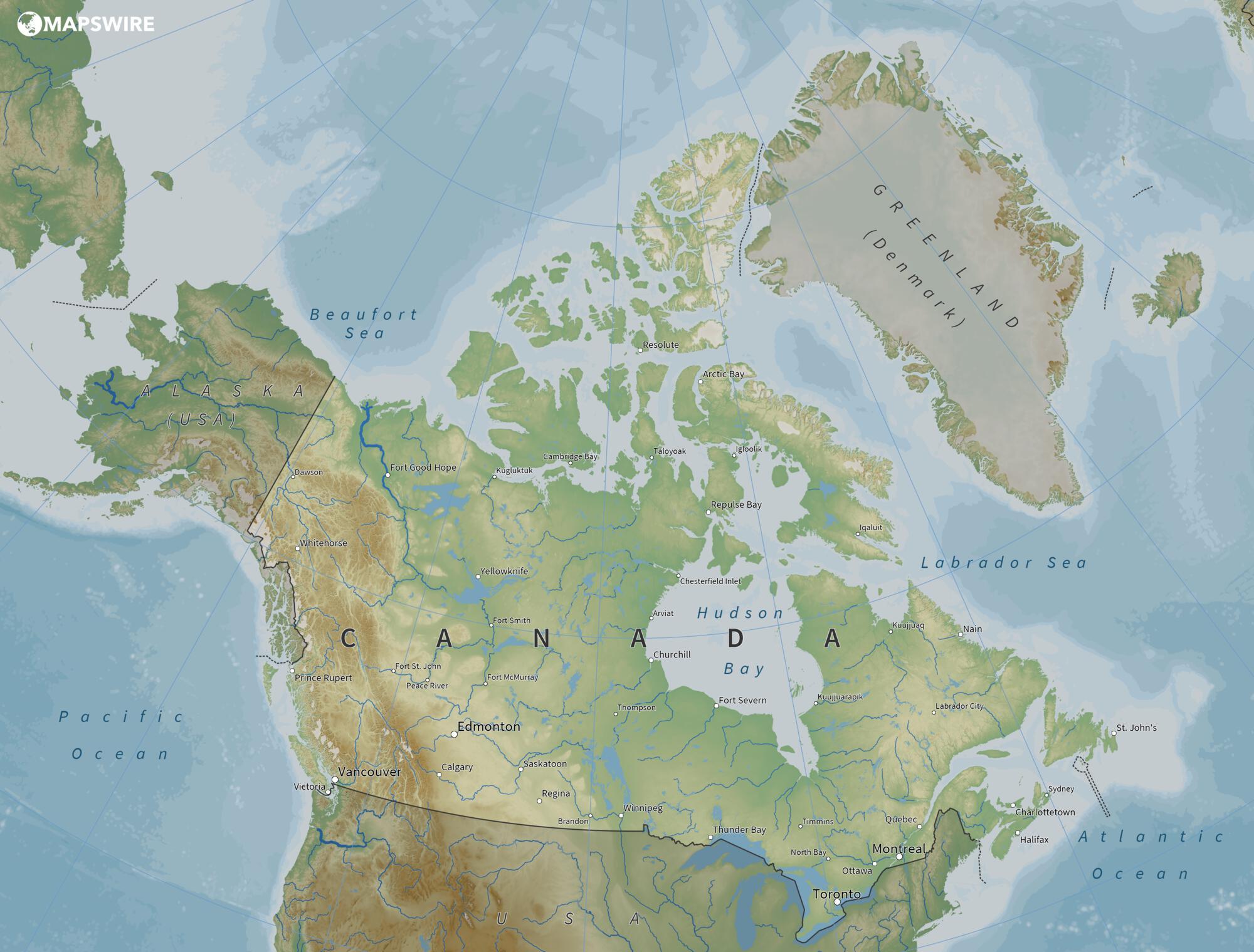
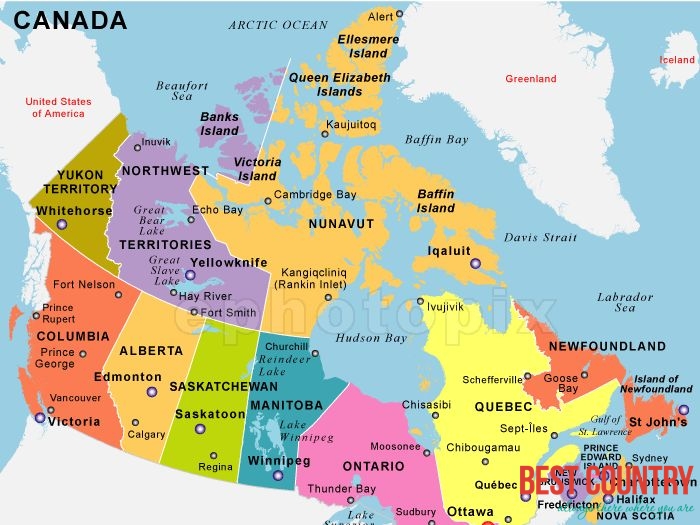
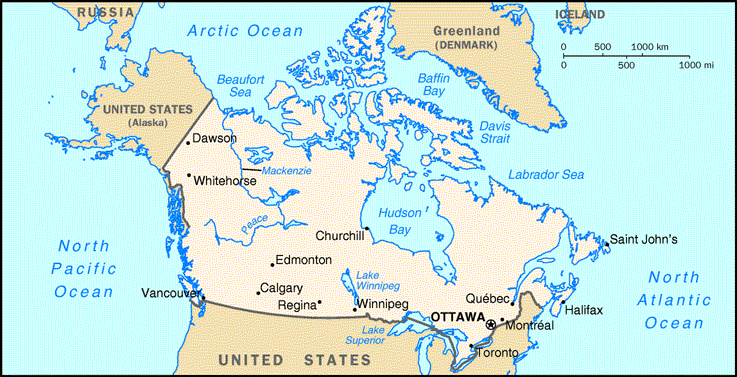
Canada, a nation of vast landscapes and diverse ecosystems, stretches across a significant portion of the North American continent. Its geographical expanse is best understood by examining its position on the globe, specifically its latitude. Latitude, measured in degrees north or south of the equator, plays a crucial role in shaping Canada’s climate, natural features, and human settlements.
The Latitude Spectrum: A Glimpse into Canada’s Diverse Landscape
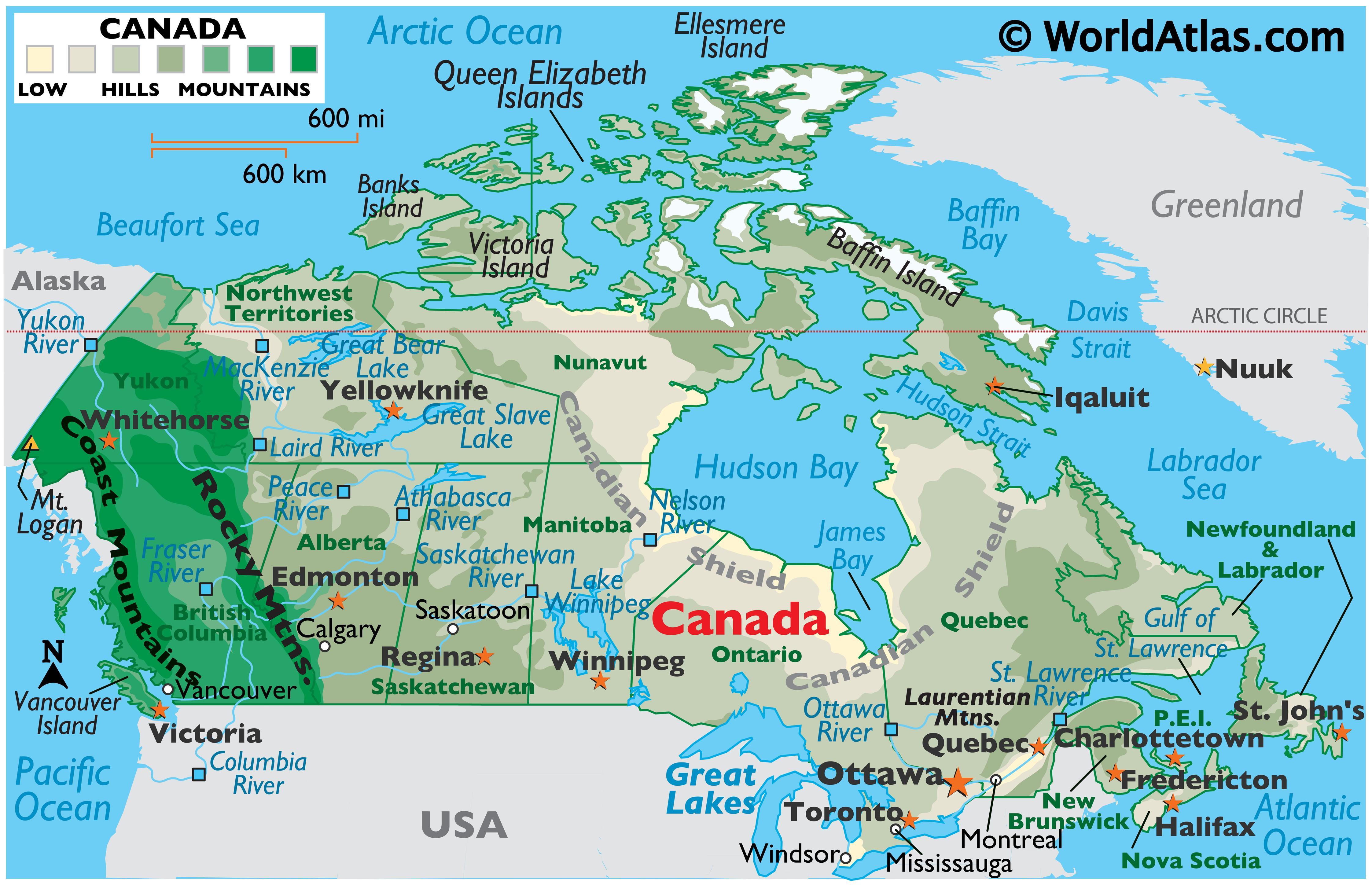
Canada’s latitude ranges from approximately 41° N to 83° N, placing it firmly within the northern hemisphere. This significant latitudinal spread directly influences the country’s climate and geography.
-
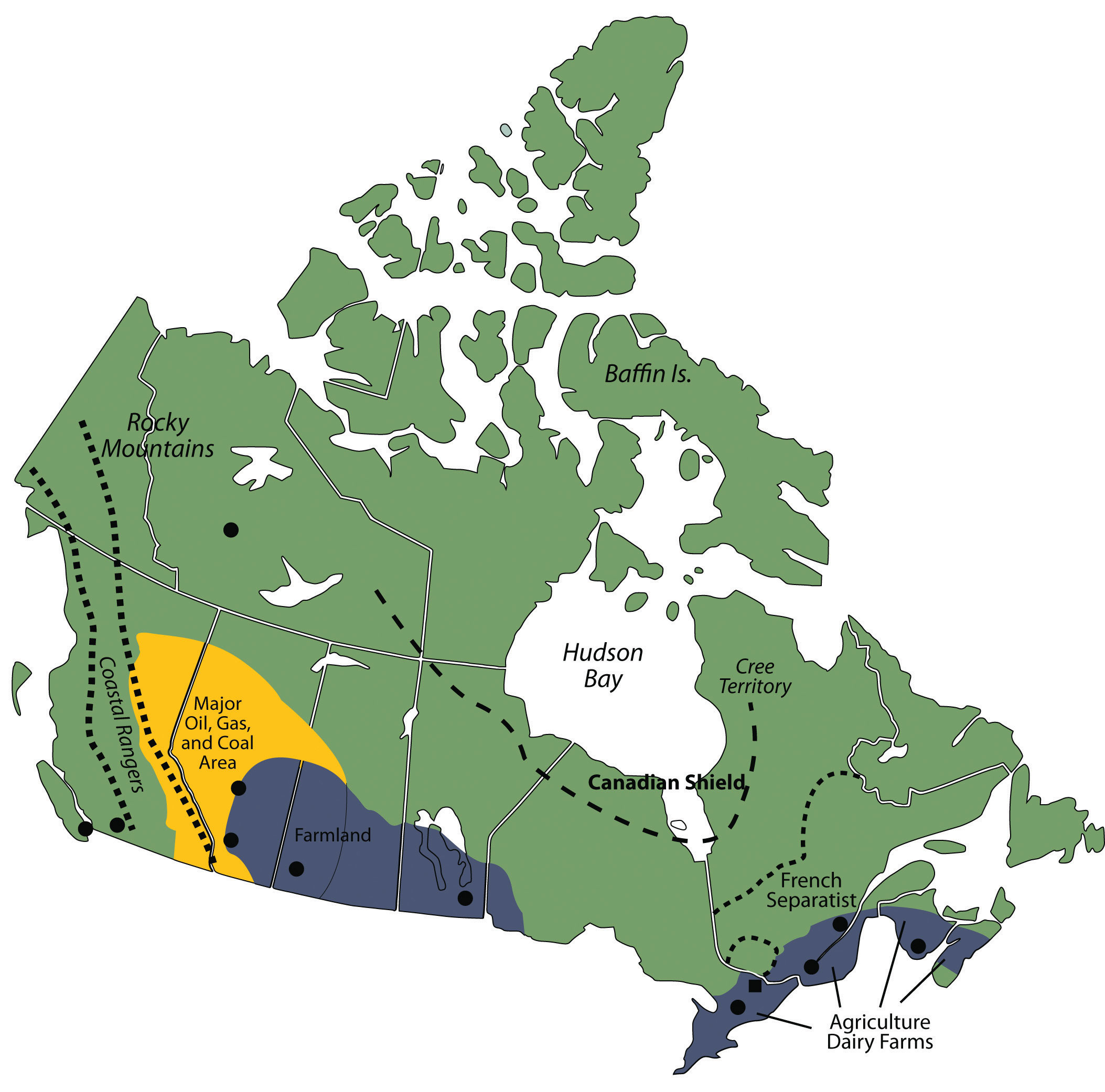
Southern Canada (41° N to 50° N): This region, encompassing provinces like Ontario and Quebec, experiences a humid continental climate with distinct seasons. The southernmost parts of this region are characterized by fertile agricultural land, while the northern regions transition into boreal forests.
-
Central Canada (50° N to 60° N): This region, including provinces like Manitoba and Saskatchewan, is characterized by a more extreme continental climate with cold winters and warm summers. The landscape is dominated by vast prairies, interspersed with forests and lakes.
-
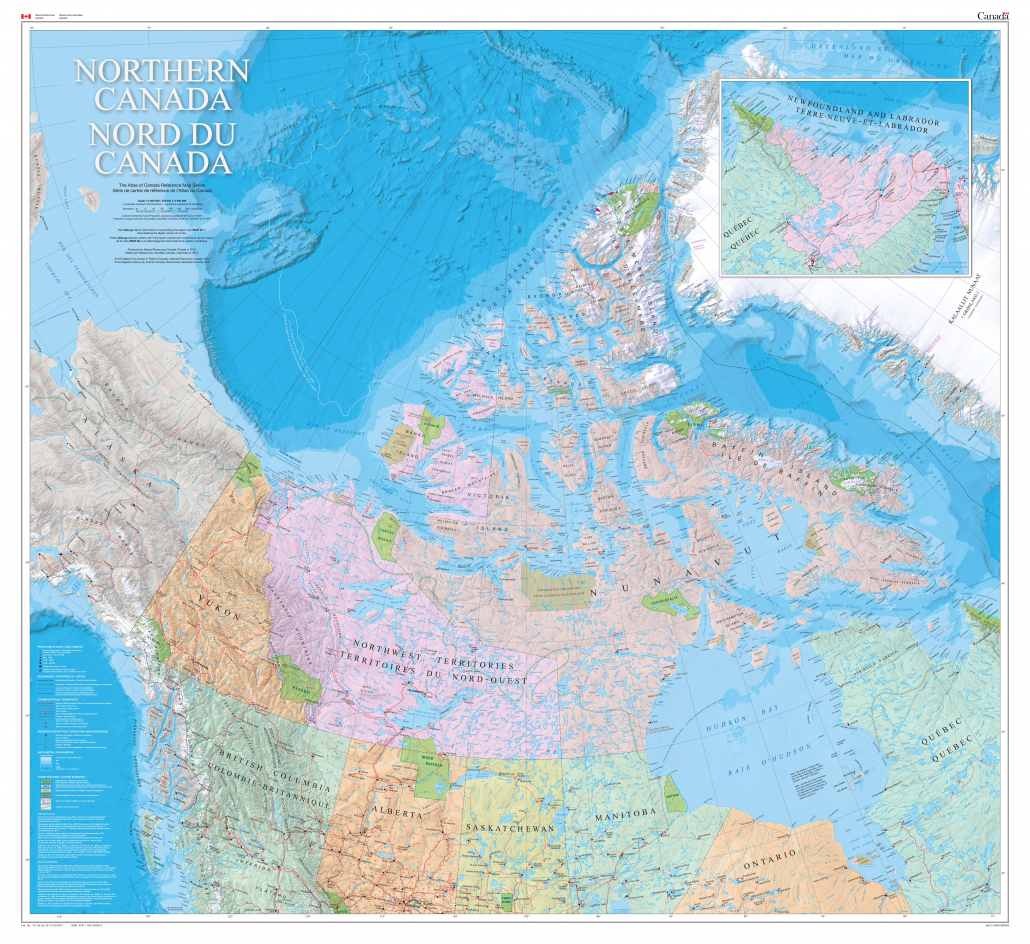
Northern Canada (60° N to 83° N): This region, encompassing the territories of Nunavut, Yukon, and Northwest Territories, is dominated by the Arctic tundra and subarctic regions. The climate is characterized by long, cold winters and short, cool summers. The landscape is dotted with permafrost, glaciers, and vast stretches of wilderness.
The Impact of Latitude on Canada’s Climate:
Latitude is a primary factor influencing Canada’s climate. The sun’s rays hit the earth at an angle that varies depending on latitude. Higher latitudes, like those found in northern Canada, receive less direct sunlight, resulting in colder temperatures. This phenomenon explains why northern Canada experiences long, frigid winters, while southern Canada enjoys milder winters.
Furthermore, the length of daylight hours also varies significantly with latitude. Northern Canada experiences long periods of daylight during the summer months, known as the "midnight sun," while winter days are short. This variation in daylight hours directly influences plant and animal life, creating distinct ecosystems across the country.
Latitude’s Influence on Canada’s Natural Features:
Latitude plays a significant role in shaping Canada’s natural features. The southern regions, with their warmer temperatures, are home to diverse ecosystems, including deciduous forests, prairies, and agricultural lands. As you move north, the climate becomes colder, and the landscape transitions into boreal forests, tundra, and vast stretches of permafrost.
The presence of mountains, rivers, and lakes further contributes to the diversity of Canada’s landscape. These features are influenced by geological processes, including plate tectonics and glacial activity, which are themselves impacted by latitude.
Latitude and Human Settlements:
Canada’s latitudinal spread has also shaped the distribution of human settlements. The southern regions, with their milder climates and fertile land, have historically been the most densely populated areas. The northern regions, with their harsher climates and challenging terrain, have seen more limited settlement.
However, Canada’s northern regions are experiencing a growing population, driven by resource extraction, tourism, and cultural preservation. This growth presents both opportunities and challenges, requiring careful consideration of environmental sustainability and cultural preservation.
Understanding Latitude: A Key to Unlocking Canada’s Potential
By understanding the influence of latitude on Canada’s geography, climate, and human settlements, we gain a deeper appreciation for the country’s unique character. This knowledge is crucial for informed decision-making in various sectors, including agriculture, resource management, transportation, and infrastructure development.
FAQs about Latitude in Canada:
Q: What is the highest latitude in Canada?
A: The highest latitude in Canada is approximately 83° N, located in the northernmost part of Ellesmere Island in Nunavut.
Q: How does latitude affect Canada’s biodiversity?
A: Latitude directly influences biodiversity in Canada by shaping the climate and creating distinct ecosystems. The southern regions, with their warmer temperatures, support a greater diversity of species, while the northern regions have a more limited range of flora and fauna.
Q: How does latitude impact transportation in Canada?
A: Latitude impacts transportation in Canada by influencing the availability and accessibility of different modes of transportation. The southern regions, with their denser population and developed infrastructure, have extensive road and rail networks. Northern Canada, with its remote and challenging terrain, relies heavily on air travel and water transportation.
Q: How does latitude affect agriculture in Canada?
A: Latitude plays a crucial role in Canadian agriculture by determining the length of the growing season and the types of crops that can be cultivated. The southern regions, with their longer growing seasons, are ideal for growing a wide variety of crops, while the northern regions are more suited for specialized crops like barley and oats.
Tips for Understanding Latitude in Canada:
-
Consult maps and atlases: Visualizing Canada’s latitude on a map provides a clear understanding of its geographical extent.
-
Explore online resources: Websites and educational platforms offer comprehensive information on Canada’s geography, climate, and ecosystems.
-
Engage in hands-on learning: Visit museums, science centers, and outdoor educational facilities to learn about Canada’s natural history and the influence of latitude.
Conclusion:
Latitude is a fundamental aspect of understanding Canada’s diverse geography, climate, and human settlements. By appreciating the impact of latitude on the country’s natural features, ecosystems, and human development, we gain a deeper understanding of Canada’s unique character and the challenges and opportunities it faces. This knowledge is essential for informed decision-making and sustainable development across all sectors of Canadian society.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Vastness: Understanding Canada’s Geography through Latitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!