Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Essentials
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Essentials
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Essentials. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Essentials

Maps, those ubiquitous representations of our physical world, are more than just colorful illustrations. They are indispensable tools for understanding, exploring, and navigating our surroundings. From the intricate details of city streets to the vast expanse of global oceans, maps provide a visual language that allows us to comprehend spatial relationships, plan journeys, and make informed decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential components of maps, revealing their significance and the critical role they play in our lives.
Understanding the Basics: The Foundation of Map Comprehension
Before embarking on a detailed exploration, it’s crucial to understand the fundamental elements that constitute a map.
-
Scale: A map’s scale defines the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This crucial element determines the level of detail a map can portray. Large-scale maps, with a smaller ratio, represent smaller areas in greater detail, ideal for urban planning or hiking trails. Conversely, small-scale maps, with a larger ratio, depict vast regions with less detail, suitable for global navigation or geological studies.
-
Projection: The Earth, being a sphere, cannot be accurately represented on a flat surface without some distortion. Projections are mathematical methods used to transform the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane. Different projections emphasize specific aspects, such as preserving area, shape, or distance. Common projections include Mercator, Lambert Conformal Conic, and Robinson, each with its strengths and limitations.
-
Legend: The legend, or key, acts as a glossary for map symbols and colors. It clarifies the meaning of different features, from roads and rivers to buildings and parks. A well-designed legend ensures clarity and facilitates map interpretation.
-
Compass Rose: A compass rose, often found on maps, indicates cardinal directions (north, south, east, west) and their intermediate points. It serves as a visual reference for orientation and understanding the direction of travel.
-
Grid System: Many maps utilize a grid system, typically composed of latitude and longitude lines. These lines form a network that facilitates precise location identification and helps users pinpoint specific points on the map.
Beyond the Basics: Unveiling the Layers of Information
While the fundamental elements provide a framework for map understanding, additional features enrich the information conveyed.
-
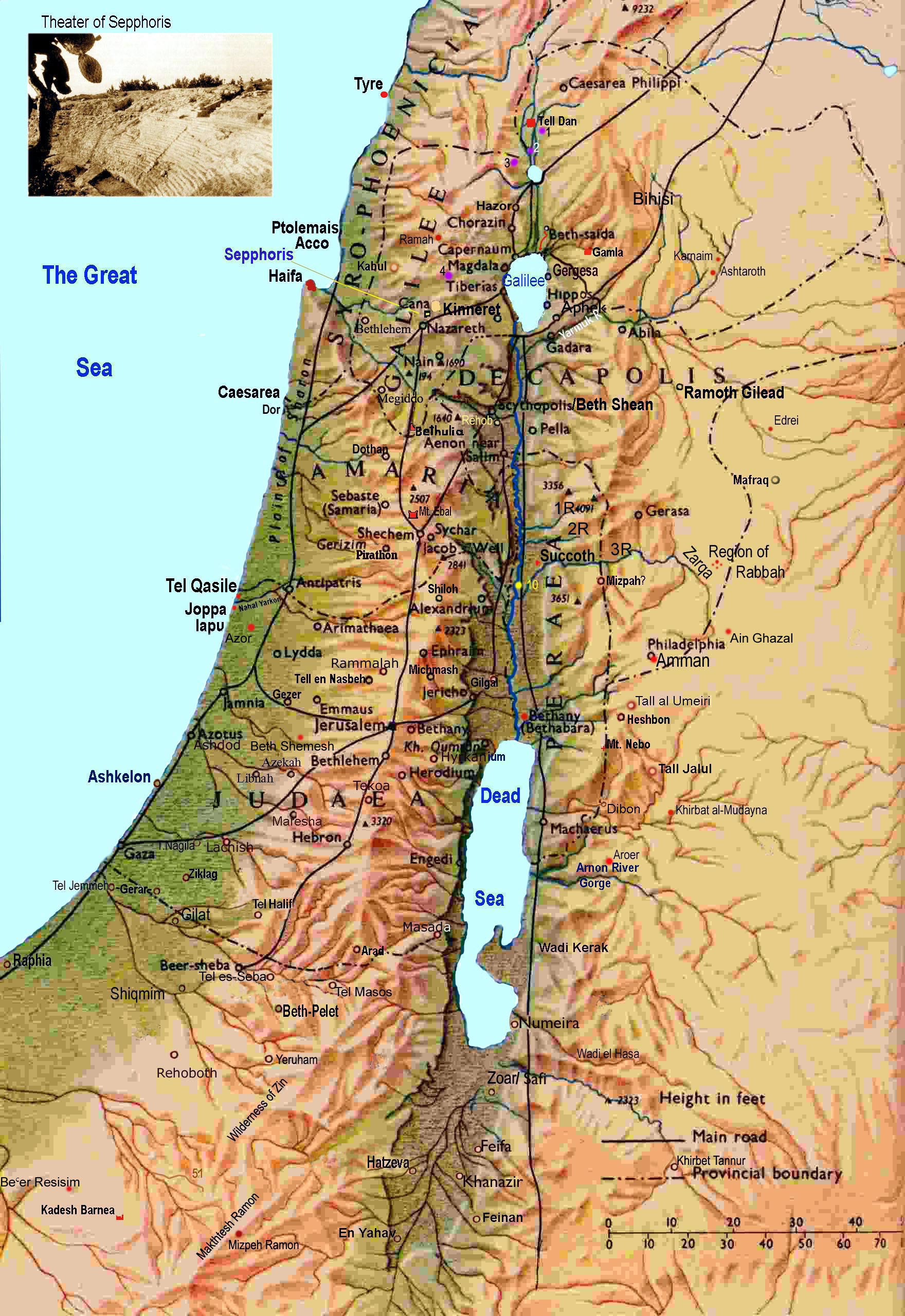
Topographic Maps: These maps depict the Earth’s surface relief, showcasing elevation changes through contour lines. Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of hills, valleys, and other landforms. Topographic maps are indispensable for hiking, mountaineering, and understanding the terrain.
-
Thematic Maps: Thematic maps focus on specific themes, highlighting data related to population density, climate, economic activity, or other relevant topics. By using colors, symbols, or patterns, these maps effectively communicate spatial patterns and trends.
-
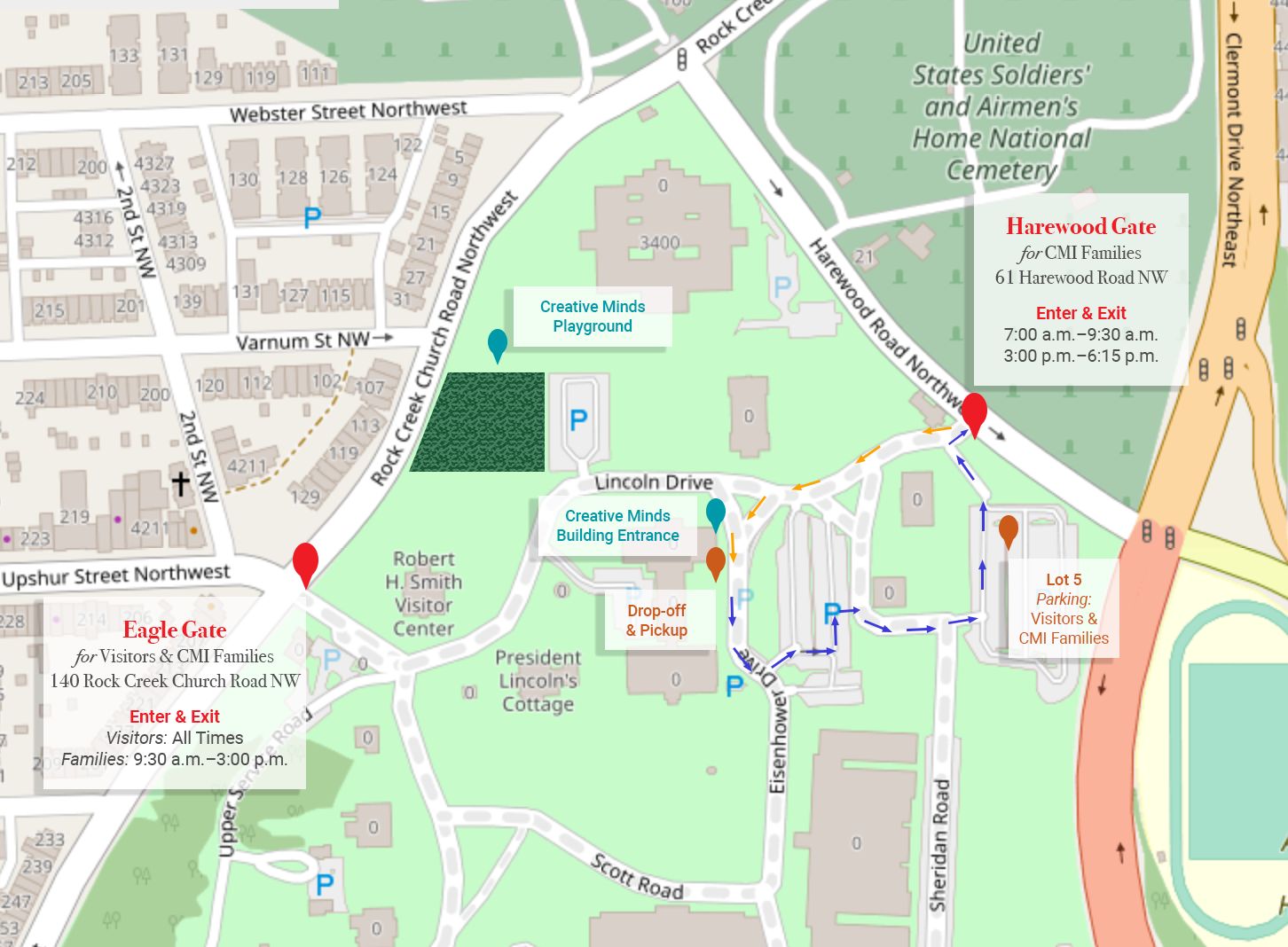
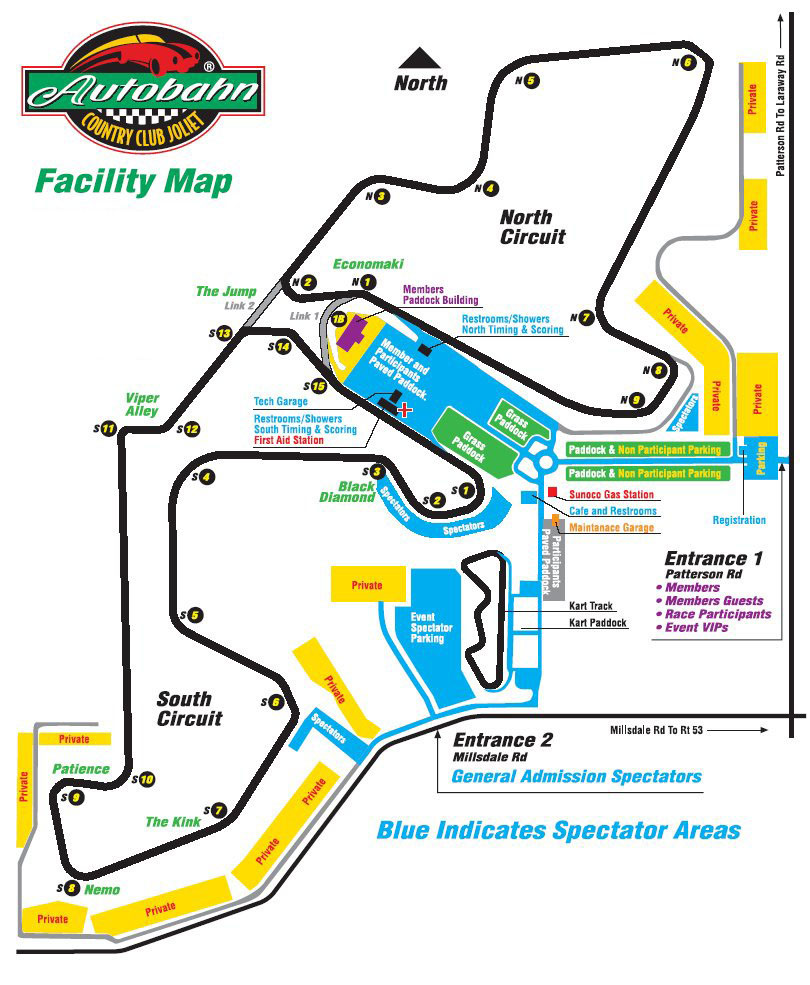
Navigation Maps: Navigation maps, often used for road travel or marine navigation, emphasize routes and pathways. They typically include road networks, landmarks, and points of interest, facilitating safe and efficient travel.
-
Satellite Imagery: Satellite imagery, captured from space, provides a bird’s-eye view of the Earth’s surface. This imagery offers high-resolution detail, revealing land cover, urban sprawl, and natural features.
The Power of Technology: Embracing Digital Mapping
The advent of digital technology has revolutionized mapmaking and usage. Digital maps offer several advantages over traditional paper maps:
-
Interactivity: Digital maps allow users to zoom, pan, and rotate, exploring different perspectives and levels of detail.
-
Real-Time Updates: Digital maps can be updated in real time, incorporating live traffic conditions, weather information, and other dynamic data.
-
Integration with Other Services: Digital maps seamlessly integrate with GPS navigation, location-based services, and other applications, enhancing user experience and providing comprehensive information.
-
Accessibility: Digital maps are readily accessible through smartphones, tablets, and computers, allowing users to navigate from anywhere with an internet connection.
Map Essentials: A Practical Guide to Effective Navigation
Understanding map essentials is not merely an academic pursuit; it’s a practical skill with real-world implications. Whether navigating unfamiliar cities, planning hiking expeditions, or simply understanding the world around us, maps empower us to make informed decisions and navigate our surroundings with confidence.
Tips for Effective Map Usage:
-
Identify Your Objective: Before using a map, clearly define your purpose. Are you looking for a specific location, planning a route, or understanding a particular feature? This clarity will guide your map selection and interpretation.
-
Choose the Right Map: Select a map with the appropriate scale and projection for your needs. A large-scale map is ideal for local navigation, while a small-scale map is suitable for regional or global exploration.
-
Familiarize Yourself with the Legend: Take time to understand the symbols and colors used on the map. This will ensure you can accurately interpret the information presented.
-
Orient Yourself: Use the compass rose or other directional indicators to determine your position and the direction of travel.
-
Use Landmarks: Identify prominent landmarks on the map and correlate them with your surroundings. This will help you maintain orientation and navigate effectively.
-
Practice Map Reading: Regularly engage with maps, even for familiar areas. This will sharpen your map reading skills and enhance your spatial awareness.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
-
What are the different types of maps? Maps come in various forms, including topographic maps, thematic maps, navigation maps, and digital maps. Each type serves a specific purpose and caters to different information needs.
-
How do I choose the right map for my needs? Consider the scale, projection, and thematic focus of the map. Choose a map that provides the level of detail and information relevant to your objective.
-
What are some common map symbols? Map symbols vary depending on the type of map, but common symbols include roads, rivers, buildings, parks, and points of interest.
-
How do I read a topographic map? Contour lines on topographic maps indicate elevation changes. The closer the lines, the steeper the terrain.
-
How do I use a compass with a map? Align the compass needle with the north arrow on the map. Then, rotate the map until the compass needle points to magnetic north. This will ensure your map is properly oriented.
Conclusion: Navigating the World with Confidence
Maps, in their various forms, provide a powerful tool for understanding, exploring, and navigating our world. From the fundamental elements of scale, projection, and legend to the advanced features of topographic maps and digital mapping, maps empower us with knowledge, clarity, and confidence. By understanding the essential components and utilizing them effectively, we can navigate our surroundings with precision and ease.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Essentials. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!