Navigating the World of Alerts: A Comprehensive Guide to Alert Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World of Alerts: A Comprehensive Guide to Alert Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World of Alerts: A Comprehensive Guide to Alert Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World of Alerts: A Comprehensive Guide to Alert Maps

In a world saturated with information, staying informed and proactive is crucial. Whether it’s keeping track of breaking news, monitoring financial markets, or managing a complex IT infrastructure, the ability to quickly identify and respond to critical events is paramount. This is where alert maps come into play, serving as powerful tools for visualizing and understanding real-time data streams.
Understanding the Concept of Alert Maps
At its core, an alert map is a visual representation of data points that trigger specific alerts. These maps leverage the power of geographic information systems (GIS) to overlay data onto a map, providing a clear and intuitive spatial understanding of the events being monitored.
Key Components of an Alert Map:
- Base Map: This forms the foundation of the alert map, providing a geographical context for the data being displayed. It can range from a global view to a localized area, depending on the specific needs.
- Data Points: These represent the individual events or occurrences that trigger alerts. They can be anything from natural disasters like earthquakes and floods to system failures in a network infrastructure or price fluctuations in financial markets.
- Markers: These are visual symbols used to represent data points on the map. They can be customized with different colors, sizes, and shapes to convey specific information about the nature of the alert.
- Pop-up Information: When a marker is clicked, detailed information about the corresponding data point is displayed, providing context and additional insights. This information might include the date and time of the event, severity level, and relevant links to further resources.
- Filters and Layers: Alert maps often allow users to filter data by different criteria, such as time period, event type, or severity level. This helps to focus on specific areas of interest and manage the volume of information displayed.
- Real-time Updates: A key feature of alert maps is their ability to display real-time data, ensuring users are always working with the most up-to-date information. This is particularly important for critical situations where timely responses are essential.
Benefits of Using Alert Maps:
- Improved Situational Awareness: By providing a visual representation of data, alert maps enhance situational awareness, enabling users to quickly grasp the overall context of a situation and make informed decisions.
- Faster Response Times: The ability to identify critical events quickly and efficiently leads to faster response times, minimizing potential damage and maximizing effectiveness.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Alert maps can be shared with multiple stakeholders, facilitating collaboration and ensuring everyone is working with the same information.
- Data-driven Decision Making: The visual nature of alert maps makes it easier to identify trends and patterns in data, enabling data-driven decision making and proactive problem solving.
- Increased Efficiency: By automating the process of monitoring and alerting, alert maps free up valuable time and resources, allowing teams to focus on more strategic tasks.
Applications of Alert Maps Across Industries:
The versatility of alert maps makes them applicable across a wide range of industries and use cases. Some notable examples include:
- Emergency Management: Alert maps are essential for emergency responders, enabling them to track the spread of wildfires, monitor the impact of natural disasters, and coordinate rescue efforts.
- Public Health: Health authorities use alert maps to track the spread of diseases, identify outbreaks, and implement targeted interventions.
- Law Enforcement: Police departments utilize alert maps to monitor crime patterns, identify high-risk areas, and allocate resources efficiently.
- Finance: Financial institutions rely on alert maps to track market trends, identify potential risks, and manage investment portfolios.
- IT Infrastructure Management: Network administrators use alert maps to monitor system performance, identify network outages, and troubleshoot technical issues.
- Environmental Monitoring: Environmental agencies use alert maps to track air quality, monitor pollution levels, and assess the impact of climate change.
FAQs about Alert Maps:
Q: What are some popular tools for creating alert maps?
A: There are numerous software platforms available for creating alert maps, each offering different features and functionalities. Some popular options include:
- ArcGIS: A comprehensive GIS platform offering advanced mapping and analysis capabilities.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software, suitable for both personal and professional use.
- Google Maps Platform: Provides tools for creating custom maps and integrating them with other applications.
- Mapbox: A cloud-based platform for building interactive maps and location-based applications.
- Tableau: A data visualization tool that can be used to create interactive maps and dashboards.
Q: What are some key considerations when designing an alert map?
A: The design of an alert map should be tailored to the specific needs of the user and the data being displayed. Some key considerations include:
- Target Audience: Who will be using the map? Consider their technical skills and information needs.
- Data Sources: What data will be displayed on the map? Ensure the data is accurate, reliable, and relevant.
- Visualization Techniques: Choose appropriate markers, colors, and symbols to effectively convey the information.
- User Interface: Design a user-friendly interface that allows users to easily navigate, filter, and interact with the map.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy and reliability of data displayed on an alert map?
A: The accuracy and reliability of data are crucial for making informed decisions. Here are some tips to ensure data integrity:
- Validate Data Sources: Verify the credibility and accuracy of the data sources used.
- Implement Data Quality Controls: Establish mechanisms to monitor data quality and identify potential errors.
- Regularly Update Data: Ensure the map displays the most up-to-date information by implementing regular data updates.
- Use Multiple Data Sources: Cross-reference data from different sources to minimize the risk of errors.
Tips for Effective Use of Alert Maps:
- Define Clear Objectives: Before creating an alert map, clearly define the goals and objectives you want to achieve.
- Identify Relevant Data: Focus on collecting and displaying data that is relevant to your objectives.
- Use Visualizations Effectively: Choose appropriate markers, colors, and symbols to clearly and effectively convey the information.
- Regularly Review and Update: Continuously review and update the map to ensure it remains relevant and accurate.
- Promote Collaboration: Share the map with relevant stakeholders to facilitate collaboration and information sharing.
Conclusion:
Alert maps have become indispensable tools for navigating the complexities of the modern world, providing a clear and intuitive way to visualize and understand real-time data streams. By leveraging the power of GIS and data visualization, alert maps enhance situational awareness, improve response times, and facilitate data-driven decision making. Whether used for emergency management, public health, finance, or IT infrastructure management, alert maps play a vital role in enabling individuals and organizations to stay informed, proactive, and resilient in a rapidly changing world.
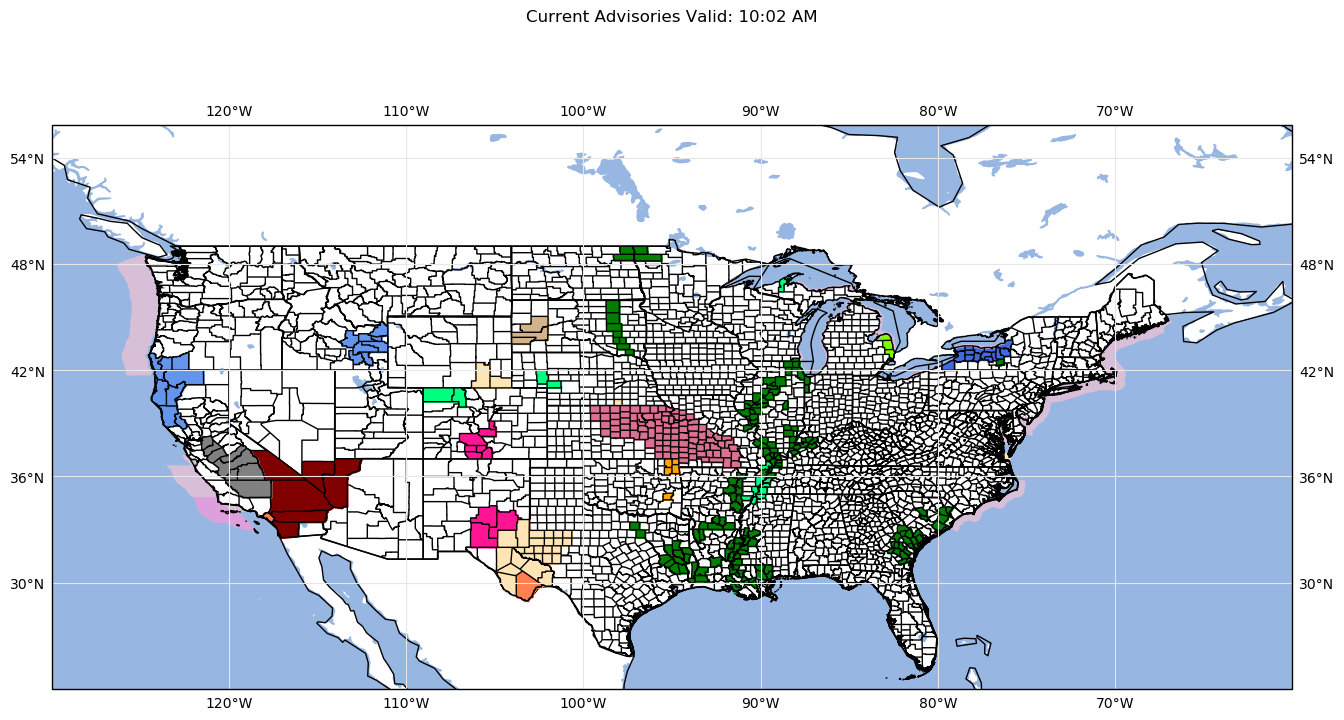


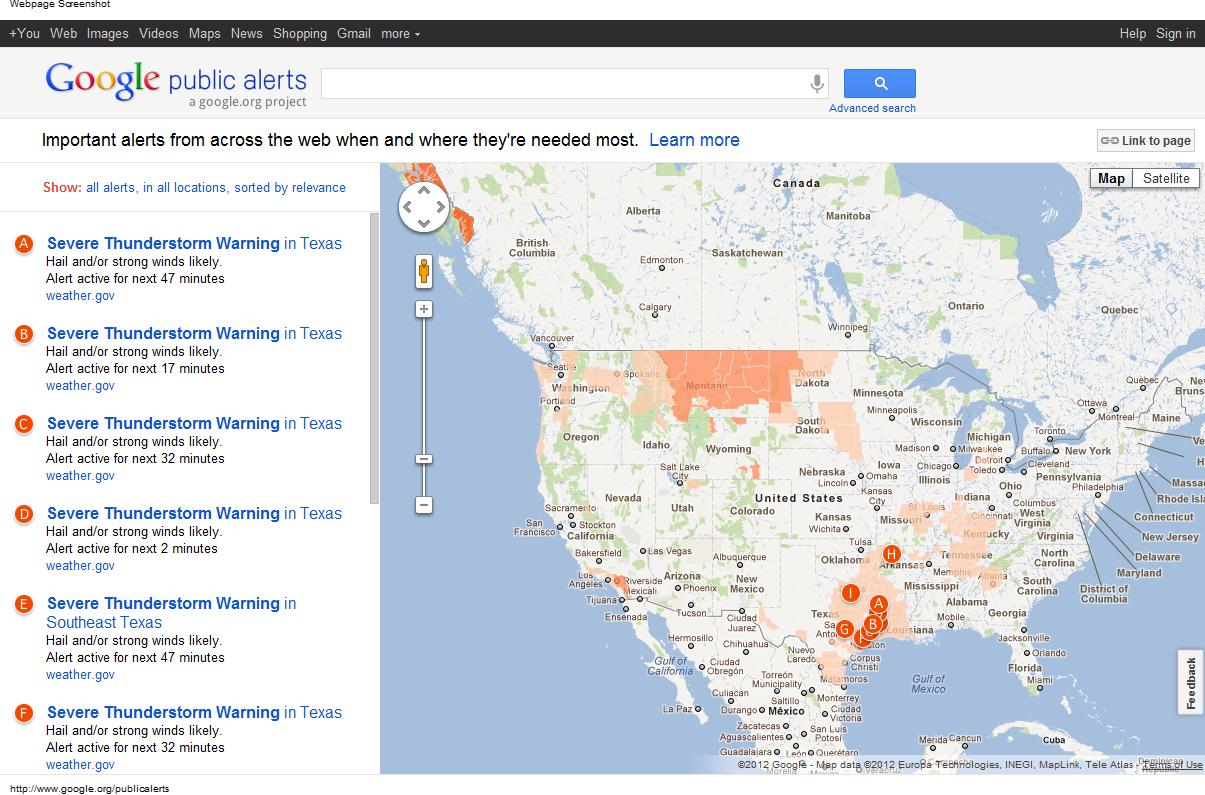
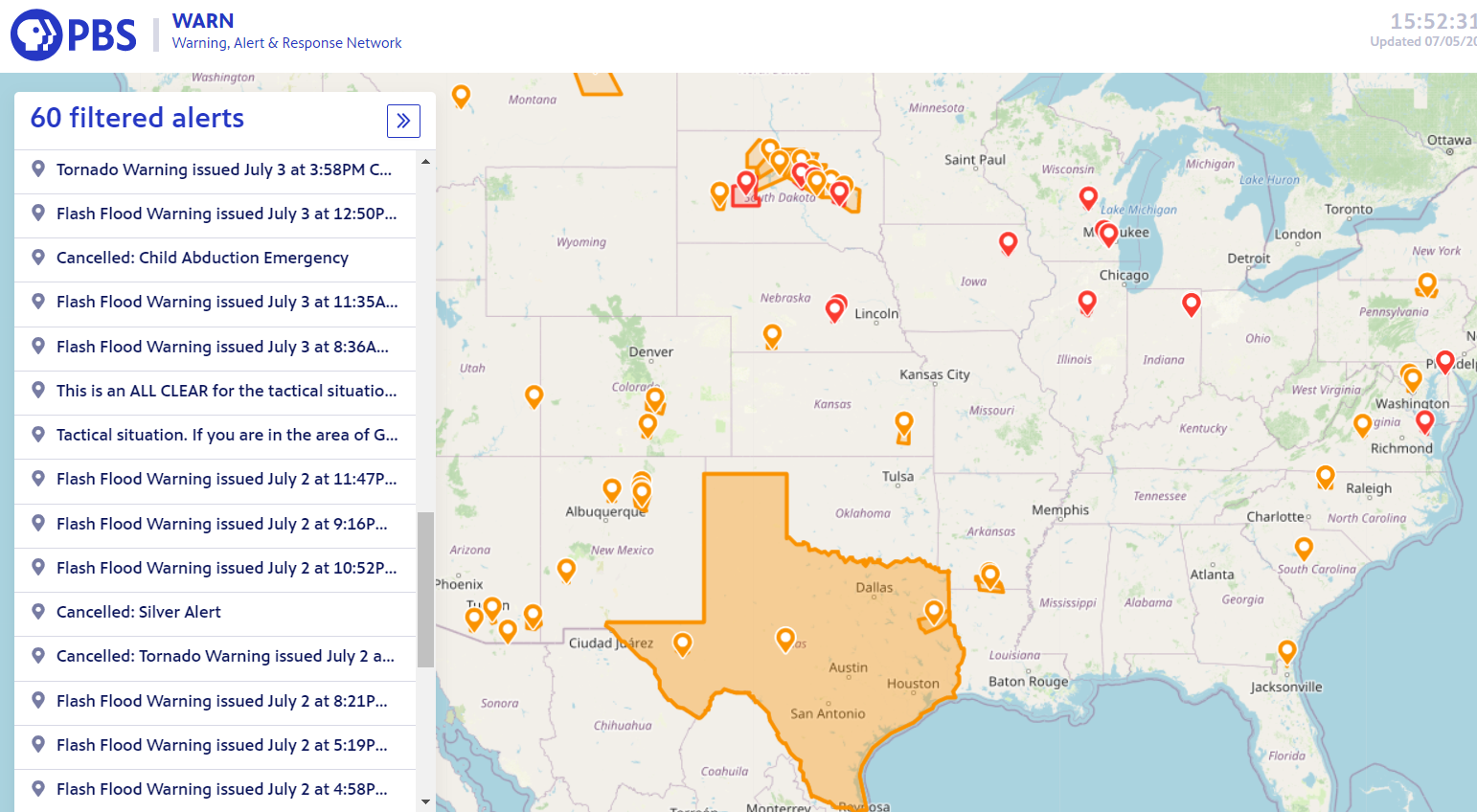

![Piwik Pro Alerts Comprehensive Guide [Setup, Strategy & More]](https://dumbdata.co/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/DD-Piwik-Pro-Alert-navigate-to-the-alerts-in-Piwik-Pro-Analytics.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World of Alerts: A Comprehensive Guide to Alert Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!