Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
- 3.1 Latitude: Measuring North and South
- 3.2 Longitude: Measuring East and West
- 3.3 The Power of Latitude and Longitude
- 3.4 Understanding the Grid: Latitude and Longitude in Action
- 3.5 Benefits of Latitude and Longitude
- 3.6 Latitude and Longitude in the Digital Age
- 3.7 FAQs about Latitude and Longitude
- 3.8 Tips for Using Latitude and Longitude
- 3.9 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude

The Earth, a vast and complex sphere, presents a challenge when it comes to pinpointing specific locations. To address this, a system of coordinates known as latitude and longitude was developed, providing a universal language for describing any point on our planet. This system, akin to a grid overlaid on the Earth’s surface, allows for precise identification and communication of locations, enabling navigation, mapping, and countless other applications.
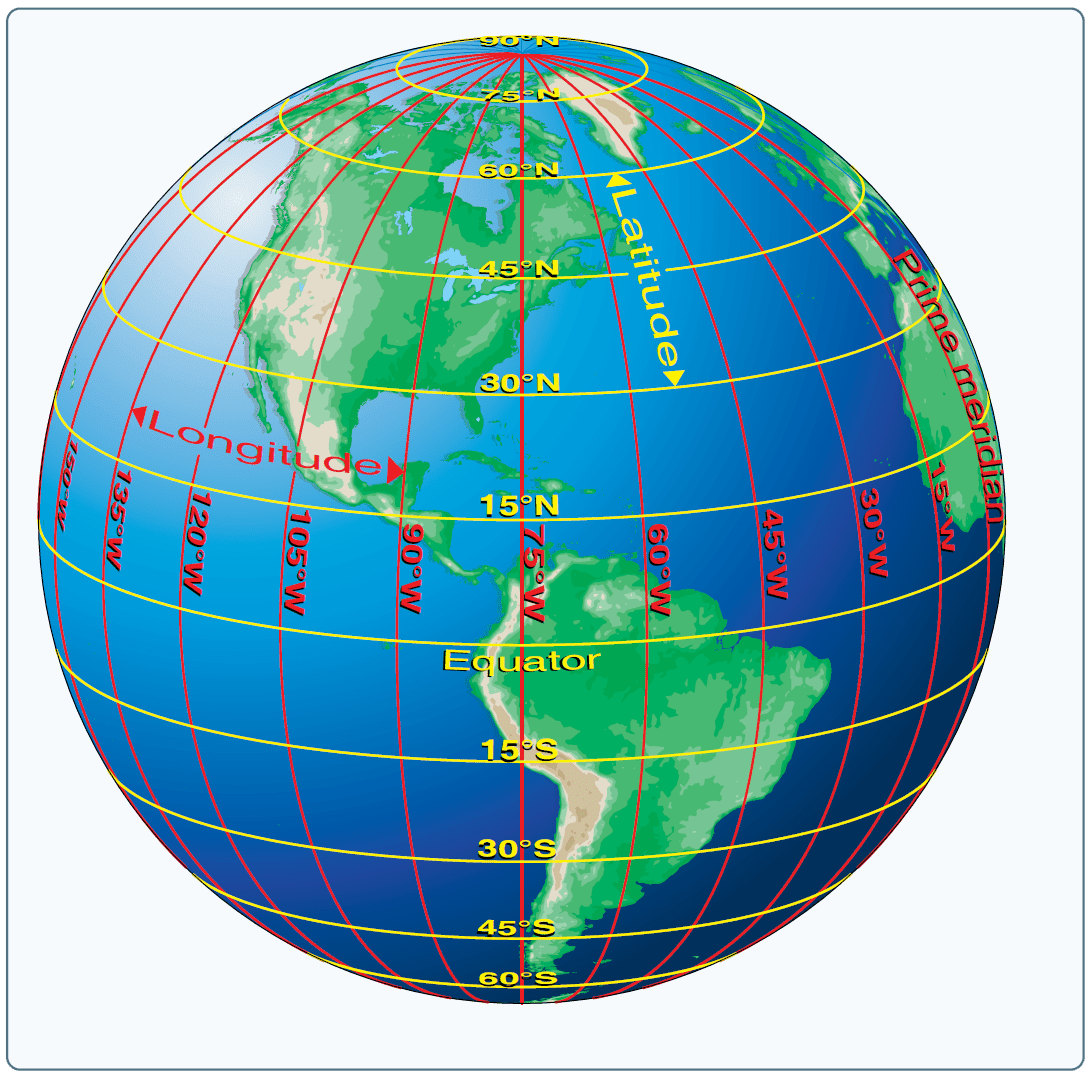
Latitude: Measuring North and South
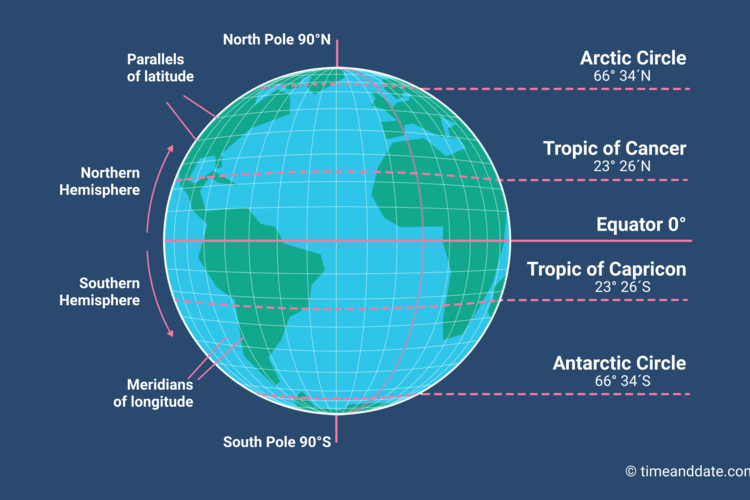
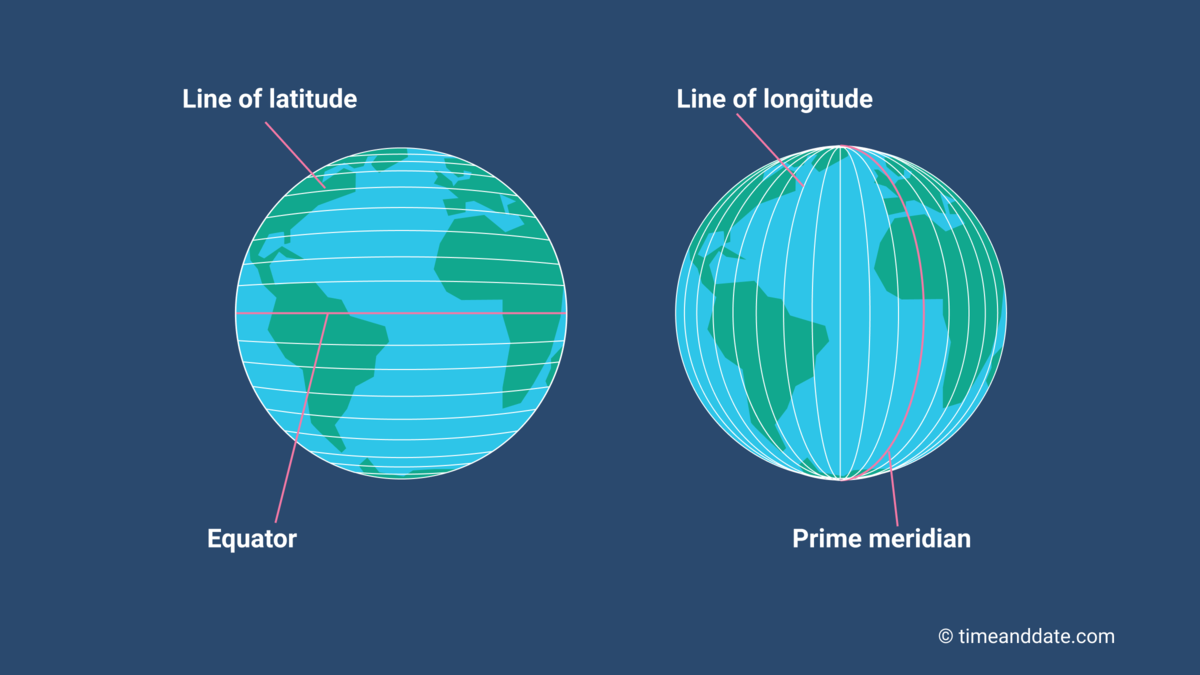
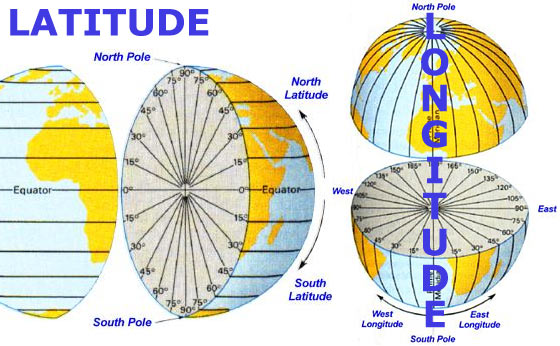
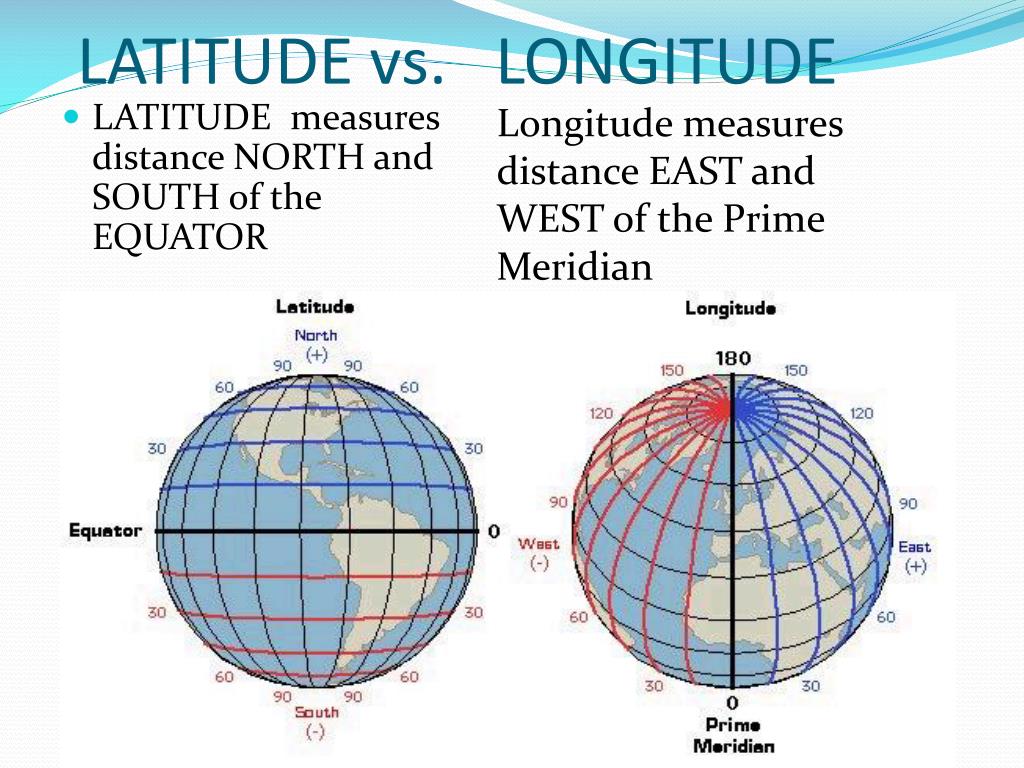
Latitude, represented by horizontal lines on a map, measures a location’s position north or south of the equator, an imaginary circle that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The equator serves as the zero-degree line, with latitude increasing towards the poles.
- Degrees: Latitude is measured in degrees, ranging from 0° at the equator to 90° at the North and South Poles. Each degree is further divided into 60 minutes (‘), and each minute into 60 seconds (").
- Hemispheres: Locations north of the equator are designated as North Latitude (N), while those south of the equator are designated as South Latitude (S).
For instance, a location with a latitude of 40°N is 40 degrees north of the equator, while a location with a latitude of 20°S is 20 degrees south of the equator.
Longitude: Measuring East and West
Longitude, represented by vertical lines on a map, measures a location’s position east or west of the prime meridian, another imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole through Greenwich, England.
- Degrees: Longitude is also measured in degrees, ranging from 0° at the prime meridian to 180° east or west.
- Hemispheres: Locations east of the prime meridian are designated as East Longitude (E), while those west of the prime meridian are designated as West Longitude (W).
For instance, a location with a longitude of 75°E is 75 degrees east of the prime meridian, while a location with a longitude of 120°W is 120 degrees west of the prime meridian.
The Power of Latitude and Longitude
The combination of latitude and longitude provides a unique and precise identifier for any point on Earth. This system forms the foundation for numerous applications, including:
- Navigation: Latitude and longitude are crucial for navigation systems like GPS (Global Positioning System), allowing users to pinpoint their location and find their way.
- Mapping: Maps rely on latitude and longitude to represent locations accurately. This system enables the creation of detailed maps, both physical and digital, used for various purposes, including urban planning, disaster response, and environmental monitoring.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS uses latitude and longitude as the basis for storing, analyzing, and visualizing geographic data. This powerful tool is employed in fields like agriculture, urban planning, and environmental management.
- Weather Forecasting: Weather stations around the world report their location using latitude and longitude, enabling meteorologists to track weather patterns and create accurate forecasts.
- Astronomy: Latitude and longitude are essential for astronomers to pinpoint the location of celestial objects in the sky.
- Time Zones: Longitude plays a key role in determining time zones, as the Earth rotates on its axis, with locations at different longitudes experiencing sunrise and sunset at different times.
Understanding the Grid: Latitude and Longitude in Action
Imagine the Earth as a giant orange, with the equator as its center. Each slice of the orange represents a line of longitude, and each horizontal circle running around the orange represents a line of latitude. The intersection of these lines, like the meeting point of a slice and a circle, defines a specific location on the orange’s surface, just like a specific point on Earth.
Benefits of Latitude and Longitude
The use of latitude and longitude offers numerous benefits:
- Universality: The system is universally recognized, providing a standardized language for describing locations regardless of language or cultural differences.
- Precision: Latitude and longitude allow for precise location identification, enabling accurate navigation, mapping, and data analysis.
- Scalability: The system works effectively at all scales, from pinpointing a specific address to mapping entire continents.
- Integration: Latitude and longitude are readily integrated with various technologies, including GPS, mapping software, and GIS systems, enhancing their usability.
Latitude and Longitude in the Digital Age
With the advent of GPS and other location-based technologies, latitude and longitude have become even more integral to our daily lives. These coordinates are used in:
- Smartphone navigation apps: Apps like Google Maps and Waze rely on latitude and longitude to provide real-time directions and traffic updates.
- Social media platforms: Many social media platforms use latitude and longitude to enable location tagging, allowing users to share their location with others.
- E-commerce platforms: Online retailers use latitude and longitude to facilitate delivery services and optimize logistics.
- Ride-sharing services: Ride-sharing apps like Uber and Lyft rely on latitude and longitude to connect passengers with drivers.
FAQs about Latitude and Longitude
1. How do I find the latitude and longitude of a specific location?
You can find the latitude and longitude of a location using various methods:
- Online mapping services: Websites like Google Maps, Bing Maps, and OpenStreetMap allow you to search for a location and view its coordinates.
- GPS devices: GPS receivers, such as smartphones and dedicated navigation devices, provide your current latitude and longitude.
- Geographic data sources: Datasets containing geographic information, such as the Global Positioning System (GPS) data, provide latitude and longitude for various locations.
2. Can latitude and longitude be used to determine the distance between two points?
Yes, the distance between two points can be calculated using their latitude and longitude coordinates. This calculation involves applying specific formulas and considering the curvature of the Earth.
3. How accurate are latitude and longitude measurements?
The accuracy of latitude and longitude measurements depends on the technology used.
- GPS: Modern GPS devices can achieve accuracies within a few meters.
- Mapping services: Online mapping services typically provide coordinates with accuracies ranging from a few meters to several hundred meters, depending on the location and data source.
4. How do latitude and longitude relate to time zones?
Longitude plays a crucial role in determining time zones. As the Earth rotates on its axis, locations at different longitudes experience sunrise and sunset at different times. Each time zone encompasses a specific range of longitudes, with the standard time for that zone based on the time at the central meridian within that range.
5. Are latitude and longitude always constant?
While latitude and longitude are generally considered fixed for a particular location, they can change slightly over time due to tectonic plate movements and other geological processes. However, these changes are typically very small and are not significant for most practical applications.
Tips for Using Latitude and Longitude
- Understand the units: Always remember that latitude and longitude are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
- Use the correct notation: When writing latitude and longitude, use the correct format, including degrees, minutes, seconds, and the appropriate hemisphere designation (N, S, E, W).
- Consider accuracy requirements: The accuracy needed for latitude and longitude will depend on the application. For example, a navigation system requires higher accuracy than a general map.
- Utilize online tools: Online mapping services and GPS devices offer convenient ways to find and use latitude and longitude coordinates.
- Be aware of potential errors: While latitude and longitude provide a precise way to describe locations, errors can occur in measurements and data sources.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude are essential tools for understanding and navigating the world. This system of coordinates provides a universal language for describing locations, enabling accurate navigation, mapping, and data analysis. From guiding our daily commutes to tracking weather patterns and mapping the universe, latitude and longitude continues to play a vital role in our understanding and interaction with the Earth. As technology advances, the importance of this fundamental system will only continue to grow, further shaping our understanding and exploration of our planet.


![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!