Powerpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data and Enhancing Presentations
Related Articles: Powerpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data and Enhancing Presentations
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Powerpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data and Enhancing Presentations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Powerpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data and Enhancing Presentations
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Powerpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data and Enhancing Presentations
- 3.1 The Importance of Maps in Powerpoint Presentations
- 3.2 Exploring the Types of Powerpoint Maps
- 3.3 Powerpoint Map Features: Enhancing Your Presentations
- 3.4 Creating Powerpoint Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.5 Powerpoint Map Free: Exploring Options and Resources
- 3.6 FAQs about Powerpoint Maps
- 3.7 Tips for Creating Effective Powerpoint Maps
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Powerpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data and Enhancing Presentations

In the realm of presentations and visual communication, maps hold a unique power to convey information in a compelling and easily digestible manner. Powerpoint, the ubiquitous presentation software, offers a range of tools for incorporating maps into presentations, enabling users to visualize data, illustrate geographic relationships, and enhance the impact of their message. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various aspects of using maps in Powerpoint, exploring their benefits, features, and applications.
The Importance of Maps in Powerpoint Presentations
Maps serve as powerful visual aids, offering a distinct advantage over traditional text-based presentations. They provide a clear and intuitive way to:
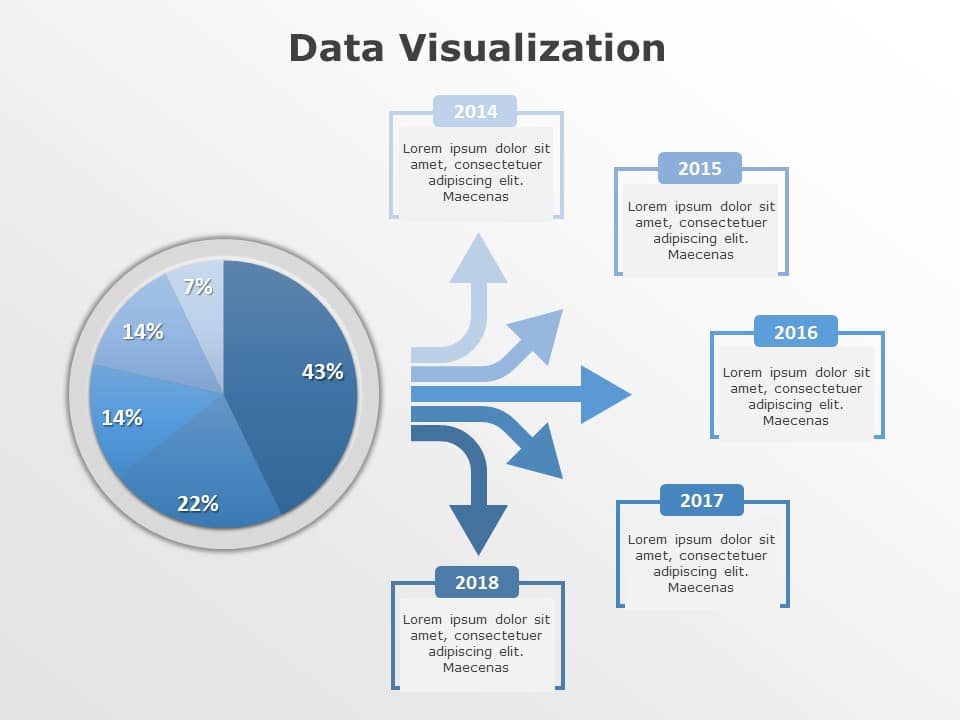
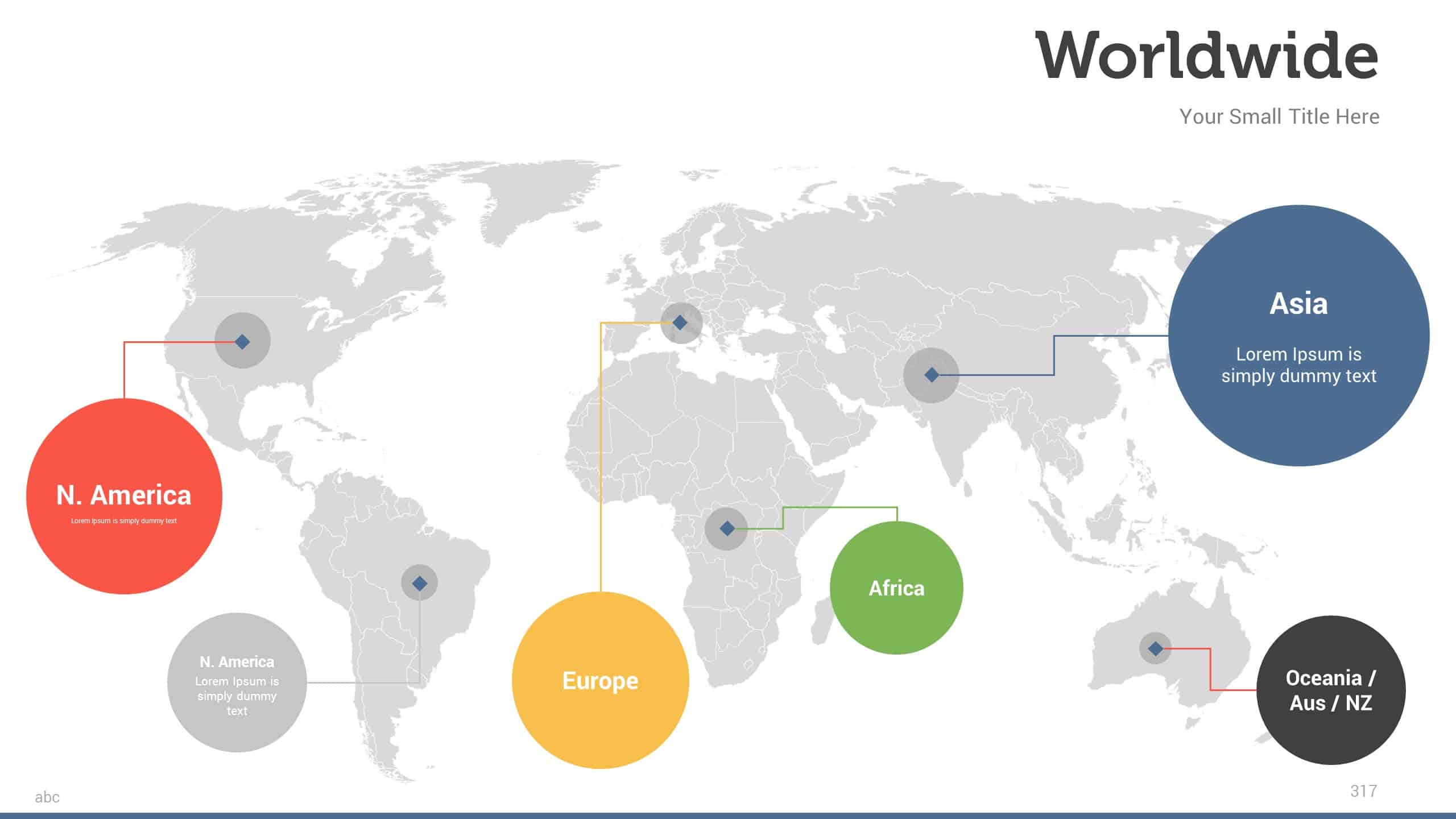
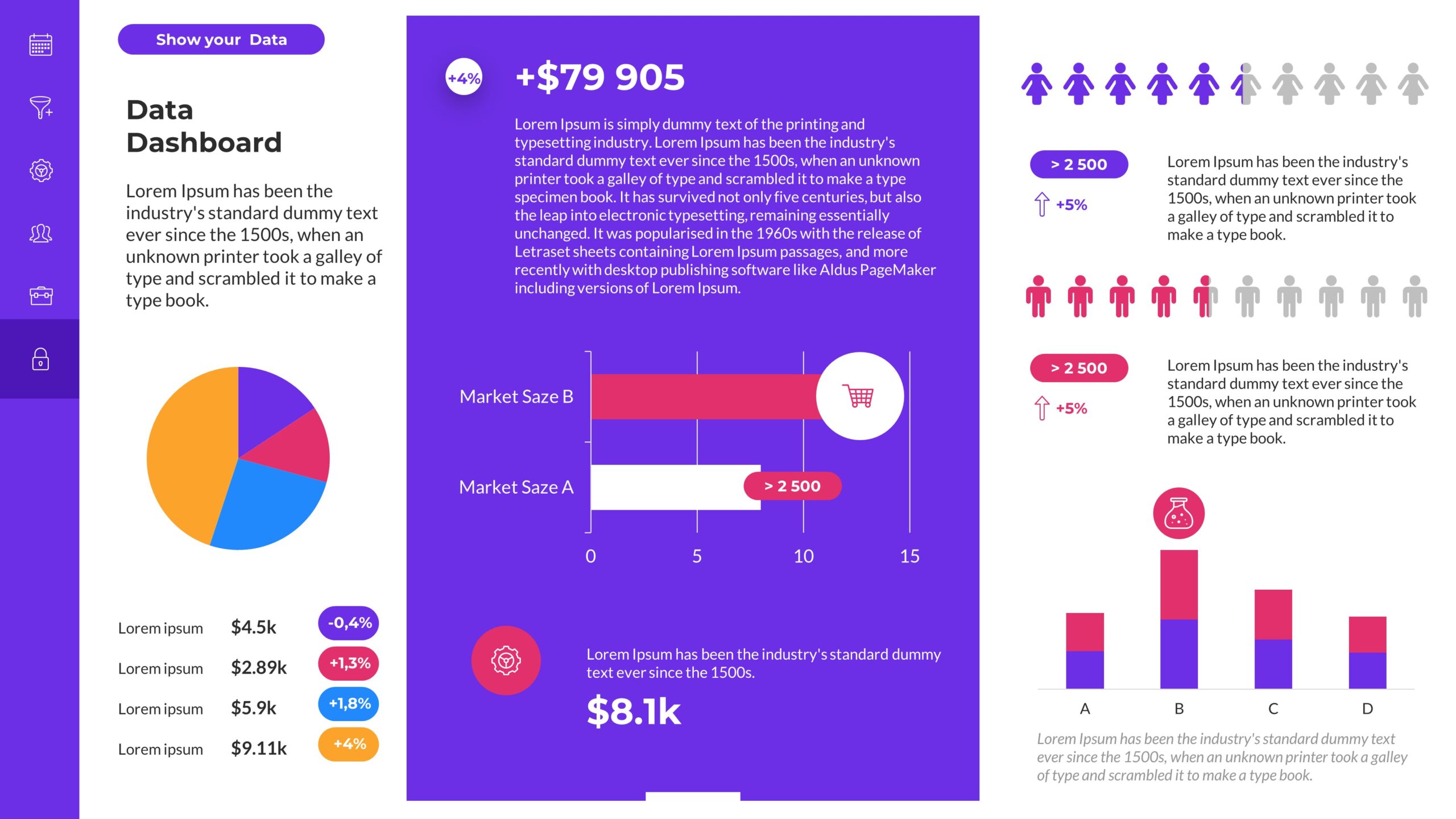
- Visualize Data: Maps can effectively represent geographic data, such as population density, sales figures, or disease prevalence, allowing for a quick understanding of spatial patterns and trends.
- Illustrate Relationships: By overlaying data onto maps, users can demonstrate connections between geographic locations, showcasing relationships between variables like demographics, economic activity, or environmental factors.
- Enhance Engagement: Maps inherently capture attention and pique curiosity, making presentations more engaging and memorable. They offer a visual storytelling element, captivating audiences and leaving a lasting impression.
- Clarify Complex Information: Maps simplify complex data by presenting it in a visually appealing and easily comprehensible format, making it easier for audiences to grasp key insights.
- Promote Understanding: Maps provide a context for data, helping audiences understand its significance and relevance within a geographic framework.
Exploring the Types of Powerpoint Maps
Powerpoint offers a variety of map options, each tailored to specific needs and presentation goals. Understanding these options is crucial for selecting the most effective map for your presentation:
1. Built-in Maps: Powerpoint’s built-in map feature provides a basic but functional option for creating maps. It allows users to select a region, add pins, and customize the map’s appearance. While simple, this feature can be sufficient for basic presentations.
2. Map Templates: Numerous free and paid map templates are available online, offering pre-designed maps with specific themes and layouts. These templates can save time and effort while providing a professional look and feel.
3. Map Add-ins: Third-party add-ins offer advanced mapping capabilities within Powerpoint. These add-ins provide features like real-time data integration, interactive maps, and advanced customization options.
4. Importing External Maps: Users can import maps created in other software, such as Google Maps or ArcGIS, into Powerpoint presentations. This allows for greater flexibility and customization, enabling the use of specialized maps with specific data and functionalities.
Powerpoint Map Features: Enhancing Your Presentations
Powerpoint maps come equipped with various features that enhance their functionality and visual appeal:
- Pin Customization: Pins can be customized with different colors, sizes, and icons to represent various data points or categories.
- Data Linking: Maps can be linked to external data sources, allowing for dynamic updates and real-time data visualization.
- Labeling and Annotations: Labels and annotations can be added to maps to provide context, highlight specific locations, or explain data points.
- Zoom and Pan: Users can zoom in and out of maps to focus on specific areas or provide a broader view, enhancing exploration and understanding.
- Map Styles: Powerpoint offers various map styles, including satellite imagery, terrain maps, and road maps, allowing for customization to suit the presentation’s theme and message.
Creating Powerpoint Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating effective Powerpoint maps requires a methodical approach, ensuring clarity, accuracy, and visual appeal:
1. Determine Your Purpose: Clearly define the objective of the map and the data it will represent. This step guides the map’s design and data selection.
2. Choose the Right Map Type: Select the map type that best suits the data and the presentation’s message. Consider factors like the geographic scope, data types, and desired level of detail.
3. Gather and Prepare Data: Ensure the data is accurate, relevant, and properly formatted for map integration. Consider using spreadsheets or databases for data organization.
4. Design the Map: Choose a suitable map style, color scheme, and font to enhance readability and visual appeal. Ensure the map is consistent with the presentation’s overall design.
5. Add Data and Labels: Integrate the data onto the map, using pins, markers, or color gradients to represent different values. Add clear labels and annotations to provide context and explain data points.
6. Refine and Optimize: Review the map for clarity, accuracy, and visual appeal. Make adjustments to improve readability and ensure the map effectively conveys the intended message.
Powerpoint Map Free: Exploring Options and Resources
While Powerpoint offers basic mapping features, users can explore numerous free resources to enhance their map creation process:
- Free Map Templates: Websites like Canva, Slidesgo, and Freepik offer a wide selection of free map templates, providing pre-designed maps with various themes and layouts.
- OpenStreetMap: This collaborative project provides free and open-source map data, enabling users to create custom maps with detailed information and customization options.
- Google Maps: Google Maps offers a free API that allows developers to integrate maps into their applications, including Powerpoint presentations. This integration enables access to real-time data and advanced map features.
- Mapbox: Mapbox provides a platform for creating custom maps with advanced styling and data visualization capabilities. While not free, Mapbox offers a free tier with limited features.
FAQs about Powerpoint Maps
Q: Can I use Powerpoint maps for presentations outside the business context?
A: Absolutely! Powerpoint maps are versatile and can be used in various contexts, including academic presentations, research reports, educational materials, and even personal projects.
Q: How do I ensure my Powerpoint maps are accessible to all users?
A: Accessibility is crucial for ensuring all users can understand and interact with your maps. Consider using high-contrast colors, descriptive labels, and alternative text for images to make your maps accessible to individuals with visual impairments.
Q: Are there any limitations to using Powerpoint maps?
A: Powerpoint’s built-in mapping features might be limited for complex data visualization or advanced customization. In such cases, consider using external mapping software or add-ins for greater flexibility.
Q: Can I use Powerpoint maps for real-time data visualization?
A: While Powerpoint itself doesn’t offer real-time data visualization, you can link maps to external data sources and use add-ins to dynamically update map data.
Tips for Creating Effective Powerpoint Maps
- Keep it Simple: Avoid overcrowding the map with too much data or complex annotations. Focus on conveying key insights and information clearly.
- Use Color Strategically: Choose a color scheme that enhances readability and helps differentiate data points. Consider using color gradients to represent data ranges.
- Focus on Legibility: Ensure text and labels are legible and easily understandable. Use appropriate font sizes and styles for clarity.
- Prioritize Visual Appeal: Design the map with a visually appealing and consistent style, aligning with the overall presentation theme.
- Test Your Map: Preview the map on different devices and screen sizes to ensure it displays correctly and remains legible.
Conclusion
Powerpoint maps provide a powerful tool for enhancing presentations, conveying data visually, and engaging audiences. By understanding the different types of maps, their features, and best practices for creation, users can leverage maps to elevate their presentations, make complex information more accessible, and leave a lasting impact on their audience. Whether for business presentations, academic reports, or personal projects, Powerpoint maps offer a valuable resource for visualizing data and telling compelling stories within a geographic context.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Powerpoint Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Data and Enhancing Presentations. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!