The Shifting Landscape of Detroit: A Look at the City’s Racial Geography in 2000
Related Articles: The Shifting Landscape of Detroit: A Look at the City’s Racial Geography in 2000
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Landscape of Detroit: A Look at the City’s Racial Geography in 2000. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Landscape of Detroit: A Look at the City’s Racial Geography in 2000

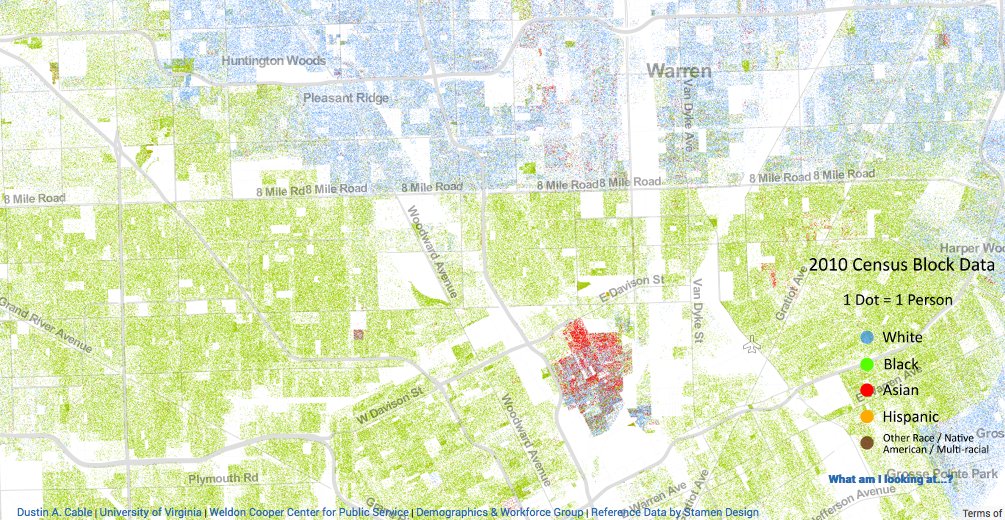
Detroit, Michigan, a city steeped in industrial history and cultural vibrancy, has experienced profound demographic shifts over the decades. Understanding the racial makeup of Detroit, particularly as it stood in the year 2000, provides crucial insights into the city’s social, economic, and political landscape. This article explores the racial geography of Detroit in 2000, examining the patterns of segregation, the factors contributing to these patterns, and the implications for the city’s future.
A City in Transition: The Racial Geography of Detroit in 2000
The year 2000 marked a pivotal point in Detroit’s demographic history. The city, once a predominantly white industrial powerhouse, had undergone a significant transformation, becoming majority Black. This shift was a result of several interconnected factors, including:
- The Great Migration: The early 20th century saw a mass exodus of African Americans from the rural South to urban centers like Detroit, seeking economic opportunities and escaping Jim Crow laws. This migration dramatically altered the city’s racial composition.
- White Flight: As the Black population grew, many white residents moved to the suburbs, seeking greater homogeneity and escaping perceived racial tensions. This "white flight" further exacerbated the racial divide in Detroit.
- Economic Decline: The decline of the automotive industry in the latter half of the 20th century led to job losses and economic hardship in Detroit, disproportionately affecting Black communities.
These factors combined to create a distinct racial geography in Detroit by 2000. The city’s central neighborhoods, historically home to the city’s industrial heart, became predominantly Black, while the suburbs remained largely white. This spatial separation resulted in significant disparities in access to resources, opportunities, and quality of life.
Analyzing the Racial Map: Key Insights and Observations
Examining a racial map of Detroit in 2000 reveals several key observations:
- High Levels of Segregation: The map clearly demonstrates high levels of residential segregation, with Black neighborhoods clustered in the city center and white neighborhoods concentrated in the suburbs. This spatial separation was not accidental but a result of deliberate policies and practices, including redlining, restrictive covenants, and discriminatory lending practices.
- Concentration of Poverty: The map highlights the concentration of poverty in predominantly Black neighborhoods. The economic decline of Detroit disproportionately impacted Black communities, leading to higher unemployment rates, lower incomes, and limited access to essential services.
- Spatial Disparities in Resources: The racial map reveals stark disparities in access to resources, such as quality education, healthcare, and public transportation. Black neighborhoods often lacked adequate infrastructure and investment, creating a cycle of poverty and disadvantage.
The Importance of Understanding Racial Geography
Understanding the racial geography of Detroit in 2000 is crucial for several reasons:
- Addressing Historical Injustices: It sheds light on the historical injustices that have shaped the city’s racial landscape, emphasizing the need for policies and programs aimed at redressing these inequities.
- Promoting Equitable Development: Recognizing the spatial disparities in resources and opportunities allows for the development of targeted strategies to promote equitable development and improve the quality of life for all residents.
- Building a More Inclusive City: Understanding the racial geography of Detroit is essential for fostering a more inclusive and equitable city, where residents of all backgrounds have access to the same opportunities and resources.
FAQs about the Racial Map of Detroit in 2000
Q: What were the primary causes of racial segregation in Detroit?
A: The primary causes of racial segregation in Detroit include discriminatory housing policies like redlining, restrictive covenants, and discriminatory lending practices, as well as the combined effects of the Great Migration, white flight, and the decline of the automotive industry.
Q: What were the consequences of racial segregation in Detroit?
A: Racial segregation in Detroit resulted in significant disparities in access to resources, opportunities, and quality of life. Black neighborhoods often lacked adequate infrastructure and investment, leading to higher poverty rates, lower incomes, and limited access to essential services.
Q: How did the racial geography of Detroit in 2000 influence the city’s future?
A: The racial geography of Detroit in 2000 laid the foundation for the challenges the city faced in the decades that followed. The legacy of segregation, poverty, and disinvestment continues to influence the city’s social, economic, and political landscape, shaping its future trajectory.
Tips for Studying the Racial Map of Detroit in 2000
- Use Multiple Sources: Consult various sources, including historical maps, census data, and academic studies, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the city’s racial geography.
- Consider Context: Analyze the map in the context of historical events, social movements, and political policies that shaped the city’s racial landscape.
- Focus on Disparities: Pay attention to the disparities in access to resources, opportunities, and quality of life between different racial groups.
- Connect to Contemporary Issues: Reflect on how the racial geography of Detroit in 2000 continues to influence the city’s present-day challenges and opportunities.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Segregation and a Path Forward
The racial map of Detroit in 2000 serves as a powerful reminder of the legacy of segregation and the enduring challenges faced by the city. It highlights the need for continued efforts to address historical injustices, promote equitable development, and build a more inclusive and equitable city for all residents. By understanding the city’s racial geography, we can better inform policies and programs that promote social justice, economic opportunity, and a brighter future for Detroit.





![City boundaries of Detroit overlaid on racial dot map [946 × 584] : MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/b4ANvuotzp-v0WvkHr6GpIlxb3r8eqTNKhDH6S9C_X8.jpg?auto=webpu0026s=898176c87de507f87e1436941de7627843a4af8f)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Landscape of Detroit: A Look at the City’s Racial Geography in 2000. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!