Understanding the Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at India’s Political Map
Related Articles: Understanding the Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at India’s Political Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at India’s Political Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at India’s Political Map
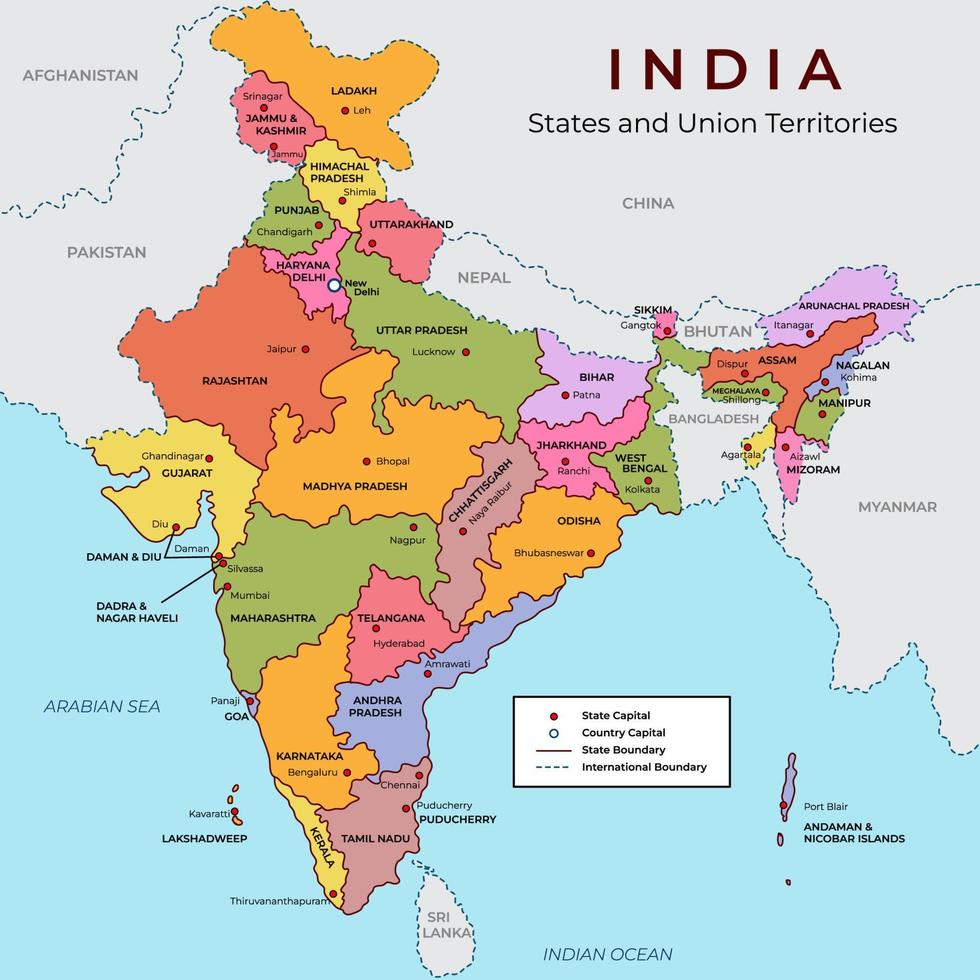
India, a land of immense diversity and vibrant democracy, undergoes constant evolution. This dynamism is reflected in its political landscape, which has witnessed significant changes over the years. The political map of India, a visual representation of its administrative divisions, provides a crucial window into the country’s governance and the dynamic interplay of power within its vast expanse.
The Evolution of India’s Political Map:
India’s political map has undergone several transformations since its independence in 1947. The initial map consisted of 14 states and 6 centrally administered territories. Over time, this structure evolved due to various factors including linguistic, cultural, and administrative considerations.
Key Milestones in the Evolution:
- 1956: The States Reorganization Act of 1956 was a landmark event that reshaped India’s political map. Based on language, it reorganized the existing states, leading to the formation of 14 states and 6 union territories.
- 1960: The creation of the states of Gujarat and Maharashtra from the erstwhile Bombay state marked a significant shift in the political landscape.
- 1966: The formation of Haryana and Punjab from the state of Punjab further altered the political map.
- 1972: The creation of the states of Manipur, Meghalaya, and Tripura, along with the reorganization of Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh, added more states to the map.
- 1987: The state of Mizoram became the 23rd state of India, further solidifying the country’s federal structure.
- 2000: The creation of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Uttarakhand from Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, and Uttar Pradesh respectively, marked a significant shift towards regional autonomy.
- 2014: The formation of Telangana from Andhra Pradesh, signifying a growing emphasis on regional aspirations and identity.
The Current Political Map of India:
The current political map of India comprises 28 states and 8 union territories, each possessing distinct features and administrative structures. This intricate tapestry of states and territories reflects the diversity of India’s population, languages, cultures, and geographical landscapes.
Understanding the Components of India’s Political Map:
- States: States form the core of India’s federal structure. They are governed by elected legislatures and have their own executive branches, led by a Chief Minister.
- Union Territories: Union territories are administrative divisions under the direct control of the central government. They are governed by an administrator appointed by the President of India.
- Boundaries: The boundaries between states and union territories are clearly demarcated on the political map. These boundaries are often defined by geographical features, historical events, or linguistic considerations.
- Capital Cities: Each state and union territory has a designated capital city, which serves as the center of administration and governance.
Importance of India’s Political Map:
The political map of India serves several crucial purposes:
- Administrative Framework: It provides a visual representation of the country’s administrative structure, highlighting the distribution of power and responsibilities among different levels of government.
- Regional Identity: The map reflects the distinct identities and cultures of different regions, acknowledging their unique characteristics and contributions.
- Political Dynamics: It provides insights into the political landscape, highlighting the distribution of political power, the influence of different parties, and the dynamics of regional alliances.
- Resource Allocation: The map helps in understanding the distribution of resources, infrastructure, and development initiatives across different regions.
- National Unity: The map emphasizes the unity of India, showcasing the interconnectedness of its diverse regions and the shared identity of its people.
FAQs on India’s Political Map:
-
Q: What is the largest state in India by area?
A: Rajasthan is the largest state in India by area.
-
Q: Which state has the highest population in India?
A: Uttar Pradesh is the most populous state in India.
-
Q: How many union territories are there in India?
A: India currently has eight union territories.
-
Q: What is the significance of the state boundaries on the political map?
A: State boundaries are crucial for understanding the administrative divisions, regional identities, and resource allocation within India.
-
Q: How often does India’s political map change?
A: While changes to India’s political map are not frequent, they have occurred throughout history based on various factors like linguistic, cultural, and administrative considerations.
Tips for Understanding India’s Political Map:
- Study the map carefully: Pay attention to the names of states and union territories, their locations, and their boundaries.
- Research the history of state formation: Understand the factors that led to the creation of different states and their impact on the political landscape.
- Explore the cultural and linguistic diversity: Recognize the diverse languages, cultures, and traditions that contribute to the richness of India’s political map.
- Follow current political developments: Stay informed about the latest political developments in different states and their implications for the national map.
Conclusion:
India’s political map is a dynamic and ever-evolving reflection of its complex and diverse society. It provides a valuable tool for understanding the country’s administrative structure, regional identities, and political dynamics. By studying the map and its evolution, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that shape India’s governance and its journey towards a more inclusive and prosperous future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at India’s Political Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!