Unveiling Haiti’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Look at its Topographic Map
Related Articles: Unveiling Haiti’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Look at its Topographic Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Haiti’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Look at its Topographic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Haiti’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Look at its Topographic Map
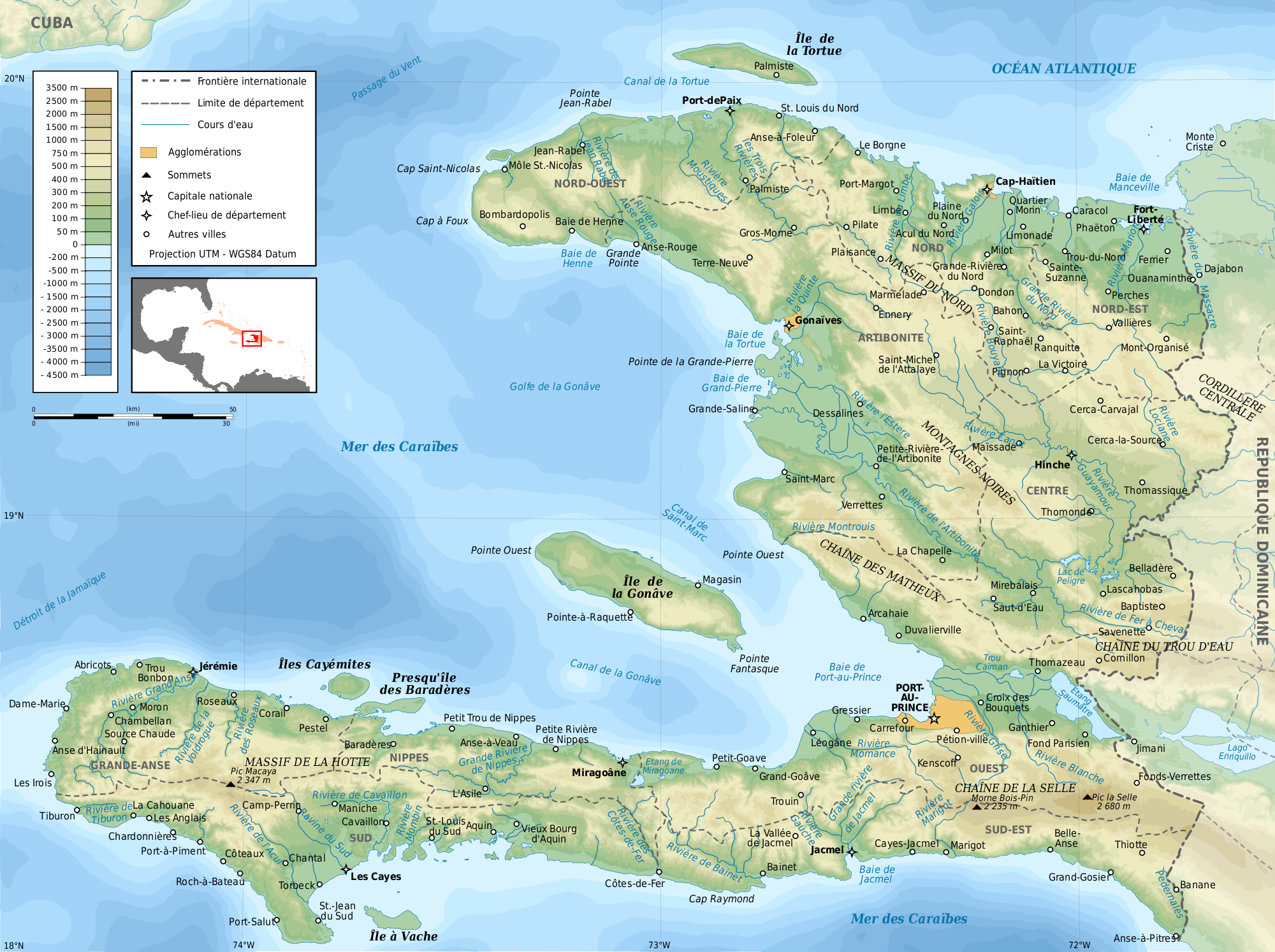
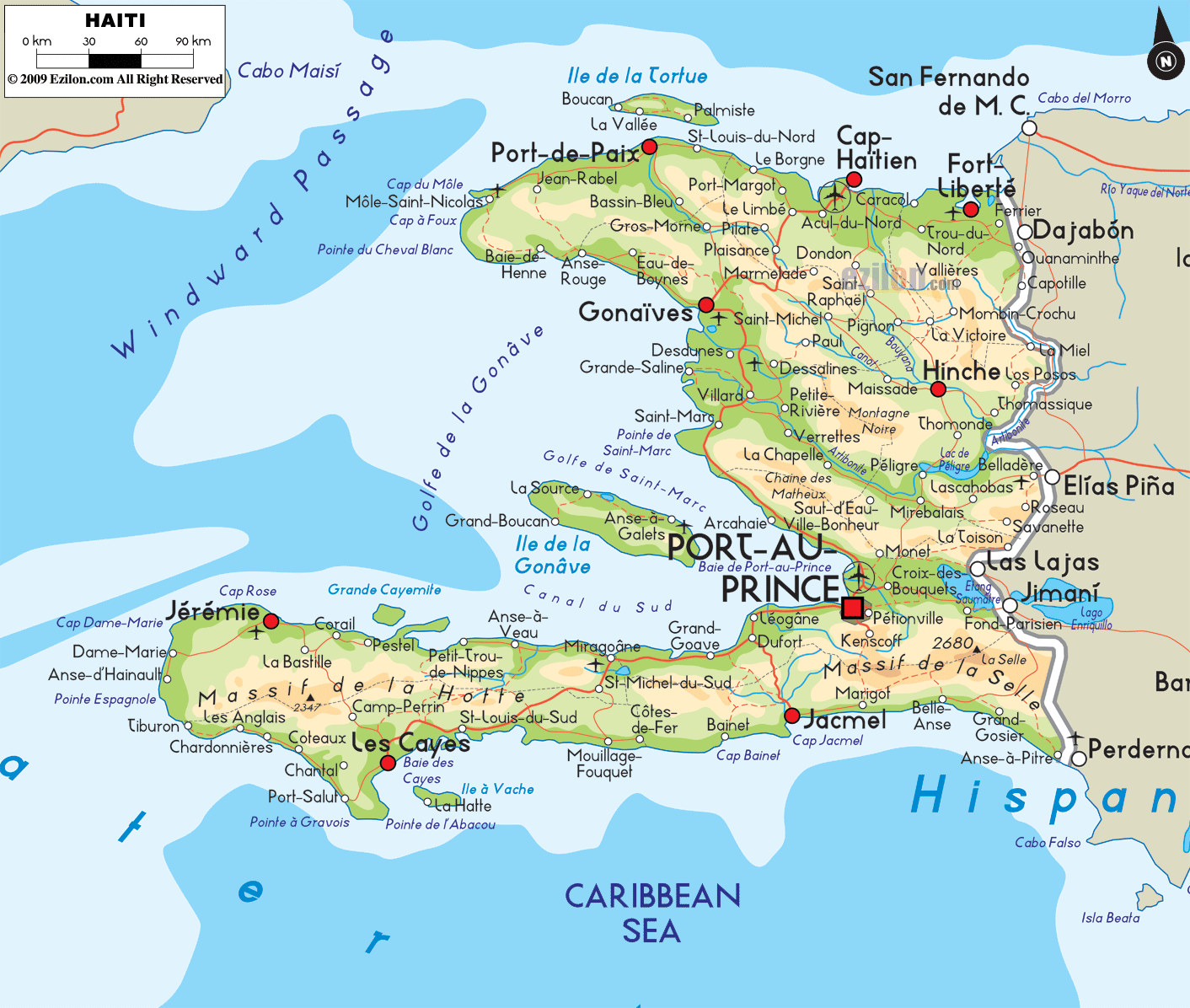
Haiti, the second-largest island nation in the Caribbean, is a land of diverse landscapes, ranging from coastal plains to towering mountains. Understanding the intricate interplay of these geographical features is crucial for various fields, from disaster preparedness and resource management to infrastructure development and tourism. This comprehensive exploration delves into the topographic map of Haiti, revealing its intricate details and highlighting its importance in understanding the nation’s physical characteristics and their influence on its people.
A Visual Representation of Haiti’s Terrain:
A topographic map is a specialized map that portrays the three-dimensional shape of the Earth’s surface, using contour lines to depict elevation changes. In the case of Haiti, these contour lines, like fingerprints, reveal the intricate tapestry of its terrain. The map’s colors, typically ranging from green for lowlands to brown for higher elevations, further enhance the visual representation of the country’s diverse topography.
Unraveling the Physical Landscape:
The topographic map of Haiti clearly showcases the country’s dramatic landscape, characterized by:
-
The Massif de la Hotte: This mountainous region, dominating the southwest, houses Haiti’s highest peak, Pic la Selle, reaching an elevation of 2,680 meters. The Massif de la Hotte is a testament to the island’s volcanic past, its rugged terrain sculpted by ancient geological forces.
-
The Massif du Nord: This vast mountain range, extending along the northern coast, exhibits a gentler slope compared to its southwestern counterpart. It plays a crucial role in moderating the climate of the northern plains, while also serving as a watershed for numerous rivers.
-
The Central Plateau: Situated between the two major mountain ranges, the Central Plateau is a relatively flat region, dotted with fertile valleys and rolling hills. This area is vital for agriculture, supporting a significant portion of the country’s food production.
-
Coastal Plains: Haiti’s coastline is fringed by narrow coastal plains, particularly along the north and south coasts. These plains, often susceptible to flooding and erosion, provide valuable land for agriculture and urban development.
The Importance of Topographic Maps for Haiti:
Beyond its visual appeal, the topographic map of Haiti holds immense practical value, serving as a fundamental tool for:
-
Disaster Preparedness: The map’s detailed depiction of terrain, including steep slopes and flood-prone areas, is invaluable for disaster management agencies. It helps in identifying areas vulnerable to earthquakes, landslides, and hurricanes, enabling the development of targeted mitigation strategies and evacuation plans.
-
Resource Management: The map reveals the distribution of natural resources, including water sources, forests, and mineral deposits. This information is crucial for sustainable resource management, ensuring equitable access and minimizing environmental impact.
-
Infrastructure Development: The topographic map provides essential data for planning and constructing infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and dams. It helps engineers and planners navigate challenging terrain, minimizing construction costs and maximizing efficiency.
-
Tourism and Recreation: The map highlights scenic areas, hiking trails, and potential eco-tourism destinations, attracting visitors and boosting the tourism industry. It also plays a role in promoting sustainable tourism practices, minimizing environmental impact and preserving natural beauty.
-
Scientific Research: The topographic map serves as a valuable tool for researchers studying various aspects of Haiti’s environment, including climate change, biodiversity, and land use patterns. It provides a baseline for monitoring changes over time and understanding the complex interactions within the ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Topographic Map of Haiti:
Q: What is the scale of the topographic map of Haiti?
A: The scale of a topographic map can vary depending on its intended use. Maps used for planning infrastructure projects may have a larger scale, providing more detailed information than maps used for general overview purposes.
Q: How accurate is the topographic map of Haiti?
A: The accuracy of a topographic map depends on the method used for data collection and the technology employed for its creation. Modern maps utilize advanced satellite imagery and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to achieve high accuracy, providing reliable information for various applications.
Q: Where can I access a topographic map of Haiti?
A: Topographic maps of Haiti can be obtained from various sources, including government agencies like the Haitian Institute of Geography (IGH), online mapping platforms like Google Maps, and specialized map providers.
Q: How is the topographic map of Haiti updated?
A: The topographic map of Haiti is updated periodically based on new data collected through aerial photography, satellite imagery, and ground surveys. These updates ensure the map reflects the latest changes in terrain and infrastructure.
Tips for Using a Topographic Map of Haiti:
-
Understand the map’s legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols, colors, and contour lines used on the map to interpret elevation changes, water bodies, and other features.
-
Consider the map’s scale: Choose a map with a scale appropriate for your intended use. Larger-scale maps provide greater detail, while smaller-scale maps offer a wider overview.
-
Use a compass and ruler: A compass helps determine direction, while a ruler aids in measuring distances on the map.
-
Consult additional resources: Combine the topographic map with other sources of information, such as satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and field observations, for a more comprehensive understanding of the terrain.
Conclusion:
The topographic map of Haiti is not merely a visual representation of the country’s terrain; it is a powerful tool that unlocks crucial insights into its physical characteristics and their influence on its people. From disaster preparedness to resource management and infrastructure development, the map serves as a foundation for informed decision-making, contributing to the nation’s sustainable development and resilience. As Haiti continues to face challenges related to climate change, natural disasters, and poverty, understanding its topography becomes even more critical in shaping a brighter future.
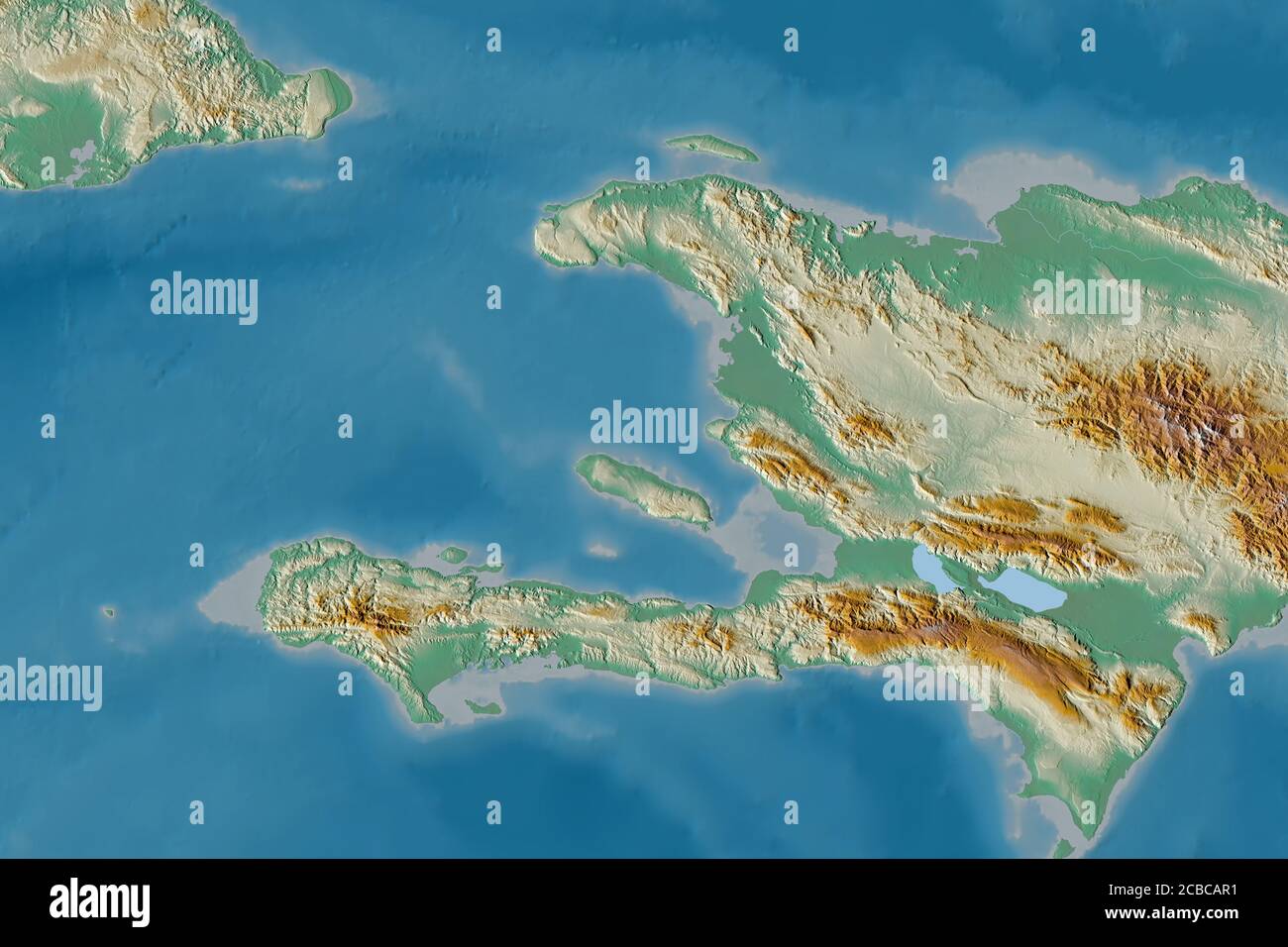


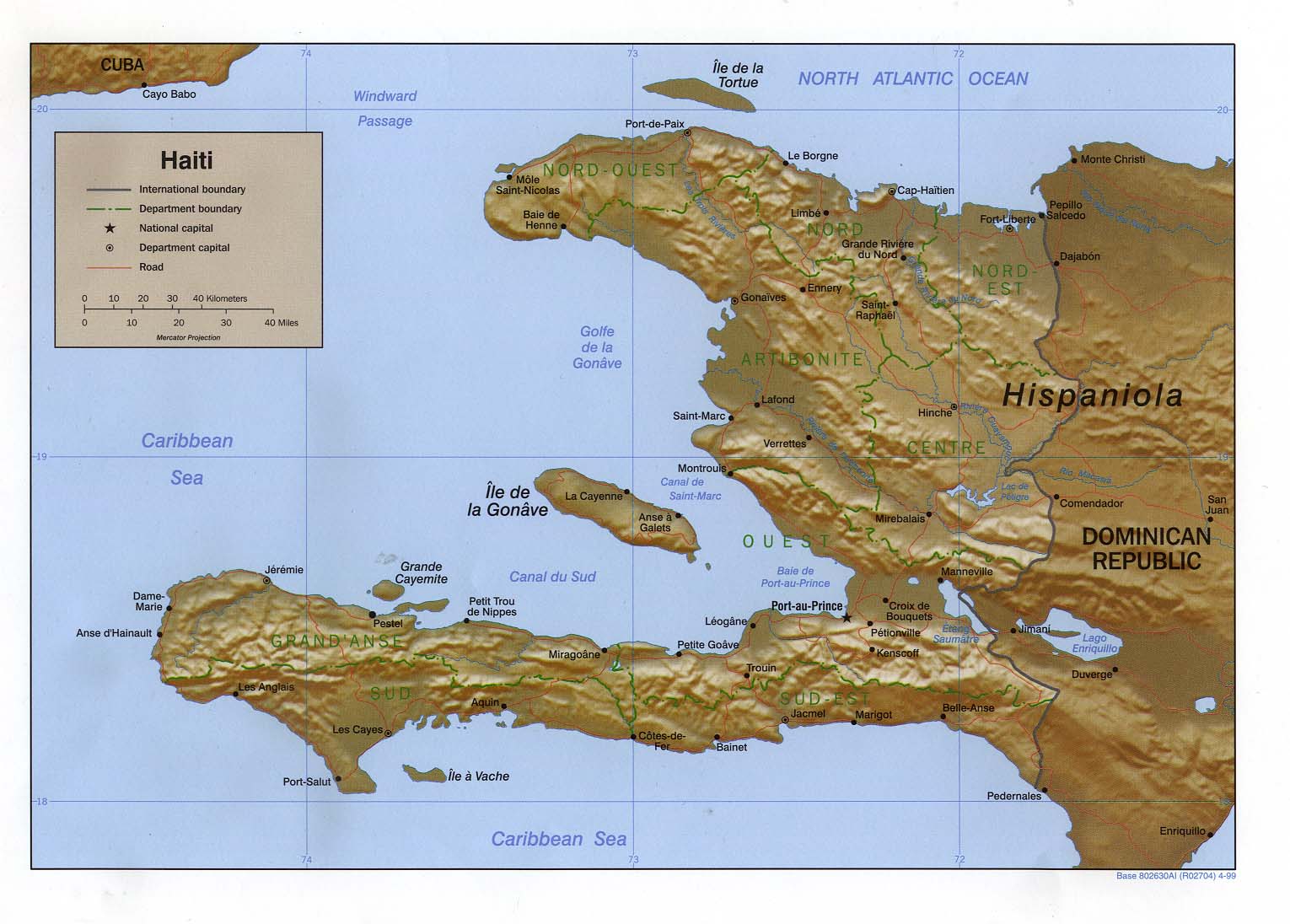
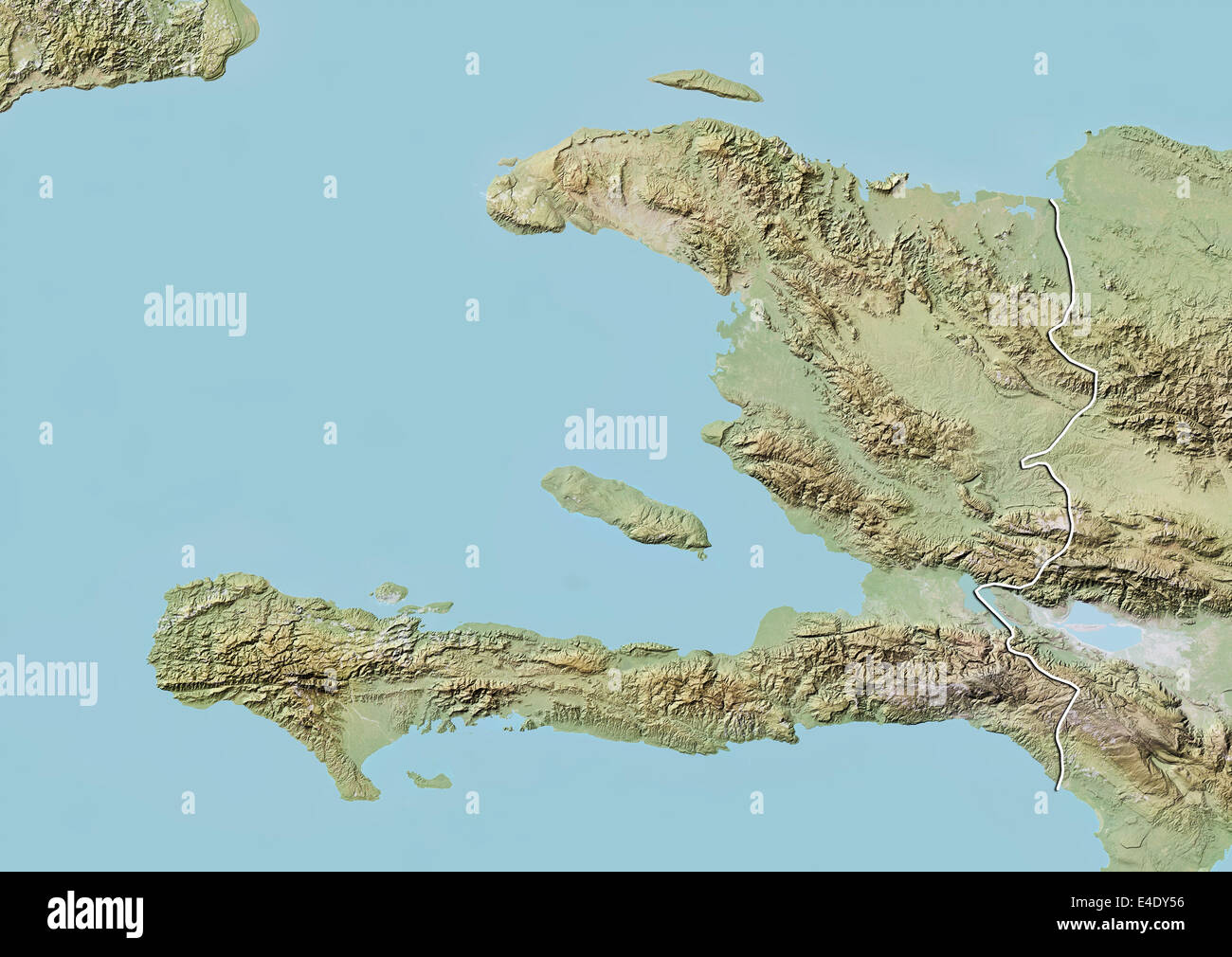


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Haiti’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Look at its Topographic Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!