Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to North American Islands
Related Articles: Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to North American Islands
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to North American Islands. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to North American Islands

The North American continent, with its vast landscapes and diverse ecosystems, is often visualized as a single landmass. However, beneath the surface of this familiar image lies a hidden world of countless islands, forming a complex and fascinating archipelago. These islands, scattered across the vast expanse of the North American waters, offer a unique perspective on the continent’s geography, history, and cultural tapestry.
This article delves into the captivating world of North American islands, exploring their diverse landscapes, historical significance, and the ecological treasures they hold. We will embark on a journey through the intricate tapestry of these islands, highlighting their individual characteristics while emphasizing their interconnectedness within the larger North American context.
Navigating the North American Archipelago: A Geographical Overview
The North American archipelago encompasses a vast array of islands, ranging from the towering peaks of the Aleutian Islands in the north to the sun-drenched shores of the Caribbean in the south. These islands are geographically categorized into distinct groups, each possessing its own unique features:
-
The Arctic Islands: This group, located north of the mainland, comprises a vast collection of islands, including Baffin Island, Ellesmere Island, and Victoria Island. These islands are characterized by their harsh Arctic climate, icy landscapes, and unique wildlife, including polar bears, walruses, and Arctic foxes.
-
The Greenlandic Islands: Greenland, the largest island in the world, is technically part of the Kingdom of Denmark but geographically considered part of North America. This vast island, covered in ice for the most part, is home to a unique Inuit culture and a diverse ecosystem that includes caribou, musk oxen, and narwhals.
-
The Canadian Archipelago: This group includes the islands in the Canadian Arctic, along with numerous islands off the Atlantic and Pacific coasts of Canada. Notable islands include Prince Edward Island, Newfoundland, and Vancouver Island, each possessing distinct landscapes and cultural heritage.
-
The United States Islands: The United States claims numerous islands, including the Hawaiian Islands in the Pacific Ocean, the Aleutian Islands in the Bering Sea, and various islands in the Caribbean Sea. These islands exhibit diverse landscapes, from volcanic peaks to lush rainforests, and represent a rich tapestry of cultures and histories.
-
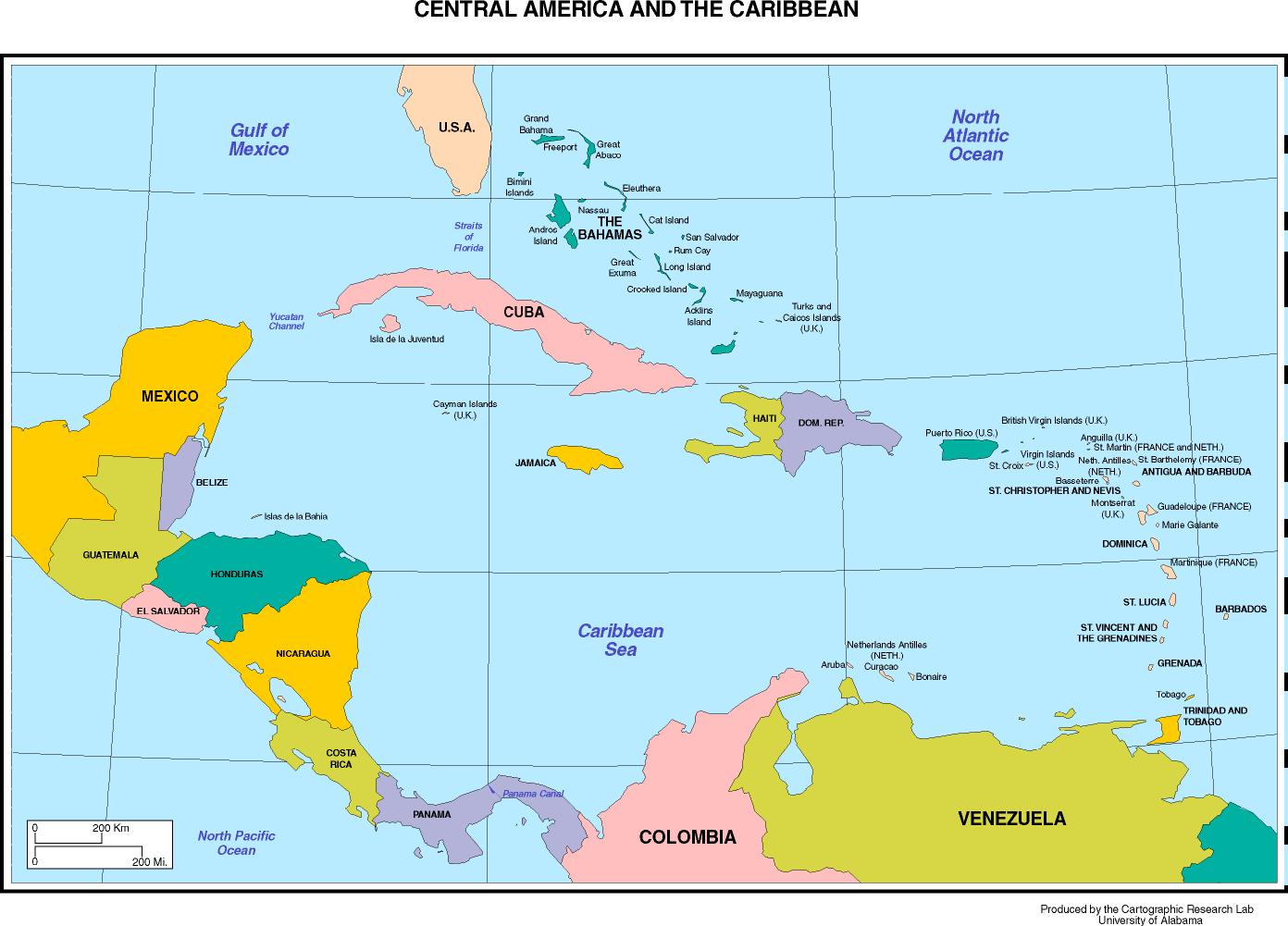
The Caribbean Islands: This group, situated in the southeastern part of North America, includes numerous islands belonging to various countries, including Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Dominican Republic. These islands are known for their tropical climate, stunning beaches, and vibrant cultures influenced by European, African, and indigenous roots.
The Historical Significance of North American Islands
The history of North American islands is intertwined with the stories of exploration, colonization, and cultural exchange. These islands have played a pivotal role in shaping the continent’s history, serving as strategic outposts, trading centers, and cultural melting pots.
-
Indigenous Heritage: The islands were originally inhabited by indigenous peoples who developed unique cultures and traditions adapted to their specific environments. From the Inuit of the Arctic to the indigenous communities of the Caribbean, these islanders have left an indelible mark on the history and culture of North America.
-
European Exploration and Colonization: European explorers and colonists arrived on the islands, seeking new lands, resources, and trade opportunities. This led to the establishment of settlements, the introduction of new crops and animals, and, unfortunately, the displacement and oppression of indigenous populations.
-
The Struggle for Independence: Many islands, particularly in the Caribbean, experienced struggles for independence from European colonial powers. These struggles resulted in the establishment of independent nations, fostering a spirit of self-determination and cultural revitalization.
Ecological Treasures: The Islands’ Diverse Ecosystems
North American islands are not just historical landmarks; they are also ecological havens, harboring diverse ecosystems that contribute to the continent’s biodiversity.
-
Arctic Islands: A Fragile Ecosystem: The Arctic islands, with their harsh climate and unique wildlife, are home to a fragile ecosystem that is particularly vulnerable to climate change. These islands support a variety of marine mammals, migratory birds, and land-based animals, all adapted to survive in the harsh environment.
-
The Rich Biodiversity of the Caribbean: The Caribbean islands, with their tropical climate and abundant rainfall, boast a remarkable diversity of plant and animal life. Lush rainforests, coral reefs, and mangrove swamps provide habitats for a wide range of species, including endemic birds, reptiles, and marine life.
-
The Unique Ecosystems of the Pacific Islands: The Pacific islands, including the Hawaiian Islands and the Aleutian Islands, are characterized by unique ecosystems shaped by volcanic activity and isolation. These islands support a wide range of endemic species, including plants, birds, and insects found nowhere else on Earth.
The Importance of North American Islands: A Global Perspective
The North American islands play a significant role in the global context, contributing to the world’s biodiversity, climate, and cultural diversity.
-
Biodiversity Hotspots: Many North American islands are considered biodiversity hotspots, meaning they harbor a high concentration of endemic species found nowhere else on Earth. These islands are crucial for conserving biodiversity and understanding the evolution of life.
-
Climate Regulation: Islands play a vital role in regulating the global climate. They absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating climate change, and their ecosystems provide essential services, such as storm protection and water filtration.
-
Cultural Diversity: The islands are home to a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and traditions. These cultures represent a unique blend of indigenous heritage, European influences, and African traditions, contributing to the global mosaic of human diversity.
FAQs about North American Islands
Q: What are the largest islands in North America?
A: The largest islands in North America are Greenland (the largest island in the world), Baffin Island (Canada), Ellesmere Island (Canada), Victoria Island (Canada), and Newfoundland (Canada).
Q: What is the most populated island in North America?
A: The most populated island in North America is Cuba, with a population of over 11 million.
Q: What are the most popular tourist destinations among North American islands?
A: Some of the most popular tourist destinations among North American islands include:
- The Caribbean Islands: Cuba, Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic, Jamaica, Bahamas, and Turks and Caicos.
- The Hawaiian Islands: Oahu, Maui, Kauai, and Big Island.
- The Canadian Islands: Prince Edward Island, Newfoundland, and Vancouver Island.
Q: What are the main threats to North American islands?
A: The main threats to North American islands include:
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels, increased storm intensity, and changes in temperature are impacting island ecosystems and coastal communities.
- Pollution: Pollution from land-based sources, such as oil spills and agricultural runoff, is harming marine life and coastal ecosystems.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices are depleting fish stocks and disrupting marine ecosystems.
- Habitat Loss: Development, deforestation, and invasive species are destroying natural habitats and threatening biodiversity.
Tips for Exploring North American Islands
- Research your destination: Before you travel, research the island’s unique features, cultural attractions, and environmental considerations.
- Respect local customs: Learn about the island’s culture and traditions, and be respectful of local customs and beliefs.
- Travel sustainably: Minimize your environmental impact by choosing eco-friendly accommodations, reducing waste, and supporting local businesses.
- Support conservation efforts: Consider donating to or volunteering with organizations dedicated to protecting island ecosystems and wildlife.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Beauty and Resilience
The North American islands, with their diverse landscapes, rich history, and unique ecosystems, are a testament to the continent’s natural beauty and resilience. These islands, scattered across the vast expanse of North American waters, offer a unique perspective on the continent’s geography, history, and cultural tapestry. By understanding and appreciating the importance of these islands, we can contribute to their conservation and ensure that their legacy of beauty and resilience continues for generations to come.



.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to North American Islands. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!