Unveiling the Geographic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Venezuela’s Physical Landscape
Related Articles: Unveiling the Geographic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Venezuela’s Physical Landscape
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Geographic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Venezuela’s Physical Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Geographic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Venezuela’s Physical Landscape
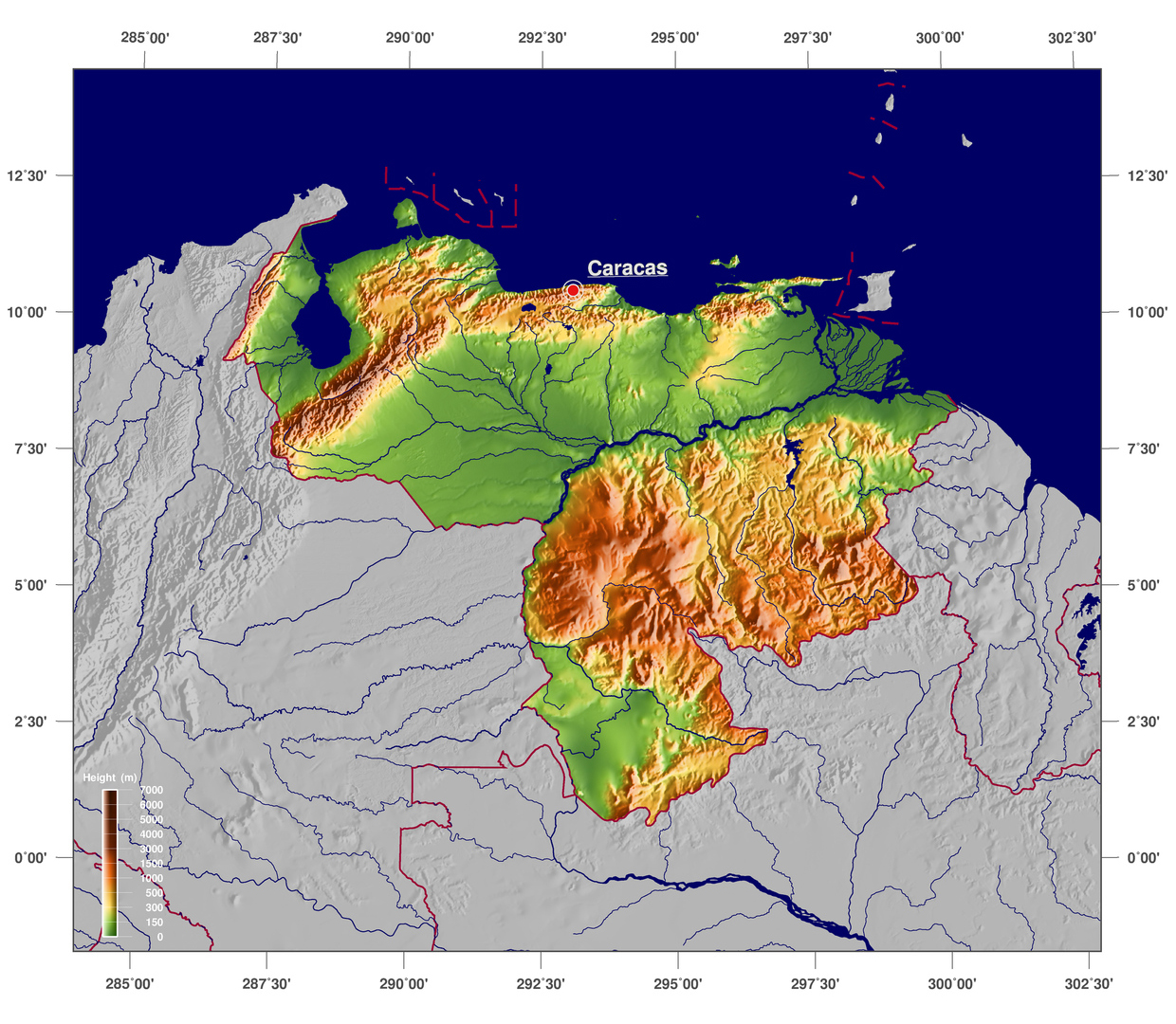
Venezuela, a nation nestled in the northern reaches of South America, boasts a captivating tapestry of diverse landscapes, shaped by powerful geological forces and a vibrant history. Understanding the physical map of Venezuela is crucial for comprehending its natural resources, biodiversity, and the challenges it faces in managing its environment. This exploration delves into the intricate details of Venezuela’s geography, unveiling its unique characteristics and highlighting its importance in shaping the nation’s identity.
A Land of Contrasts: Navigating Venezuela’s Diverse Terrain
Venezuela’s physical map reveals a remarkable contrast between its towering mountains and sprawling lowlands, its lush rainforests and arid deserts. This diversity stems from a complex interplay of geological formations, tectonic activity, and climatic influences.
The Mighty Andes: A Backbone of Elevation
The Andes mountain range, a defining feature of South America, extends into Venezuela, forming the Cordillera de Mérida, a majestic chain of peaks that rise to over 5,000 meters. This region, known for its breathtaking scenery and diverse flora and fauna, is a testament to the immense power of geological forces. The Cordillera de Mérida not only shapes the landscape but also influences rainfall patterns and the distribution of plant and animal life.
The Llanos: A Vast Expanse of Savanna
Stretching across the center of Venezuela lies the Llanos, a vast expanse of flat, grassy plains. These savannas, characterized by seasonal flooding and a dry season, are home to a unique ecosystem, supporting a wide range of wildlife, including jaguars, capybaras, and countless bird species. The Llanos play a crucial role in Venezuela’s agricultural economy, with vast cattle ranches and agricultural lands dotting the landscape.
The Orinoco Delta: Where River Meets Sea
The Orinoco River, one of the longest rivers in South America, meanders through Venezuela, eventually emptying into the Atlantic Ocean, forming a vast delta. This delta, a complex network of waterways and islands, is a vital ecosystem, teeming with biodiversity and providing a livelihood for local communities. The Orinoco Delta is also a significant source of oil and gas, making it a strategic region for Venezuela’s economy.
The Guiana Shield: A Pre-Cambrian Legacy
In southeastern Venezuela, the Guiana Shield, an ancient geological formation dating back to the Precambrian era, forms a plateau characterized by rugged mountains, cascading waterfalls, and dense rainforests. This region, home to the iconic Angel Falls, the world’s highest uninterrupted waterfall, is a testament to the geological history of the continent. The Guiana Shield is also rich in mineral resources, including diamonds, gold, and bauxite.
The Caribbean Coast: Where Mountains Meet the Sea
Venezuela’s northern coastline is defined by a series of coastal mountains that rise abruptly from the Caribbean Sea. This region, known for its stunning beaches and vibrant coastal cities, is also home to a unique ecosystem, with mangroves, coral reefs, and diverse marine life. The Caribbean coast is a vital economic hub for Venezuela, with tourism and fishing playing significant roles.
Volcanic Activity: Shaping the Landscape
Venezuela’s physical map is also shaped by volcanic activity. The country has several dormant volcanoes, remnants of past volcanic eruptions that have left their mark on the landscape. These volcanic formations, while currently inactive, serve as a reminder of the dynamic forces that continue to shape the earth.
The Importance of Understanding Venezuela’s Physical Map
Understanding Venezuela’s physical map is essential for comprehending its unique identity and the challenges it faces. The diverse landscape, with its rich biodiversity and natural resources, presents both opportunities and challenges for sustainable development.
Natural Resources: A Blessing and a Burden
Venezuela’s physical map reveals a wealth of natural resources, including oil, gas, gold, diamonds, and bauxite. These resources have played a significant role in shaping the nation’s economy and its global influence. However, the exploitation of these resources has also come at a cost, leading to environmental degradation and social inequalities.
Biodiversity: A Treasure to Be Protected
Venezuela’s diverse landscape is home to a remarkable array of biodiversity, with a rich tapestry of plant and animal life. The country is a global hotspot for biodiversity, with a vast array of endemic species found nowhere else on earth. However, deforestation, habitat loss, and climate change threaten this precious biodiversity, highlighting the need for conservation efforts.
Climate Change: A Looming Threat
Venezuela’s physical map is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, with rising sea levels threatening coastal communities and changing rainfall patterns impacting agricultural production. Understanding the country’s physical map is essential for developing strategies to mitigate these risks and adapt to the changing environment.
FAQs: Exploring the Physical Map of Venezuela
Q: What are the major landforms of Venezuela?
A: Venezuela’s major landforms include the Andes Mountains (Cordillera de Mérida), the Llanos (savannas), the Orinoco Delta, the Guiana Shield, and the Caribbean Coast.
Q: What is the highest point in Venezuela?
A: The highest point in Venezuela is Pico Bolívar, located in the Cordillera de Mérida, with an elevation of 5,007 meters (16,427 feet).
Q: What are the major rivers in Venezuela?
A: The major rivers in Venezuela include the Orinoco River, the Caroní River, and the Apure River.
Q: What is the climate like in Venezuela?
A: Venezuela’s climate varies greatly depending on the region. The Caribbean coast experiences a tropical climate with high humidity, while the Andes Mountains have a cooler, more temperate climate. The Llanos experience a wet and dry season, with heavy rainfall during the rainy season.
Q: What are the major natural resources of Venezuela?
A: Venezuela’s major natural resources include oil, gas, gold, diamonds, bauxite, and iron ore.
Tips: Navigating the Physical Map of Venezuela
- Utilize online mapping tools and interactive maps to explore the different regions of Venezuela.
- Consult atlases, physical geography textbooks, and scientific journals for in-depth information.
- Explore documentaries and videos that highlight the country’s diverse landscapes and natural wonders.
- Visit national parks and protected areas to experience Venezuela’s unique ecosystems firsthand.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Geography and Identity
Venezuela’s physical map is a testament to the power of geological forces, the richness of biodiversity, and the challenges of sustainable development. Understanding the country’s diverse landscape, its natural resources, and its environmental vulnerabilities is crucial for navigating the path towards a sustainable future. As we continue to explore and appreciate the beauty and complexity of Venezuela’s physical map, we gain a deeper understanding of this fascinating nation and its place in the world.
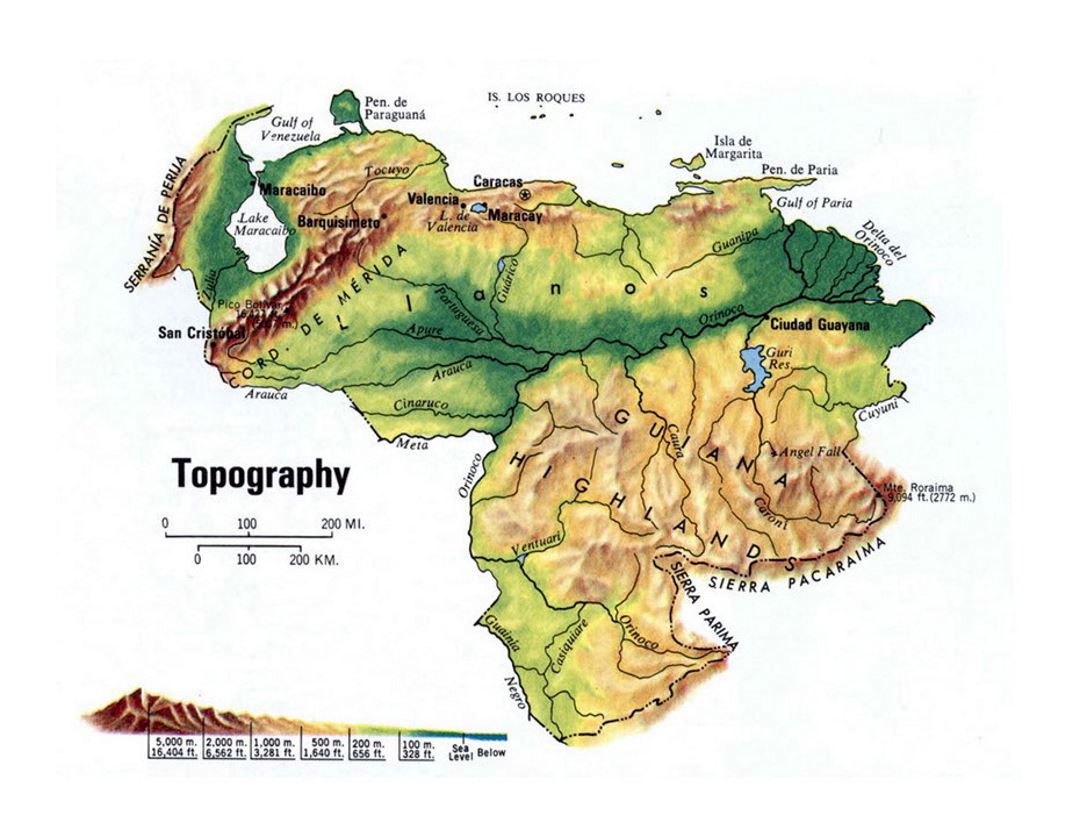

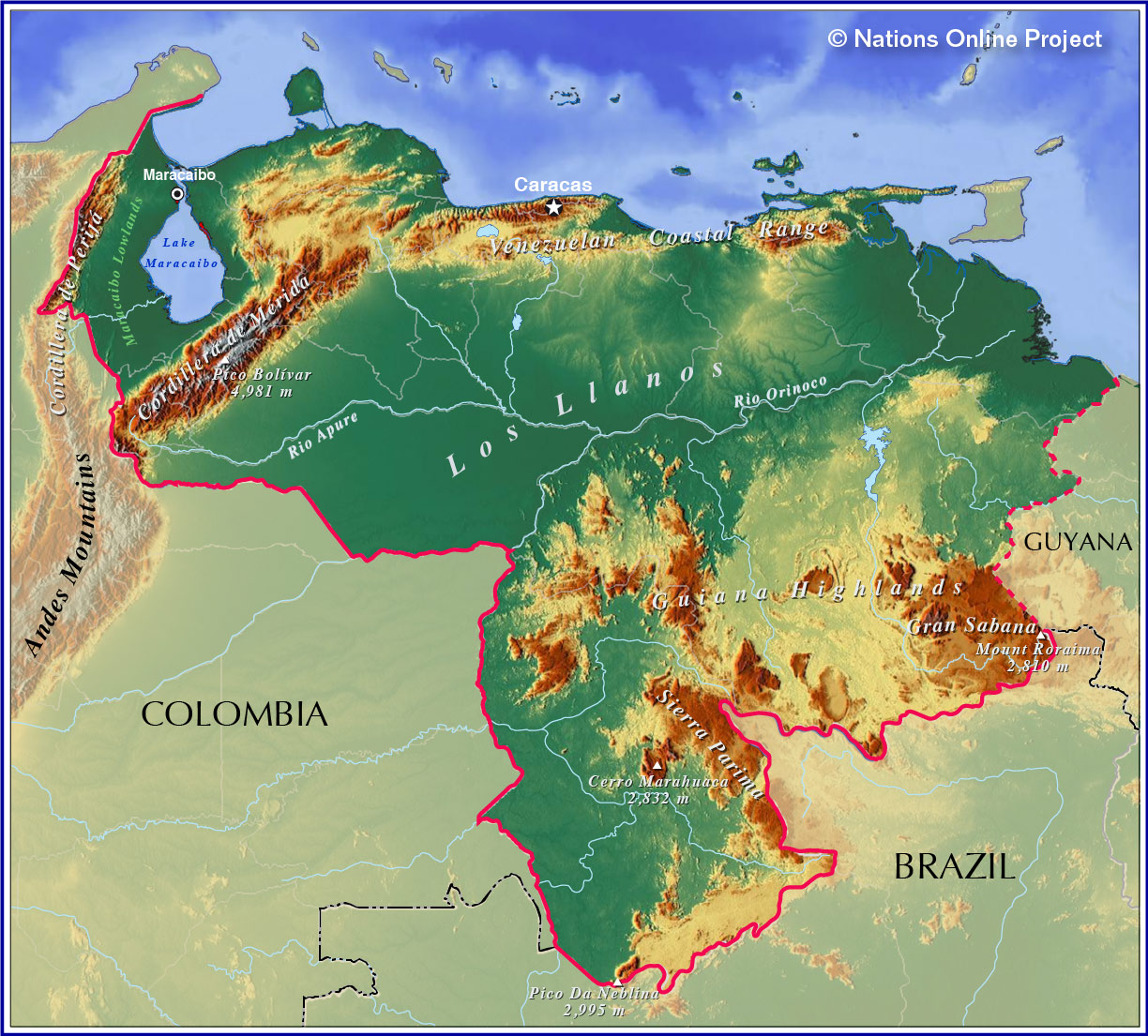


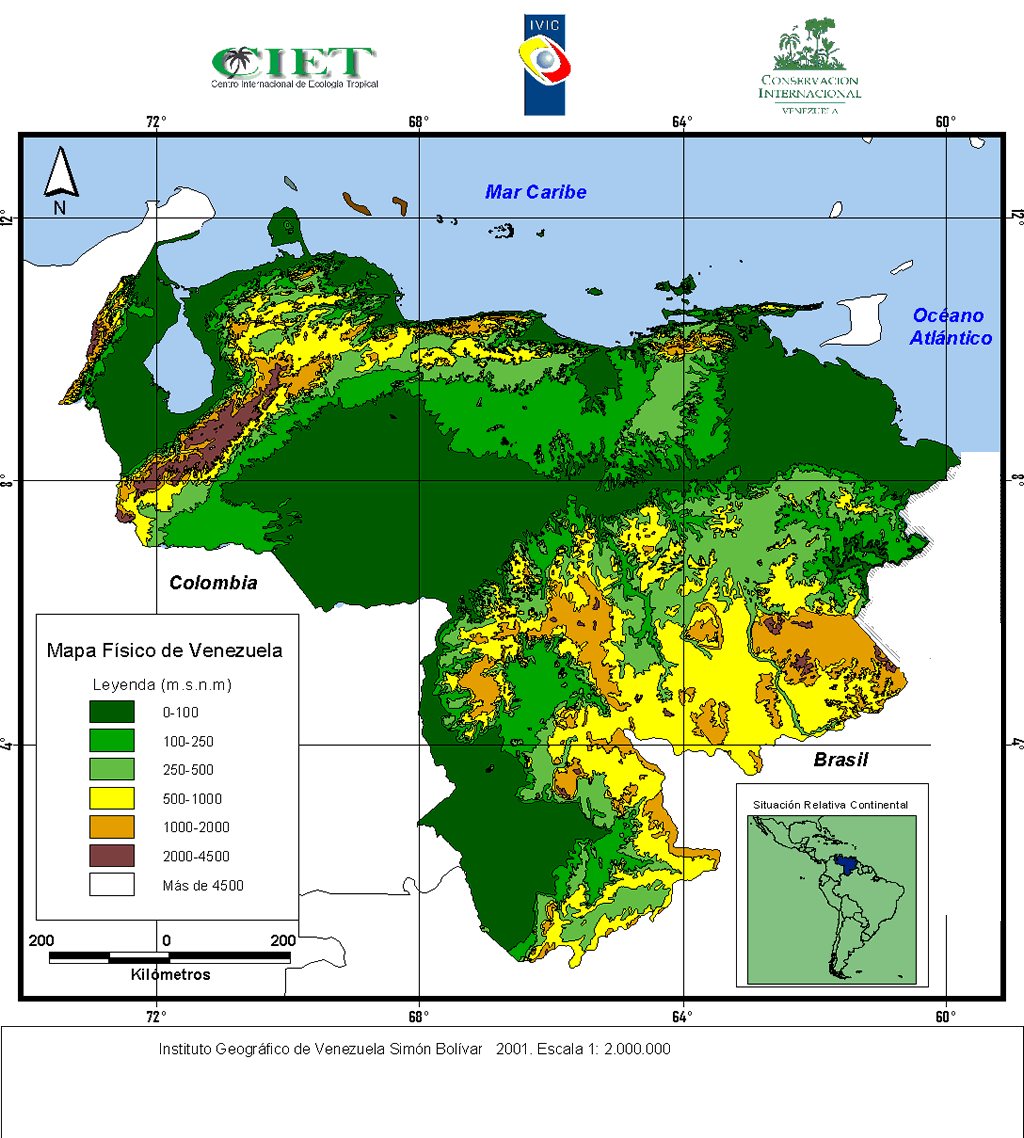


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Geographic Tapestry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Venezuela’s Physical Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!